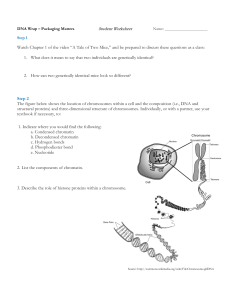
Protein Synthesis Notes Review
... If a mRNA sequence had the following nucleotides: AAGGUCAGACGGUGA, how many codons are there? What is the start codon? What is Translation? Where does Translation occur? Where in the cell does transcription occur? Where in the cell does translation occur? When does translation begin? What brings ami ...
... If a mRNA sequence had the following nucleotides: AAGGUCAGACGGUGA, how many codons are there? What is the start codon? What is Translation? Where does Translation occur? Where in the cell does transcription occur? Where in the cell does translation occur? When does translation begin? What brings ami ...
anth-260-midterm-review-sheet
... 2. External validity 3. Variables IV, DV, confoundsSample questions: • According to Boyd and Silk, stabilizing selection tends to prevent traits of organisms changing over time. a. True b. False ...
... 2. External validity 3. Variables IV, DV, confoundsSample questions: • According to Boyd and Silk, stabilizing selection tends to prevent traits of organisms changing over time. a. True b. False ...
Ch.11 Heredity
... 3. I can explain ways in which humans have influenced the inheritance of traits. 4. Explain how some genetic variations increase organisms probability of surviving and reproducing. 5. I can explain how natural selection has led to an increase or decrease in specific traits of organisms over time. ...
... 3. I can explain ways in which humans have influenced the inheritance of traits. 4. Explain how some genetic variations increase organisms probability of surviving and reproducing. 5. I can explain how natural selection has led to an increase or decrease in specific traits of organisms over time. ...
Leukaemia Section t(1;21)(p35;q22) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... DOI: 10.4267/2042/38583 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 2008 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology ...
... DOI: 10.4267/2042/38583 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 2008 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology ...
Manipulating DNA
... That may be a bargain, considering that the original Royal Blue Boon, a 26-year-old American Quarter Horse now past breeding age, has earned more than $380,000 as a competition and show horse. ...
... That may be a bargain, considering that the original Royal Blue Boon, a 26-year-old American Quarter Horse now past breeding age, has earned more than $380,000 as a competition and show horse. ...
Introduction to probability
... The results of one trial of a chance event does not affect the results of later trials of the same event ...
... The results of one trial of a chance event does not affect the results of later trials of the same event ...
Mock Exam 3 Chapters 14-18 Anthony Todd http
... 48. What are control elements found thousands of nucleotides upstream or downstream of a gene? a. Transcription factors b. Enhancers c. Promoters d. Activators e. Operators 49. Which of the following is not a way that genes can be regulated by translation? a. Binding to a ribosome can be blocked b. ...
... 48. What are control elements found thousands of nucleotides upstream or downstream of a gene? a. Transcription factors b. Enhancers c. Promoters d. Activators e. Operators 49. Which of the following is not a way that genes can be regulated by translation? a. Binding to a ribosome can be blocked b. ...
Exercise week 10 File
... 4) Feed-forward loops in gene regulatory networks a. describe the behavior e.g. of AP-1 complexes or myogenic TFs such as MyoD to amplify their own expression b. accelerate the induction of target genes c. delay the induction of target genes and filter specific signals from randomly fluctuating inpu ...
... 4) Feed-forward loops in gene regulatory networks a. describe the behavior e.g. of AP-1 complexes or myogenic TFs such as MyoD to amplify their own expression b. accelerate the induction of target genes c. delay the induction of target genes and filter specific signals from randomly fluctuating inpu ...
Gene Regulation
... • An operon includes a promoter, an operator, and one or more structural genes that code for all the proteins needed to do a job. – Operons are most common in prokaryotes. – The lac operon was one of the first examples of gene regulation to be discovered. – The lac operon has three genes that code f ...
... • An operon includes a promoter, an operator, and one or more structural genes that code for all the proteins needed to do a job. – Operons are most common in prokaryotes. – The lac operon was one of the first examples of gene regulation to be discovered. – The lac operon has three genes that code f ...
Genetics New
... Substitution: one base for another CACCTTATTA Deletion: missing a base CACCG ATTA Addition: adding a base CACCGTAATTA Inversion: bases are rearranged CACCTAGTTA ...
... Substitution: one base for another CACCTTATTA Deletion: missing a base CACCG ATTA Addition: adding a base CACCGTAATTA Inversion: bases are rearranged CACCTAGTTA ...
Genetic Notes
... whether or not you see color. (Red, Green) • Women are seldom color-blind because the gene is a recessive gene on the X-chromosome and they have two x-chromosomes. ...
... whether or not you see color. (Red, Green) • Women are seldom color-blind because the gene is a recessive gene on the X-chromosome and they have two x-chromosomes. ...
