lecture26_Polymorphi..
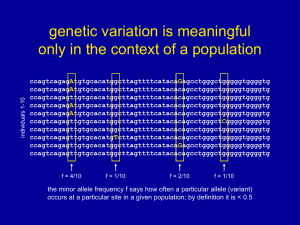
... this is the observed frequency distribution from the complete sequencing a large population; however most SNP discovery projects sequence a small population and then consider the absence or presence of those previously discovered SNPs in large population; this is known to under-estimate the number o ...
... this is the observed frequency distribution from the complete sequencing a large population; however most SNP discovery projects sequence a small population and then consider the absence or presence of those previously discovered SNPs in large population; this is known to under-estimate the number o ...
ch 16 notes mader
... d. In sexual reproducing organisms, both mutations and sexual recombination are important in generating phenotypic differences. 2. Nonrandom Mating and Gene Flow a. Random mating involves individuals pairing by chance, not according to genotype or phenotype. b. Nonrandom mating occurs when certain g ...
... d. In sexual reproducing organisms, both mutations and sexual recombination are important in generating phenotypic differences. 2. Nonrandom Mating and Gene Flow a. Random mating involves individuals pairing by chance, not according to genotype or phenotype. b. Nonrandom mating occurs when certain g ...
Document
... Genetic variation gives rise to differences between individuals that are inherited. For example, our eye color is inherited from our parents. But our phenotype is also affected by environmental variation such as: Climate, diet, physical accidents, culture, lifestyle Many kinds of variation are influ ...
... Genetic variation gives rise to differences between individuals that are inherited. For example, our eye color is inherited from our parents. But our phenotype is also affected by environmental variation such as: Climate, diet, physical accidents, culture, lifestyle Many kinds of variation are influ ...
Slide 1
... • Determine ability to identify organisms on the basis of phenotypic analysis using established reference manual(s) • Demonstrate ability to access database tools and perform RAST annotation of a genomic sequence • Determine ability to correlate genes to the particular phenotype • Determine ability ...
... • Determine ability to identify organisms on the basis of phenotypic analysis using established reference manual(s) • Demonstrate ability to access database tools and perform RAST annotation of a genomic sequence • Determine ability to correlate genes to the particular phenotype • Determine ability ...
15 genetics problems 3 Linked genes
... What is the recombination frequency between these genes for body color and wing type? (HINT: compare the phenotypes of the offspring to those of the parents…which phenotypes show a NEW combination of traits that was not present in either parent?) 10) Determine the sequence of genes along a chromosom ...
... What is the recombination frequency between these genes for body color and wing type? (HINT: compare the phenotypes of the offspring to those of the parents…which phenotypes show a NEW combination of traits that was not present in either parent?) 10) Determine the sequence of genes along a chromosom ...
If there are “CUES” listed within the question, please USE them and
... eyes? Provide a Punnett square as evidence to support your answer. (CUES: dominant, recessive, sex-linked.) 2) Use Figure 15.5 to explain whether the genes for body color & wing type are on the same or different chromosomes. (CUES: parental phenotype, recombinant phenotype, linked genes.) 3) Conside ...
... eyes? Provide a Punnett square as evidence to support your answer. (CUES: dominant, recessive, sex-linked.) 2) Use Figure 15.5 to explain whether the genes for body color & wing type are on the same or different chromosomes. (CUES: parental phenotype, recombinant phenotype, linked genes.) 3) Conside ...
Patterns of Inheritance
... interaction of at least several genes with a large number of possible environmental variables, e.g. skin pigment, melanin, is result of four genes; exposure to sun also plays a role. ...
... interaction of at least several genes with a large number of possible environmental variables, e.g. skin pigment, melanin, is result of four genes; exposure to sun also plays a role. ...
Foundations of Genetics Mendelism
... Probability and Mendel • If we toss a coin it can land either heads or tails up. There are total events possible, 2 in this example. If we say what is the possibility of heads landing up? It is ½ or 50%. • Probability is the possibility of occurrence of an event out of the total possible events. Fi ...
... Probability and Mendel • If we toss a coin it can land either heads or tails up. There are total events possible, 2 in this example. If we say what is the possibility of heads landing up? It is ½ or 50%. • Probability is the possibility of occurrence of an event out of the total possible events. Fi ...
Introduction to Genetics: - Serrano High School AP Biology
... Pleiotropy: Pleiotropy occurs when a single gene can affect more than 1 characteristic. ie. coat color in cats: white cats often have blue and eyes and are deaf. When a single gene has multiple phenotypic effects. Nature Vs. Nurture: There are certain traits that are not affected by the environment, ...
... Pleiotropy: Pleiotropy occurs when a single gene can affect more than 1 characteristic. ie. coat color in cats: white cats often have blue and eyes and are deaf. When a single gene has multiple phenotypic effects. Nature Vs. Nurture: There are certain traits that are not affected by the environment, ...
PopStratGEMS - Division of Statistical Genomics
... pop 1 and 2, the diseased individuals in admixed generations will carry disease genes/alleles that have more ancestry from pop 2 than from pop 1. If a marker is linked with disease genes, because of linkage disequilibrium, the diseased individuals will also carry the marker copies that have more an ...
... pop 1 and 2, the diseased individuals in admixed generations will carry disease genes/alleles that have more ancestry from pop 2 than from pop 1. If a marker is linked with disease genes, because of linkage disequilibrium, the diseased individuals will also carry the marker copies that have more an ...
