Key Concepts Select the term that best completes the
... 6. 4 pointsfor a response that correctly summarizes Mendel's results and uses all three terms Sample: Mendel crossed true-breeding pea plants to study how various traits were inherited. For example, he crossed a true-breeding regular height plant with a true-breeding dwarf plant. He observed that th ...
... 6. 4 pointsfor a response that correctly summarizes Mendel's results and uses all three terms Sample: Mendel crossed true-breeding pea plants to study how various traits were inherited. For example, he crossed a true-breeding regular height plant with a true-breeding dwarf plant. He observed that th ...
Chapter 13
... 2. It is made of monomers called nucleotides 3. There are two differences between a DNA & an RNA nucleotide: - RNA has ribose instead of deoxyribose - RNA has the base Uracil instead of ...
... 2. It is made of monomers called nucleotides 3. There are two differences between a DNA & an RNA nucleotide: - RNA has ribose instead of deoxyribose - RNA has the base Uracil instead of ...
Genetic Vulnerability Factors - Early Psychosis Intervention
... To properly understand what the genetic vulnerability factors are, we need to start at the beginning and make sure that we are clear that we know the answers to questions like: What is DNA? What is a chromosome? What is a gene? What is DNA? DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. This complicated name ...
... To properly understand what the genetic vulnerability factors are, we need to start at the beginning and make sure that we are clear that we know the answers to questions like: What is DNA? What is a chromosome? What is a gene? What is DNA? DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. This complicated name ...
Chapter 17- Transcription and Translation
... Reading: Campbell’s pp. 356-366 (Powerpoint: Eukaryotic Gene Expression) 1) Complete the following table by filling in the appropriate description of each property associated with prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes. Property Prokaryote Size of Genome (large or small) ...
... Reading: Campbell’s pp. 356-366 (Powerpoint: Eukaryotic Gene Expression) 1) Complete the following table by filling in the appropriate description of each property associated with prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes. Property Prokaryote Size of Genome (large or small) ...
ibbiochapter3geneticsppt(1)
... • 2013-US supreme court decided on case – AMP(Association for Molecular Pathology v. biotech company(Myraid Genetics) –Myriad had patent on BRCA genes(breast or ovarian cancer)-AMP felt BRCA gene sequences should be available freely for diagnostic purposes-Myriad said since the genes occur naturally ...
... • 2013-US supreme court decided on case – AMP(Association for Molecular Pathology v. biotech company(Myraid Genetics) –Myriad had patent on BRCA genes(breast or ovarian cancer)-AMP felt BRCA gene sequences should be available freely for diagnostic purposes-Myriad said since the genes occur naturally ...
Homework: Mutations
... 8. Which of the following is a change that could be passed on to an organism’s offspring? A Damage to the DNA of gamete cells B Damage to skin cells from exposure to sunlight C Damage to DNA in the cytoplasm of cheek cells D Damage to hair pigment cells with permanent dyes 9. The diagram to the righ ...
... 8. Which of the following is a change that could be passed on to an organism’s offspring? A Damage to the DNA of gamete cells B Damage to skin cells from exposure to sunlight C Damage to DNA in the cytoplasm of cheek cells D Damage to hair pigment cells with permanent dyes 9. The diagram to the righ ...
Chapter 7 – Are You Only as Smart as Your Genes
... used to predict the likelihood of an offspring acquiring a trait • For one trait, a four square Punnett Square is used – Each square represents a 25% chance ...
... used to predict the likelihood of an offspring acquiring a trait • For one trait, a four square Punnett Square is used – Each square represents a 25% chance ...
1-1 - We can offer most test bank and solution manual you need.
... that orthologous genes had between 60 to 80% amino acid identity between species. B. dulcis was found to have a set of genes encoding enzymes important for polysaccharide degradation that did not exist in the other species. Interestingly, sequence comparisons of these polysaccharide-degrading genes ...
... that orthologous genes had between 60 to 80% amino acid identity between species. B. dulcis was found to have a set of genes encoding enzymes important for polysaccharide degradation that did not exist in the other species. Interestingly, sequence comparisons of these polysaccharide-degrading genes ...
