Name:
... When resistors are connected in parallel, each resistor provides a path for electrons to follow and, therefore, reduces the equivalent resistance to the current. In Figure 1 (c), three resistors are connected in parallel across a voltage source. There are three paths by which the current may pass fr ...
... When resistors are connected in parallel, each resistor provides a path for electrons to follow and, therefore, reduces the equivalent resistance to the current. In Figure 1 (c), three resistors are connected in parallel across a voltage source. There are three paths by which the current may pass fr ...
Unregulated and Regulated Power Supplies
... perform properly. Exact values may not be available, so some compromises will have to be made, and it may not be possible to test the supply over the full design operating range, or perhaps for only very short periods to avoid excess heating. Also, the power capability of this dropping resistor must ...
... perform properly. Exact values may not be available, so some compromises will have to be made, and it may not be possible to test the supply over the full design operating range, or perhaps for only very short periods to avoid excess heating. Also, the power capability of this dropping resistor must ...
EE 101 Lab 2 Ohm`s and Kirchhoff`s Circuit Laws
... Kirchhoff’s current law for one of the circuit nodes and explain how this law relates to your measured currents. ...
... Kirchhoff’s current law for one of the circuit nodes and explain how this law relates to your measured currents. ...
Chapter 6-voltage regulator
... A typical 78XX series of IC regulators – three-terminal devices that provide a fixed positive output voltage. A typical 79XX series of IC regulators – three-terminal devices that provide a fixed negative output voltage Almost all applications of regulators require the device be secured to a heat sin ...
... A typical 78XX series of IC regulators – three-terminal devices that provide a fixed positive output voltage. A typical 79XX series of IC regulators – three-terminal devices that provide a fixed negative output voltage Almost all applications of regulators require the device be secured to a heat sin ...
iC-DX / iC-DXC - iC-Haus
... to 450 mA. With input OE on high level state, the output works as a push-pull driver controlled by input IN. If IN is set either to high or low level, the output acts as a high-side (PNP) or low-side (NPN) driver which is activated by a high logic level on input OE. Output transitions are slew-rate ...
... to 450 mA. With input OE on high level state, the output works as a push-pull driver controlled by input IN. If IN is set either to high or low level, the output acts as a high-side (PNP) or low-side (NPN) driver which is activated by a high logic level on input OE. Output transitions are slew-rate ...
Introduction and Digital Images
... The RC Differentiator An RC differentiator is a circuit that approximates the mathematical process of differentiation. Differentiation is a process that finds the rate of change, and a basic differentiator can produce an output that is the rate of change of the input under certain conditions. ...
... The RC Differentiator An RC differentiator is a circuit that approximates the mathematical process of differentiation. Differentiation is a process that finds the rate of change, and a basic differentiator can produce an output that is the rate of change of the input under certain conditions. ...
A Quasi-Resonant Soft Switching 48-pulse PWM inverter with closed
... resonance. The operation frequency of these control signals is set to 200 KHz meaning that the input voltage is pulled down to zero once in every 5 μseconds. This value is a hundred-fold of PWM generator’s operation frequency and thus is sufficient to ensure the realization of zero voltage switching ...
... resonance. The operation frequency of these control signals is set to 200 KHz meaning that the input voltage is pulled down to zero once in every 5 μseconds. This value is a hundred-fold of PWM generator’s operation frequency and thus is sufficient to ensure the realization of zero voltage switching ...
ICL7673 Datasheet
... ICL7673 is intended as a low-cost solution for the switching of systems between two power supplies; main and battery backup. The main application is keep-alive-battery power switching for use in volatile CMOS RAM memory systems and real time clocks. In many applications this circuit will represent a ...
... ICL7673 is intended as a low-cost solution for the switching of systems between two power supplies; main and battery backup. The main application is keep-alive-battery power switching for use in volatile CMOS RAM memory systems and real time clocks. In many applications this circuit will represent a ...
Measuring Voltage Drop and Current
... “voltage drop” in a circuit. Voltage drop refers to the amount of energy lost or gained between two points in a circuit. ...
... “voltage drop” in a circuit. Voltage drop refers to the amount of energy lost or gained between two points in a circuit. ...
PN100/PN100A/MMBT100/MMBT100A NPN General Purpose Amplifier PN100/PN100A/MMBT100/MMBT
... This datasheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data will be published at a later date. Fairchild Semiconductor reserves the right to make changes at any time without notice to improve design. ...
... This datasheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data will be published at a later date. Fairchild Semiconductor reserves the right to make changes at any time without notice to improve design. ...
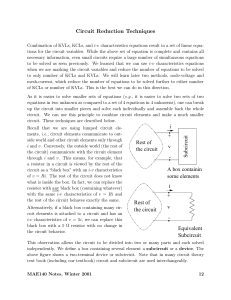
Circuit Reduction Techniques
... A typical Ohm-meter measures the resistance of a resistor by using the Ohm’s Law. It applies a known voltage of vs across the resistor, measures the current flowing through the resistor, and its dial are set to convert the measured value of current into the value of resistance by using R = vs /imeasu ...
... A typical Ohm-meter measures the resistance of a resistor by using the Ohm’s Law. It applies a known voltage of vs across the resistor, measures the current flowing through the resistor, and its dial are set to convert the measured value of current into the value of resistance by using R = vs /imeasu ...
Parallel Circuits
... 11. Determine the electric potential difference (i.e. voltage drop) across the 5-Ω resistor (from B to C). ∆VBC = 30.0 V (For parallel circuits, the branch voltages are the same as the battery voltage.) 12. Determine the current through the 5-Ω resistor (from B to C). IBC = ∆VBC / RBC = (30.0 V)/(5. ...
... 11. Determine the electric potential difference (i.e. voltage drop) across the 5-Ω resistor (from B to C). ∆VBC = 30.0 V (For parallel circuits, the branch voltages are the same as the battery voltage.) 12. Determine the current through the 5-Ω resistor (from B to C). IBC = ∆VBC / RBC = (30.0 V)/(5. ...
Lab: Series and Parallel Circuits
... Table 1: Current and Voltage for a Simple Circuit Voltage at Source (V) ...
... Table 1: Current and Voltage for a Simple Circuit Voltage at Source (V) ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.