Document
... Genotype - the traits (alleles for the trait) are represented by letters (Tt, Aa, BB, dd) Genotypic ratio is reported in the following order - Homozygous Dominant : Heterozygous: Homozygous Recessive Phenotype – the appearance of a trait; what the offspring looks like (Tall : short, curly hair : str ...
... Genotype - the traits (alleles for the trait) are represented by letters (Tt, Aa, BB, dd) Genotypic ratio is reported in the following order - Homozygous Dominant : Heterozygous: Homozygous Recessive Phenotype – the appearance of a trait; what the offspring looks like (Tall : short, curly hair : str ...
Chapter 5: Patterns of Inheritance - ahs
... Example 2: F1 generation of yellow-pea producing plants F1 generation cross results: In the F2 generation, some peas were yellow and some green. Mathematically, the ratio was 3:1 yellow:green. This ratio was the same for all seven traits that Mendel studied. ...
... Example 2: F1 generation of yellow-pea producing plants F1 generation cross results: In the F2 generation, some peas were yellow and some green. Mathematically, the ratio was 3:1 yellow:green. This ratio was the same for all seven traits that Mendel studied. ...
Biological Diversity Section 3 Student Notes
... Hybrid: An organism that is the result of a cross between two different purebred parents. Hybrid organisms are usually heterozygous (they have two different alleles) Ex. RR (homozygous mom) ...
... Hybrid: An organism that is the result of a cross between two different purebred parents. Hybrid organisms are usually heterozygous (they have two different alleles) Ex. RR (homozygous mom) ...
Oh_possibilities
... 1. Determine your genotypes for the traits listed on the table. If you’re unsure, flip a coin to determine the dominant or recessive allele. (Heads = dominant) 2. Each parent should obtain a normal male and female karyotype. (Preferably, one male and one female per group) 3. Transfer your genotypes ...
... 1. Determine your genotypes for the traits listed on the table. If you’re unsure, flip a coin to determine the dominant or recessive allele. (Heads = dominant) 2. Each parent should obtain a normal male and female karyotype. (Preferably, one male and one female per group) 3. Transfer your genotypes ...
Heredity patterns of traits - WidgetsandWhatchamacallits
... • A chromosome stained in order to see the striping pattern of some of the genes. ...
... • A chromosome stained in order to see the striping pattern of some of the genes. ...
Genetics Test - dublin.k12.ca.us
... A) a chart that tracks which members of a family have a particular trait B) a geneticist who studies the inheritance of traits in humans C) a picture of all of the chromosomes in a cell D) an allele passed from parent to child on a sex chromosome 26. If a human body cell has 46 chromosomes, how many ...
... A) a chart that tracks which members of a family have a particular trait B) a geneticist who studies the inheritance of traits in humans C) a picture of all of the chromosomes in a cell D) an allele passed from parent to child on a sex chromosome 26. If a human body cell has 46 chromosomes, how many ...
Allele - CARNES AP BIO
... Alternative versions (different alleles) of genes account for variations in inherited characters. For each character, an organism inherits two alleles, one from each parent. If the two alleles differ, the dominant allele is expressed in the organism’s appearance, and the other, a recessive allele is ...
... Alternative versions (different alleles) of genes account for variations in inherited characters. For each character, an organism inherits two alleles, one from each parent. If the two alleles differ, the dominant allele is expressed in the organism’s appearance, and the other, a recessive allele is ...
File
... What are the genotypes of a cross between pure breeding round, yellow peas with pure breeding wrinkled, green peas? Round and green are dominant Let G = green and g = yellow Let R = round and r = wrinkled The parent plants become RRgg x rrGG (Gametes are Rg x rG) ...
... What are the genotypes of a cross between pure breeding round, yellow peas with pure breeding wrinkled, green peas? Round and green are dominant Let G = green and g = yellow Let R = round and r = wrinkled The parent plants become RRgg x rrGG (Gametes are Rg x rG) ...
CHS H Bio Final Exam Review Sheet:
... gametes can each parent produce & what are the expected phenotypes of the offspring? What are the 3 alleles for human blood? Which of the two are codominant to each other and which is recessive? What are linked genes? What is more likely to occur the farther genes are position from one another on th ...
... gametes can each parent produce & what are the expected phenotypes of the offspring? What are the 3 alleles for human blood? Which of the two are codominant to each other and which is recessive? What are linked genes? What is more likely to occur the farther genes are position from one another on th ...
BIOL08012 2016 May
... Segregation of alleles and chimaerism. Crossing over and non-disjunction. Independent assortment and crossing over. Hybridisation and mosaicism. ...
... Segregation of alleles and chimaerism. Crossing over and non-disjunction. Independent assortment and crossing over. Hybridisation and mosaicism. ...
draft - Nelson Education
... Main idea: Mendel’s data revealed patterns of inheritance. Table 1 Mendel’s Data ...
... Main idea: Mendel’s data revealed patterns of inheritance. Table 1 Mendel’s Data ...
Genetics Revision List
... o Be able to explain how genetic material in offspring is the combination of the parents’ original genetic information o Be able to put information into a punnett square to work out probability of offspring carrying specific characteristics o Show using a punnett square how there is always a 50% cha ...
... o Be able to explain how genetic material in offspring is the combination of the parents’ original genetic information o Be able to put information into a punnett square to work out probability of offspring carrying specific characteristics o Show using a punnett square how there is always a 50% cha ...























