Chemical basis of Inheritance Review KEY - Pelletier Pages
... Leading strand? Strand of DNA synthesized continuously in the 5’-3’ direction. 13. What role do DNA polymerase and DNA ligase play in gene replication? DNA polymerase adds DNA nucleotides to the 3’ end of the growing DNA molecule. DNA ligase forms the phosphodiester bonds between the okazaki fragmen ...
... Leading strand? Strand of DNA synthesized continuously in the 5’-3’ direction. 13. What role do DNA polymerase and DNA ligase play in gene replication? DNA polymerase adds DNA nucleotides to the 3’ end of the growing DNA molecule. DNA ligase forms the phosphodiester bonds between the okazaki fragmen ...
Enteric bacteria as model systems
... We then screen for mutants by replica printing from rich media bearing antibiotics to defined media containing either raffinose or glucose. Colonies that fail to grow on raffinose but do grow on glucose are defective for raffinose degradation. Several rounds of mutagenesis are performed to gener ...
... We then screen for mutants by replica printing from rich media bearing antibiotics to defined media containing either raffinose or glucose. Colonies that fail to grow on raffinose but do grow on glucose are defective for raffinose degradation. Several rounds of mutagenesis are performed to gener ...
November Syllabus
... Explain how DNA is transcribed to form RNA. Be sure to include a description of RNA processing. Explain how the mRNA is translated to create a ...
... Explain how DNA is transcribed to form RNA. Be sure to include a description of RNA processing. Explain how the mRNA is translated to create a ...
Glossary( PDF format / 71KB )
... Detection of cancer or other diseases by testing blood or other bodily fluids. This type of testing is less invasive than conventional physical biopsies. M ■Modular concept Individual modules can be combined to create a diverse variety of product configurations. The series also allows for flexibilit ...
... Detection of cancer or other diseases by testing blood or other bodily fluids. This type of testing is less invasive than conventional physical biopsies. M ■Modular concept Individual modules can be combined to create a diverse variety of product configurations. The series also allows for flexibilit ...
ciliate genomics consortium - Tetrahymena Genome Database
... genes in Tetrahymena thermophila. To study the function of Tetrahymena genes, research modules have been developed for implementation as molecular biology class laboratory exercises to involve a large number of undergraduate students in original research. The experimental results produced by student ...
... genes in Tetrahymena thermophila. To study the function of Tetrahymena genes, research modules have been developed for implementation as molecular biology class laboratory exercises to involve a large number of undergraduate students in original research. The experimental results produced by student ...
BiochemLecture03
... gene is 110 kb long made up of 65 introns. • Titin has 175 introns. • With these large complex genes it is difficult to identify all of the exons and introns. ...
... gene is 110 kb long made up of 65 introns. • Titin has 175 introns. • With these large complex genes it is difficult to identify all of the exons and introns. ...
Mendelian Genetics
... One gene in a pair can mask or hide the expression of the other gene (dominant vs recessive) Dominant allele: When only ONE of the alleles affects the trait. (Use a CAPITAL letter) Recessive allele: the allele that is NOT expressed if there is a dominant allele present. (Use a small letter). ...
... One gene in a pair can mask or hide the expression of the other gene (dominant vs recessive) Dominant allele: When only ONE of the alleles affects the trait. (Use a CAPITAL letter) Recessive allele: the allele that is NOT expressed if there is a dominant allele present. (Use a small letter). ...
Mendel_and_the_genetic_engine
... Alleles at the Molecular Level Each form of a gene is an allele. The standard (wild type) and altered (mutant) forms of the gene associated with hemoglobin and sickle cell anemia provide an example. The DNA sequences of both alleles of the “hemoglobin gene” are 99.9% identical – a single nucleotide ...
... Alleles at the Molecular Level Each form of a gene is an allele. The standard (wild type) and altered (mutant) forms of the gene associated with hemoglobin and sickle cell anemia provide an example. The DNA sequences of both alleles of the “hemoglobin gene” are 99.9% identical – a single nucleotide ...
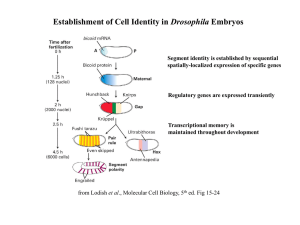
Establishment of Cell Identity in Drosophila Embryos
... Trithorax-group Proteins Maintains an active state Counteracts the action of PcG proteins Memory system composed of PcG and trxG complexes is linked to the histone code ...
... Trithorax-group Proteins Maintains an active state Counteracts the action of PcG proteins Memory system composed of PcG and trxG complexes is linked to the histone code ...
Variation and Gene Pools
... are mutations and the genetic shuffling from sexual reproduction – Remember, mutations are a change in a sequence of DNA. – Genetic shuffling occurs during the formation of gametes and subsequent fertilization • Crossing over also leads to genetic shuffling ...
... are mutations and the genetic shuffling from sexual reproduction – Remember, mutations are a change in a sequence of DNA. – Genetic shuffling occurs during the formation of gametes and subsequent fertilization • Crossing over also leads to genetic shuffling ...
ADVANCES IN COCHLEAR IMPLANTATION
... The organs and tissues of the body are made of cells. The cells contain genetic information which determines how we are, either alone or by interacting with the environment. The information is stored in a long molecule called Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) in an alphabet of four letters A, C, G and T. ...