Applications Lecture 4 - Rose
... individual proteins. (the production of these proteins is known as gene expression) b. Gene expression takes place in two stages i. Transcription—DNA is turned into RNA via the enzyme RNA polymerase. ii. Translation—RNA is turned into Protein in the rough Endoplasmic Reticulum found in the cytoplasm ...
... individual proteins. (the production of these proteins is known as gene expression) b. Gene expression takes place in two stages i. Transcription—DNA is turned into RNA via the enzyme RNA polymerase. ii. Translation—RNA is turned into Protein in the rough Endoplasmic Reticulum found in the cytoplasm ...
Student Worksheet
... Epigenetics is the study of other factors besides the DNA sequence that influence whether or not a gene is transcribed into mRNA and then translated (conversion of mRNA sequence into amino acids) into a protein. An individual’s environment, even in the womb, can influence these factors and permanent ...
... Epigenetics is the study of other factors besides the DNA sequence that influence whether or not a gene is transcribed into mRNA and then translated (conversion of mRNA sequence into amino acids) into a protein. An individual’s environment, even in the womb, can influence these factors and permanent ...
DNA
... Sexual • Two parents • Offspring different from parents • More variation • Fertilization (fusion of gametes) • Plant, humans, etc. ...
... Sexual • Two parents • Offspring different from parents • More variation • Fertilization (fusion of gametes) • Plant, humans, etc. ...
Human Genetics
... the same in all copies of the genome - Thus, a mitochondrion will have different alleles for the same gene At each cell division, the mitochondria are distributed at random into daughter cells If an oocyte is heteroplasmic, differing number of copies of a mutant mtDNA may be transmitted - The phenot ...
... the same in all copies of the genome - Thus, a mitochondrion will have different alleles for the same gene At each cell division, the mitochondria are distributed at random into daughter cells If an oocyte is heteroplasmic, differing number of copies of a mutant mtDNA may be transmitted - The phenot ...
Here is a copy. - Scarsdale Schools
... 3) What is a homeodomain? 4) Many animals had homeoboxes very similar to each other, even if the animals were not closely related. What does this suggest? 5) What happened when the eyeless gene was turned on in the wing and legs? Significance of the results? 6) What happened when the small eye gene ...
... 3) What is a homeodomain? 4) Many animals had homeoboxes very similar to each other, even if the animals were not closely related. What does this suggest? 5) What happened when the eyeless gene was turned on in the wing and legs? Significance of the results? 6) What happened when the small eye gene ...
Techniques in Mouse
... in a mutant that does not develop to stage needed. • Cre is a recombinase that excises DNA located in between LoxP sites • You generate two transgenic lines one that expresses Cre in the tissue you are interested and a second that contains gene of interest flanked by loxP sites. The gene will only b ...
... in a mutant that does not develop to stage needed. • Cre is a recombinase that excises DNA located in between LoxP sites • You generate two transgenic lines one that expresses Cre in the tissue you are interested and a second that contains gene of interest flanked by loxP sites. The gene will only b ...
BIOL 222 - philipdarrenjones.com
... A) a base insertion only but ever a deletion B) a base deletion only but never an insertion C) a base substitution only D) deletion of three consecutive bases E) either an insertion or a deletion of a base ...
... A) a base insertion only but ever a deletion B) a base deletion only but never an insertion C) a base substitution only D) deletion of three consecutive bases E) either an insertion or a deletion of a base ...
HGP - eduBuzz.org
... Repeating sequences 2 – 4 nucleotide bases found in mostly in introns (‘junk’ DNA) The number of repeats varies from person to person, but follow patterns of Mendalian inheritance These sequences can be identified using probes. A probe is ...
... Repeating sequences 2 – 4 nucleotide bases found in mostly in introns (‘junk’ DNA) The number of repeats varies from person to person, but follow patterns of Mendalian inheritance These sequences can be identified using probes. A probe is ...
APOC1 gene rs4420638 SNP
... (genetics) The interaction between nonallelic genes at two or more loci resulting in one gene masking the phenotypic expression of another gene (medicine) The arrest of a secretion or bodily discharge In genetics, epistasis pertains to the interaction of the genes at two or more loci, and as a resul ...
... (genetics) The interaction between nonallelic genes at two or more loci resulting in one gene masking the phenotypic expression of another gene (medicine) The arrest of a secretion or bodily discharge In genetics, epistasis pertains to the interaction of the genes at two or more loci, and as a resul ...
C - Bioinformatics Research Center
... • The transcribed mRNA (pre-mRNA) must first be processed into mature mRNA • The protein-coding regions (exons) are interspersed with non-coding regions (introns) which must be excised ...
... • The transcribed mRNA (pre-mRNA) must first be processed into mature mRNA • The protein-coding regions (exons) are interspersed with non-coding regions (introns) which must be excised ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.