GroupActivity_answers_final
... You took F1 and put them on separate plates for self-fertilization. ...
... You took F1 and put them on separate plates for self-fertilization. ...
Biology Notes - Chapter 6 SECTION 1
... identical daughter cells developing from a single parent cell. Meiosis is the division of a germ cell involving two fissions of the nucleus and giving rise to four gametes, or sex cells, each possessing half the number of chromosomes of the original cell. Mitosis is used by single-celled organisms t ...
... identical daughter cells developing from a single parent cell. Meiosis is the division of a germ cell involving two fissions of the nucleus and giving rise to four gametes, or sex cells, each possessing half the number of chromosomes of the original cell. Mitosis is used by single-celled organisms t ...
Chapter 2 – Genotype Frequencies
... of simplifying assumptions about the structure of populations ² random mating* ² non-overlapping generations* ² migration (gene flow), mutation, and natural selection have negligible effects ² large population size (= no genetic drift) ² sexual reproduction ² two alleles at a locus ² allele ...
... of simplifying assumptions about the structure of populations ² random mating* ² non-overlapping generations* ² migration (gene flow), mutation, and natural selection have negligible effects ² large population size (= no genetic drift) ² sexual reproduction ² two alleles at a locus ² allele ...
Course Competencies Template – Form 112
... 9. Differentiating between essential genes and both dominant and recessive lethal alleles. 10. Explaining the environmental influences on gene expression. 11. Listing examples of non-Mendelian inheritance. ...
... 9. Differentiating between essential genes and both dominant and recessive lethal alleles. 10. Explaining the environmental influences on gene expression. 11. Listing examples of non-Mendelian inheritance. ...
Course Competencies Template – Form 112
... 9. Differentiating between essential genes and both dominant and recessive lethal alleles. 10. Explaining the environmental influences on gene expression. 11. Listing examples of non-Mendelian inheritance. ...
... 9. Differentiating between essential genes and both dominant and recessive lethal alleles. 10. Explaining the environmental influences on gene expression. 11. Listing examples of non-Mendelian inheritance. ...
Spatial organization is a key difference between unicellular
... changes. Cells may change behaviour on a temporal plan, including but not limited to the cell cycle. Metazoan: Specialized cell functions and differentiation occur based on cell lineage and spatial location within a body plan. Within this body plan, cells retain their specialized function despite en ...
... changes. Cells may change behaviour on a temporal plan, including but not limited to the cell cycle. Metazoan: Specialized cell functions and differentiation occur based on cell lineage and spatial location within a body plan. Within this body plan, cells retain their specialized function despite en ...
Baby Lab
... The traits on the following pages are believed to be inherited in the explained manner. Most of the traits, however, in this activity were created to illustrate how human heredity works in a simplified model and to reinforce basic genetic principles. In actuality, inherited characteristics of the fa ...
... The traits on the following pages are believed to be inherited in the explained manner. Most of the traits, however, in this activity were created to illustrate how human heredity works in a simplified model and to reinforce basic genetic principles. In actuality, inherited characteristics of the fa ...
IB Bio Year 1 - Inglemoor High School
... 3. Assume that, in chickens, feather color and amount of down are linked. The allele for silver plumage (S) is at locus 12.0, and the allele for light down (Li) is at locus 28.0 on the same chromosome. Both alleles are dominant over their corresponding wild-type alleles. What percent of the various ...
... 3. Assume that, in chickens, feather color and amount of down are linked. The allele for silver plumage (S) is at locus 12.0, and the allele for light down (Li) is at locus 28.0 on the same chromosome. Both alleles are dominant over their corresponding wild-type alleles. What percent of the various ...
Modern Darwins - Portland Public Schools
... Darwin's greatest idea was that natural selection is largely responsible for the variety of traits one sees among related species. Now, in the beak of the finch and the fur of the mouse, we can actually see the hand of natural selection at work, molding and modifying the DNA of genes and their expr ...
... Darwin's greatest idea was that natural selection is largely responsible for the variety of traits one sees among related species. Now, in the beak of the finch and the fur of the mouse, we can actually see the hand of natural selection at work, molding and modifying the DNA of genes and their expr ...
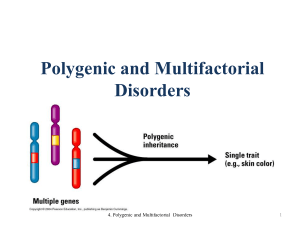
Natural Selection in Polygenic Traits
... Natural Selection in Polygenic Traits Most traits are polygenic, meaning they are coded for by more than one gene. Because many genes influence these traits, polygenic traits come in a range of phenotypes. For example, height is a polygenic trait. As a result, people come in a variety of sizes, rath ...
... Natural Selection in Polygenic Traits Most traits are polygenic, meaning they are coded for by more than one gene. Because many genes influence these traits, polygenic traits come in a range of phenotypes. For example, height is a polygenic trait. As a result, people come in a variety of sizes, rath ...
Origins of Mendelism
... million to get the Japanese pitcher Daisuke Matsuzaka in a Boston uniform for the next six seasons, For intrigued baseball fans in the United States, Matsuzaka's relevant statistics are no-brainers: 26 years old, 6 feet, 187 pounds and a 108-60 record with a 2.95 earned run average in eight seasons ...