... The organs and tissues of the body are made of cells. The cells contain genetic information which determines how we are, either alone or by interacting with the environment. The information is stored in a long molecule called Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) in an alphabet of four letters A, C, G and T. ...
7.1: Variations, Mutations, and Selective Advantage Learning Check:
... The offspring of sexually reproducing organisms inherit a combination of genetic material (genes) from both biological parents. The number of possible combinations of genes that offspring inherit from their parents results in genetic variation among individuals within the population. ...
... The offspring of sexually reproducing organisms inherit a combination of genetic material (genes) from both biological parents. The number of possible combinations of genes that offspring inherit from their parents results in genetic variation among individuals within the population. ...
Exam 2
... Begins later in the lifespan of human males than females __________________________ Requires homologous pairs of chromosomes _______________________________ Used for asexual reproduction ______________________________ Timing is controlled by sex hormones ___________________________ Chromatids are co ...
... Begins later in the lifespan of human males than females __________________________ Requires homologous pairs of chromosomes _______________________________ Used for asexual reproduction ______________________________ Timing is controlled by sex hormones ___________________________ Chromatids are co ...
File
... dominant. B. The allele for blue eye color is dominant. C. The allele for brown eye color is recessive. ...
... dominant. B. The allele for blue eye color is dominant. C. The allele for brown eye color is recessive. ...
Transcription and Translation Work Sheet:
... 3) If a second strand of DNA was created (semiconservative replication) using the above strand of DNA as the template, what would the sequence be? (Remember that the two single DNA strands are anti-parallel and held together as complimentary base pairs across the alpha-helix by hydrogen bonds) 4) If ...
... 3) If a second strand of DNA was created (semiconservative replication) using the above strand of DNA as the template, what would the sequence be? (Remember that the two single DNA strands are anti-parallel and held together as complimentary base pairs across the alpha-helix by hydrogen bonds) 4) If ...
Transcription and Translation Work Sheet:
... 3) If a second strand of DNA was created (semiconservative replication) using the above strand of DNA as the template, what would the sequence be? (Remember that the two single DNA strands are anti-parallel and held together as complimentary base pairs across the alpha-helix by hydrogen bonds) 4) If ...
... 3) If a second strand of DNA was created (semiconservative replication) using the above strand of DNA as the template, what would the sequence be? (Remember that the two single DNA strands are anti-parallel and held together as complimentary base pairs across the alpha-helix by hydrogen bonds) 4) If ...
Lesson 3
... What is DNA? •Each side of the DNA ladder is made up of sugar-phosphate molecules, and the rungs of the ladder are made up of nitrogen bases. •When DNA is copied, the new DNA has bases that are identical to those of the original DNA. ...
... What is DNA? •Each side of the DNA ladder is made up of sugar-phosphate molecules, and the rungs of the ladder are made up of nitrogen bases. •When DNA is copied, the new DNA has bases that are identical to those of the original DNA. ...
Molecules of Life
... • The molecule is very long and is split into genes which are codes for making proteins. • A chromosome is simply a very long DNA molecule that has been folded into a shape like this: There’s a lot more DNA packed into the chromosomes than shown here! ...
... • The molecule is very long and is split into genes which are codes for making proteins. • A chromosome is simply a very long DNA molecule that has been folded into a shape like this: There’s a lot more DNA packed into the chromosomes than shown here! ...
DNA and RNA Chapter 12 - St. Louis Public Schools
... GENETIC MATERIAL In the middle of the 1900’s scientists were asking questions about genes. What is a gene made of? How do genes work? How do genes determine characteristics of organisms? ...
... GENETIC MATERIAL In the middle of the 1900’s scientists were asking questions about genes. What is a gene made of? How do genes work? How do genes determine characteristics of organisms? ...
Repressor protein - Edwin C. Foreman High School
... if bacterium encounters new sugar (energy source), like lactose, then it needs to start making enzymes used to digest lactose ...
... if bacterium encounters new sugar (energy source), like lactose, then it needs to start making enzymes used to digest lactose ...
TB1 - BIOCHEM, Broyles
... site of transcription…the TATA box is an example Distal promoter - DNA sites between 100 and 200 base pairs upstream, known to bind to a variety of trans-acting factors Enhancers – DNA regions involved in positive regulation distances away, upstream or downstream from the gene and oriented in ei ...
... site of transcription…the TATA box is an example Distal promoter - DNA sites between 100 and 200 base pairs upstream, known to bind to a variety of trans-acting factors Enhancers – DNA regions involved in positive regulation distances away, upstream or downstream from the gene and oriented in ei ...
outline21590
... 3. Prognosis 4. Alternatives: Pre-conception and post-conception 5. Exact Diagnosis 6. Physical examination 7. Laboratory studies 8. Family studies 9. Study of previous abortus or stillborn 10. Molecular genetic analysis 11. Risk Estimate a. How big a risk is 25%? b. 25% risk means 75% normal which ...
... 3. Prognosis 4. Alternatives: Pre-conception and post-conception 5. Exact Diagnosis 6. Physical examination 7. Laboratory studies 8. Family studies 9. Study of previous abortus or stillborn 10. Molecular genetic analysis 11. Risk Estimate a. How big a risk is 25%? b. 25% risk means 75% normal which ...
RNA and protein synthesis
... Different order of amino acids = different protein! The types of proteins an organism possesses depend upon the sequence of nucleotides in DNA ...
... Different order of amino acids = different protein! The types of proteins an organism possesses depend upon the sequence of nucleotides in DNA ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.