Slide 1 - TeacherTube
... • Each trait – an expressed characteristic is produced by a pair of hereditary factors collectively know as GENES. Within a chromosome, there are many genes, each of which controls the inheritance of a particular trait. • A GENE is a segment of a chromosome that produces a particular trait. For exam ...
... • Each trait – an expressed characteristic is produced by a pair of hereditary factors collectively know as GENES. Within a chromosome, there are many genes, each of which controls the inheritance of a particular trait. • A GENE is a segment of a chromosome that produces a particular trait. For exam ...
Automatic Annotation of Gene Lists from Literature Analysis
... 1) For a gene i, if the term count xi is significantly higher than expected by chance (determined by λ0 and di), then the term may be related to the gene i; 2) If there are many genes related to the term, then this term is enriched in the given gene list. ...
... 1) For a gene i, if the term count xi is significantly higher than expected by chance (determined by λ0 and di), then the term may be related to the gene i; 2) If there are many genes related to the term, then this term is enriched in the given gene list. ...
Genetics and Heredity Outline
... studies started by ________________ in the middle 1800’s. Because of his work, he is called the “father of __________.” Mendel did not know about _________, but thought that certain “____________” were responsible for ________ passed from parents to offspring. ...
... studies started by ________________ in the middle 1800’s. Because of his work, he is called the “father of __________.” Mendel did not know about _________, but thought that certain “____________” were responsible for ________ passed from parents to offspring. ...
What are mutations and how do they affect the production
... When the base sequence of DNA is __________________, the ______________________ sequence is also changed. Since amino acids chain together to create a specific ____________________, mutations could affect the operation of an ____________________, preventing it from properly catalyzing a reaction or ...
... When the base sequence of DNA is __________________, the ______________________ sequence is also changed. Since amino acids chain together to create a specific ____________________, mutations could affect the operation of an ____________________, preventing it from properly catalyzing a reaction or ...
Final Review - Bishop Lynch High School
... e. female hormones such as estrogen often compensate for the effects of mutations on the X. How many unique gametes could be produced through independent assortment by an individual with the genotype AaBbCCDdEE? a. 16 b. 64 c. 8 d. 32 e. 4 Pea plants were particularly well suited for use in Mendel's ...
... e. female hormones such as estrogen often compensate for the effects of mutations on the X. How many unique gametes could be produced through independent assortment by an individual with the genotype AaBbCCDdEE? a. 16 b. 64 c. 8 d. 32 e. 4 Pea plants were particularly well suited for use in Mendel's ...
L15 Gene Regulation Part1 Fa08
... – Gene that codes for a protein that controls the transcription of another gene or group of genes • Repressor – Protein that inhibits gene transcription – Binds to operator & prevents RNA polymerase from attaching to promoter ...
... – Gene that codes for a protein that controls the transcription of another gene or group of genes • Repressor – Protein that inhibits gene transcription – Binds to operator & prevents RNA polymerase from attaching to promoter ...
Gene Section MSH3 (mutS homolog 3 (E. coli)) in Oncology and Haematology
... This phenotype is present in 15% of colorectal cancer, gastric cancer and endometrial cancer, and with lower incidence in some other tissues. Oncogenesis The average frequencies of the microsatellite mutation reported in sporadic MSI from colorectal, gastric and endometrial cancer are 38%, 39% and 2 ...
... This phenotype is present in 15% of colorectal cancer, gastric cancer and endometrial cancer, and with lower incidence in some other tissues. Oncogenesis The average frequencies of the microsatellite mutation reported in sporadic MSI from colorectal, gastric and endometrial cancer are 38%, 39% and 2 ...
Genetics - National Multiple Sclerosis Society
... Genes are the units of heredity discovered by Gregor Mendel more than a century ago. They contain the recipes, or instructions, for making the proteins of which all living things, from bacteria to humans, are built and which all organisms use to carry out their functions. Since the 1970s, scientists ...
... Genes are the units of heredity discovered by Gregor Mendel more than a century ago. They contain the recipes, or instructions, for making the proteins of which all living things, from bacteria to humans, are built and which all organisms use to carry out their functions. Since the 1970s, scientists ...
Key for Exam 1 Part 1 - Evolutionary Biology
... intermediate flower color are aborted within the seed pod and thus never develop (B) The seeds coding for intermediate flower color have deleterious alleles that prevent them from germinating (C) These variations in human are affected by lack of dominance in the alleles that control these traits (D) ...
... intermediate flower color are aborted within the seed pod and thus never develop (B) The seeds coding for intermediate flower color have deleterious alleles that prevent them from germinating (C) These variations in human are affected by lack of dominance in the alleles that control these traits (D) ...
DNA - NRF IR Repository
... material of the cell. It is found in the chromosomes in the nucleus of the cell, as well as in other cellular organelles like the mitochodria in animals and chloroplasts in plants. DNA is the biological code that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all living ...
... material of the cell. It is found in the chromosomes in the nucleus of the cell, as well as in other cellular organelles like the mitochodria in animals and chloroplasts in plants. DNA is the biological code that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all living ...
More Exam Practice - Iowa State University
... 1.Describe where the light reactions and the calvin cycle take place in a plant cell and what the inputs and outputs are of the two stages. The light reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts. The inputs are H2O and light energy and the outputs are NADPH, ATP, and oxygen. The calvi ...
... 1.Describe where the light reactions and the calvin cycle take place in a plant cell and what the inputs and outputs are of the two stages. The light reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts. The inputs are H2O and light energy and the outputs are NADPH, ATP, and oxygen. The calvi ...