... million to get the Japanese pitcher Daisuke Matsuzaka in a Boston uniform for the next six seasons, For intrigued baseball fans in the United States, Matsuzaka's relevant statistics are no-brainers: 26 years old, 6 feet, 187 pounds and a 108-60 record with a 2.95 earned run average in eight seasons ...
Mutations and Selective Advantage
... mutations that occurred as your DNA was copied. Mutagens, such as UV radiation, are environmental agents that can also cause mutations in DNA. Mutations can be harmful but they can sometimes be beneficial. Mutations that occur in body cells disappear from the population when the organism dies. If th ...
... mutations that occurred as your DNA was copied. Mutagens, such as UV radiation, are environmental agents that can also cause mutations in DNA. Mutations can be harmful but they can sometimes be beneficial. Mutations that occur in body cells disappear from the population when the organism dies. If th ...
Genetics-Technology
... This study assessed heavy metals (lead, cadmium, arsenic, nickel, copper, iron and zinc) concentration in lettuce, cabbage and spring onions grown along River Subin and its tributaries; Rivers Wiwi, Oda and Sisa which are extensively used by urban vegetable farmers in Kumasi to irrigate their vegeta ...
... This study assessed heavy metals (lead, cadmium, arsenic, nickel, copper, iron and zinc) concentration in lettuce, cabbage and spring onions grown along River Subin and its tributaries; Rivers Wiwi, Oda and Sisa which are extensively used by urban vegetable farmers in Kumasi to irrigate their vegeta ...
Notes - Sex-Linked Inheritance
... • Colorblindness is an example of a sex-linked incomplete dominance disorder in humans. • It is a recessive trait. • The colorblind trait is carried on the X chromosome. • Colorblindness in Females • XC= normal • Xc=defective • Normal Female = XC XC • Colorblind Female = Xc Xc • Carrier Female = XC ...
... • Colorblindness is an example of a sex-linked incomplete dominance disorder in humans. • It is a recessive trait. • The colorblind trait is carried on the X chromosome. • Colorblindness in Females • XC= normal • Xc=defective • Normal Female = XC XC • Colorblind Female = Xc Xc • Carrier Female = XC ...
Ch16 Population Evolution
... chemicals in the environment Only some mutations change the phenotype & affect fitness ...
... chemicals in the environment Only some mutations change the phenotype & affect fitness ...
evolution/population genetics
... phenotype will show if either the homozygous "AA" or heterozygous "Aa" genotypes occur. The recessive phenotype is controlled by the homozygous aa genotype. Therefore, the frequency of the dominant phenotype equals the sum of the frequencies of AA and Aa, and the recessive phenotype is simply the fr ...
... phenotype will show if either the homozygous "AA" or heterozygous "Aa" genotypes occur. The recessive phenotype is controlled by the homozygous aa genotype. Therefore, the frequency of the dominant phenotype equals the sum of the frequencies of AA and Aa, and the recessive phenotype is simply the fr ...
Linkage and Mapping
... within the context of the Independent assortment of genes will not be possible if the genes are linked. The linked status of genes is paper indicated by the number of genes in an organism and the relative number of chromosomes carrying them. Linkage between genes leads to varied inheritance, depende ...
... within the context of the Independent assortment of genes will not be possible if the genes are linked. The linked status of genes is paper indicated by the number of genes in an organism and the relative number of chromosomes carrying them. Linkage between genes leads to varied inheritance, depende ...
Fish sampling - BioMed Central
... In order to evaluate reference gene stability four different populations of Atlantic cod were chosen. Male Atlantic cod were sampled from three wild populations and from an aquaculture facility in February and March 2006. Fish from Sørfjorden (Odda, 60.1°N/6.5°E, N=6, mean weight 335±94 g) and from ...
... In order to evaluate reference gene stability four different populations of Atlantic cod were chosen. Male Atlantic cod were sampled from three wild populations and from an aquaculture facility in February and March 2006. Fish from Sørfjorden (Odda, 60.1°N/6.5°E, N=6, mean weight 335±94 g) and from ...
The Third PowerPoint (DNA and Sex Determination)
... A child must be similar enough to its parents to survive in a similar environment, but have the chance to be different enough to survive in a changing environment. It is a benefit to be genetically different from our parents, in case we must survive in an environment that is different from the one t ...
... A child must be similar enough to its parents to survive in a similar environment, but have the chance to be different enough to survive in a changing environment. It is a benefit to be genetically different from our parents, in case we must survive in an environment that is different from the one t ...
Biology EOCT Review
... mapping out locations of genes (and the traits they code for) in the 23 pairs of chromosomes Phenotype – physical appearance of a trait (tall plant) Genotype – allele combonation in an organism (TT, Tt) Homozygous – alleles are the same Heterozygous – alleles are different (hybrid) ...
... mapping out locations of genes (and the traits they code for) in the 23 pairs of chromosomes Phenotype – physical appearance of a trait (tall plant) Genotype – allele combonation in an organism (TT, Tt) Homozygous – alleles are the same Heterozygous – alleles are different (hybrid) ...