Chemistry
... Properties that can be measured or observed without changing it’s identity ◦ Length, mass, color, odor, density, boiling point, melting point ...
... Properties that can be measured or observed without changing it’s identity ◦ Length, mass, color, odor, density, boiling point, melting point ...
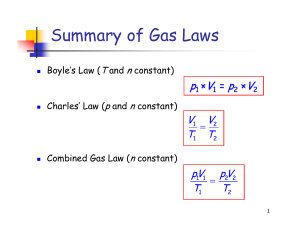
Summary of Gas Laws
... fraction of molecules that possess enough kinetic energy to break away into a gas phase This process is called evaporation Therefore, some part of a liquid substance is always present in form of vapor (gas phase) over the surface of the liquid Gas phase molecules can strike the liquid surface and be ...
... fraction of molecules that possess enough kinetic energy to break away into a gas phase This process is called evaporation Therefore, some part of a liquid substance is always present in form of vapor (gas phase) over the surface of the liquid Gas phase molecules can strike the liquid surface and be ...
Pre-AP Chemistry Kinetic Theory and Heat Quiz
... 1. According to the kinetic theory, the primary difference in the phases of matter (of the same substance) is the __speed_ of the particles. Thus, the two factors that influence which state of matter exists are __pressure_ and temperature. 2. The higher the energy of the particles, the faster they m ...
... 1. According to the kinetic theory, the primary difference in the phases of matter (of the same substance) is the __speed_ of the particles. Thus, the two factors that influence which state of matter exists are __pressure_ and temperature. 2. The higher the energy of the particles, the faster they m ...
6.2 Solution Varieties
... This is the rapid release of a dissolved gas from a solvent liquid. For example: the fizzing sound and small gas bubbles leaving your soft drink when you open it. Keeping the lid on helps your soda not go flat as the gas cannot escape into the air. The gas is CO2. ii. Adding Kinetic energy in the fo ...
... This is the rapid release of a dissolved gas from a solvent liquid. For example: the fizzing sound and small gas bubbles leaving your soft drink when you open it. Keeping the lid on helps your soda not go flat as the gas cannot escape into the air. The gas is CO2. ii. Adding Kinetic energy in the fo ...
MATTER QUIZ: What to Study From: PHASE CHANGES
... 3. Process by which a liquid becomes a gas identified by the formation of bubbles. __________________________________________ 4. Temperature at which a liquid becomes a solid. ________________________________ 5. Process by which a solid becomes a liquid. _____________________________________ 6. Icic ...
... 3. Process by which a liquid becomes a gas identified by the formation of bubbles. __________________________________________ 4. Temperature at which a liquid becomes a solid. ________________________________ 5. Process by which a solid becomes a liquid. _____________________________________ 6. Icic ...
Unit 4: Physical Properties and Changes
... Magnetic – having the properties of a magnet, an object that can attract iron Melting – phase change where a solid becomes a liquid Solid – phase of matter that has definite shape and volume Substance – matter; anything that has mass and takes up space Texture – the appearance and feel of a substanc ...
... Magnetic – having the properties of a magnet, an object that can attract iron Melting – phase change where a solid becomes a liquid Solid – phase of matter that has definite shape and volume Substance – matter; anything that has mass and takes up space Texture – the appearance and feel of a substanc ...
Packed Bed Reactors - EngineeringDuniya.com
... – Because shear levels are much lower than in STRs ...
... – Because shear levels are much lower than in STRs ...
Low Cycle Fatigue in Aluminum Foam with Notch
... Metal foams are a new material being used in industry. These materials are used in lightweight structures due to their high strength to weight and stiffness to weight ratios. However, these materials have not been fully characterized yet. This research examined Alporas, a closed cell aluminum foam, ...
... Metal foams are a new material being used in industry. These materials are used in lightweight structures due to their high strength to weight and stiffness to weight ratios. However, these materials have not been fully characterized yet. This research examined Alporas, a closed cell aluminum foam, ...
Foam

A foam is a substance that is formed by trapping pockets of gas in a liquid or solid. A bath sponge and the head on a glass of beer are examples of foams. In most foams, the volume of gas is large, with thin films of liquid or solid separating the regions of gas.An important division of solid foams is into closed-cell foams and open-cell foams. In a closed-cell foam, the gas forms discrete pockets, each completely surrounded by the solid material. In an open-cell foam, the gas pockets connect with each other. A bath sponge is an example of an open-cell foam: water can easily flow through the entire structure, displacing the air. A camping mat is an example of a closed-cell foam: the gas pockets are sealed from each other so the mat cannot soak up water.Foams are examples of dispersed media. In general, gas is present in large amount so it will be divided into gas bubbles of many different sizes (the material is polydisperse) separated by liquid regions which may form films, thinner and thinner when the liquid phase is drained out of the system films. When the principal scale is small, i.e. for a very fine foam, this dispersed medium can be considered as a type of colloid.The term foam may also refer to anything that is analogous to such a foam, such as quantum foam, polyurethane foam (foam rubber), XPS foam, polystyrene, phenolic, or many other manufactured foams.