Blueprint of Life #2
... If the alleles are the same, they form a homozygous genotype. A pure breeding organism is homozygous for that characteristic (e.g. TT) If the alleles are different, they form a heterozygous genotype. A non-pure breeding or hybrid organism (Tt) is heterozygous. Alleles and genes: An allele is a ...
... If the alleles are the same, they form a homozygous genotype. A pure breeding organism is homozygous for that characteristic (e.g. TT) If the alleles are different, they form a heterozygous genotype. A non-pure breeding or hybrid organism (Tt) is heterozygous. Alleles and genes: An allele is a ...
The Genetic Basis of Development
... conservation of developmental genes in animals: homeobox (180-nucleotide sequence) region found in homeotic genes & other developmental genes of many invertebrates and vertebrates is similar/identical many developmental genes are highly conserved among species but may play different developmen ...
... conservation of developmental genes in animals: homeobox (180-nucleotide sequence) region found in homeotic genes & other developmental genes of many invertebrates and vertebrates is similar/identical many developmental genes are highly conserved among species but may play different developmen ...
Document
... You are a researcher trying to determine whether Scenario III or Scenario IV from problem 6 is the more likely mechanism for regulating the gene expression of pGLO. You perform the following experiments. First pGLO alone is digested by DNAase and the fragments are separated by gel electrophoresis. N ...
... You are a researcher trying to determine whether Scenario III or Scenario IV from problem 6 is the more likely mechanism for regulating the gene expression of pGLO. You perform the following experiments. First pGLO alone is digested by DNAase and the fragments are separated by gel electrophoresis. N ...
Two trait Crosses
... Summary of Mendel’s Principles • Principle of Segregation – In most sexually reproducing organisms, each adult has two copies of each gene- one from each parent. These genes are segregated from each other when gametes are formed. • Principle of Independent Assortment – The alleles for different gen ...
... Summary of Mendel’s Principles • Principle of Segregation – In most sexually reproducing organisms, each adult has two copies of each gene- one from each parent. These genes are segregated from each other when gametes are formed. • Principle of Independent Assortment – The alleles for different gen ...
Molecular Biology of the Cell
... 3. The authors built a Markov model using the TF sequence motifs as parent nodes, and the expression data as data values. 4. This can be applied to a gene of interest by identifying the upstream TF motifs for that gene, and finding the model(s) that best fits the known upstream TF motifs. 5. If the ...
... 3. The authors built a Markov model using the TF sequence motifs as parent nodes, and the expression data as data values. 4. This can be applied to a gene of interest by identifying the upstream TF motifs for that gene, and finding the model(s) that best fits the known upstream TF motifs. 5. If the ...
BIO 420 – Mammalian Physiology
... V. Dihybrid Crosses with Mendelian Deviations A. Dihybrid crosses involving at least one non-classical ratio will result in F2 progeny with altered ratios as well. B. Example – Inheritance of albinism and blood type in the same individual VI. Gene Interaction A. Definition – phenotype may be affecte ...
... V. Dihybrid Crosses with Mendelian Deviations A. Dihybrid crosses involving at least one non-classical ratio will result in F2 progeny with altered ratios as well. B. Example – Inheritance of albinism and blood type in the same individual VI. Gene Interaction A. Definition – phenotype may be affecte ...
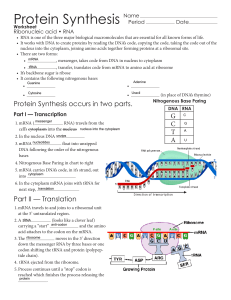
Protein Synthesis - Issaquah Connect
... DNA following the order of the nitrogenous bases 4. Nitrogenous Base Paring in chart to right 5. mRNA carries DNA’s code, in it’s strand, out into cytoplasm 6. In the cytoplasm mRNA joins with tRNA for next step, translation ...
... DNA following the order of the nitrogenous bases 4. Nitrogenous Base Paring in chart to right 5. mRNA carries DNA’s code, in it’s strand, out into cytoplasm 6. In the cytoplasm mRNA joins with tRNA for next step, translation ...
Old exam 2 from 2002
... observation of their pollen mother cells showed no chromosome pairing (no bivalents, only univalents). A section from one of the hybrids that grew vigorously was propagated vegetatively, producing a plant with 36 chromosomes in its somatic cells. This plant was fertile, and produced large, showy flo ...
... observation of their pollen mother cells showed no chromosome pairing (no bivalents, only univalents). A section from one of the hybrids that grew vigorously was propagated vegetatively, producing a plant with 36 chromosomes in its somatic cells. This plant was fertile, and produced large, showy flo ...
Complex Germline Architecture: Two Genes
... sometimes called nanochromosomes (Doak et al. 2003) because of their size and because they typically contain just one gene each. These together comprise the gene-dense somatic genome. The process of deletion of up to 98% of the germline DNA removes internal eliminated segments (IES) that interrupt g ...
... sometimes called nanochromosomes (Doak et al. 2003) because of their size and because they typically contain just one gene each. These together comprise the gene-dense somatic genome. The process of deletion of up to 98% of the germline DNA removes internal eliminated segments (IES) that interrupt g ...
DNA - KK College of Nursing
... Genetics • Genetics deals with the molecular structure and function of genes, gene behavior, patterns of inheritance from parent to offspring, and gene distribution, variation and change in populations. ...
... Genetics • Genetics deals with the molecular structure and function of genes, gene behavior, patterns of inheritance from parent to offspring, and gene distribution, variation and change in populations. ...
Genetics Vocabulary Review
... Strands of DNA and protein found in the nucleus of a cell carrying the code for the characteristics of an organism. CHROMOSOME ...
... Strands of DNA and protein found in the nucleus of a cell carrying the code for the characteristics of an organism. CHROMOSOME ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.