Slide 1
... Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes in total cell, which have also been made to fluoresce ...
... Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes in total cell, which have also been made to fluoresce ...
Microarray_module_lecture_(both_courses)
... M: the greater distance from 0= the greater the R/G ratio A: the greater the distance from 0 the darker the spot on the microarray (redder or greener). ...
... M: the greater distance from 0= the greater the R/G ratio A: the greater the distance from 0 the darker the spot on the microarray (redder or greener). ...
Keystone Review Module B
... Which type of reproduction results in offspring that are usually genetically identical to the previous generation and explain why this occurs. One other was these methods of reproduction differ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... Which type of reproduction results in offspring that are usually genetically identical to the previous generation and explain why this occurs. One other was these methods of reproduction differ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Iterative literature searching
... Large negative SAM score: gene expressed more highly in Type I lesions. ...
... Large negative SAM score: gene expressed more highly in Type I lesions. ...
Topic 12 (Ch9/7) – Microbial Genetics Genetics Chromosome
... Fertility factors Resistance factors Bacteriocin factors Virulence plasmids ...
... Fertility factors Resistance factors Bacteriocin factors Virulence plasmids ...
BIOL 241 Nucleic Acids and Gene Expression I. Genes (Overview) A
... 2. cytosine and thymine------> pyrimidines - single ring D. Nucleotides bonded by phosphate groups 1. phosphates (5’) bind to sugars (3’) ---> dehydration synthesis 2. sugars and phosphates form “backbone” 3. bases project from backbone (forming side chains) 4. H-bonds can form between bases (on oth ...
... 2. cytosine and thymine------> pyrimidines - single ring D. Nucleotides bonded by phosphate groups 1. phosphates (5’) bind to sugars (3’) ---> dehydration synthesis 2. sugars and phosphates form “backbone” 3. bases project from backbone (forming side chains) 4. H-bonds can form between bases (on oth ...
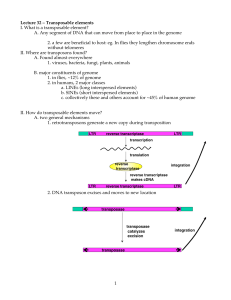
Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element?
... 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. viruses, bacteria, fungi, plants, animals B. major constituents of genome 1. in flies, ~12% of genome 2. in humans, 2 major classes a. LINEs (l ...
... 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. viruses, bacteria, fungi, plants, animals B. major constituents of genome 1. in flies, ~12% of genome 2. in humans, 2 major classes a. LINEs (l ...
transfer RNA
... This pre-mRNA still contains non-coding sections. Some human genes can have 50 introns in a single gene! Typically there are four introns within five exons, but the introns are generally much larger than the exons. Introns must be spliced out from between the exons before the mRNA can leave the nuc ...
... This pre-mRNA still contains non-coding sections. Some human genes can have 50 introns in a single gene! Typically there are four introns within five exons, but the introns are generally much larger than the exons. Introns must be spliced out from between the exons before the mRNA can leave the nuc ...
Applying Mendel`s Principles Power Point
... F1 plants to produce F2 offspring. • This produced offspring ...
... F1 plants to produce F2 offspring. • This produced offspring ...
Document
... Hemophilia in humans is due to an X-chromosome mutation. What will be the results of mating between a normal (non-carrier) female and a hemophiliac male? A. half of daughters are normal and half of sons are hemophilic. B. all sons are normal and all daughters are carriers. C. half of sons are norma ...
... Hemophilia in humans is due to an X-chromosome mutation. What will be the results of mating between a normal (non-carrier) female and a hemophiliac male? A. half of daughters are normal and half of sons are hemophilic. B. all sons are normal and all daughters are carriers. C. half of sons are norma ...
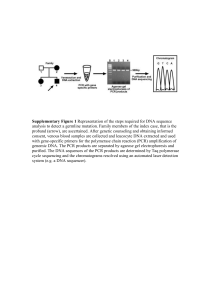
Figure 2 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.