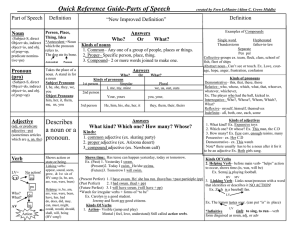
The dreaded grammar cards
... Conjunction Connect groups of words 1) And, but, or, nor, for, so, yet 2) Either/or, neither/nor, but/and 3) (adverbs) After, although, as, as if, when, where, while, though, unless, until ...
... Conjunction Connect groups of words 1) And, but, or, nor, for, so, yet 2) Either/or, neither/nor, but/and 3) (adverbs) After, although, as, as if, when, where, while, though, unless, until ...
Nouns * people, places, things, and ideas
... Examples: girl, boy, school, lake, monument, city, loyalty, friendship Proper Nouns – specific, capitalized nouns (names) Examples: Sarah, Jake, Shaker Junior High, Lake George, Washington Monument, Statue of Liberty Singular Noun – only one person, place, thing, or idea (single) Examples: girl, boy ...
... Examples: girl, boy, school, lake, monument, city, loyalty, friendship Proper Nouns – specific, capitalized nouns (names) Examples: Sarah, Jake, Shaker Junior High, Lake George, Washington Monument, Statue of Liberty Singular Noun – only one person, place, thing, or idea (single) Examples: girl, boy ...
Parts of Speech and Parts of the Sentence
... will always come before the pronoun— sometimes even a couple sentences before! EX: When the moped stalled, I gave it a swift kick. Pronoun “it” refers to the noun “moped” ...
... will always come before the pronoun— sometimes even a couple sentences before! EX: When the moped stalled, I gave it a swift kick. Pronoun “it” refers to the noun “moped” ...
Stay and write 2015 y1 [ ppt 5MB ]
... Conjunction- A conjunction links two words or phrases together. There are two main types of conjunctions: coordinating conjunctions (e.g. and) link two words or phrases together as an equal pair subordinating conjunctions (e.g. when) introduce a subordinate clause ...
... Conjunction- A conjunction links two words or phrases together. There are two main types of conjunctions: coordinating conjunctions (e.g. and) link two words or phrases together as an equal pair subordinating conjunctions (e.g. when) introduce a subordinate clause ...
Document
... Adverbs (adv.) are heads of (AdvP). They describe verbs, and adjectives, and other adverbs. They are formed by adding –ly to the corresponding adjectives: Charlotte spoke kindly to the confused man. The man said he was completely alone in the world. Charlotte listened very sympathetically to his sto ...
... Adverbs (adv.) are heads of (AdvP). They describe verbs, and adjectives, and other adverbs. They are formed by adding –ly to the corresponding adjectives: Charlotte spoke kindly to the confused man. The man said he was completely alone in the world. Charlotte listened very sympathetically to his sto ...
PARTS OF SPEECH
... WORD IN THE SENTENCE is, are, was , were, am, been smell, look, taste, remain, feel ...
... WORD IN THE SENTENCE is, are, was , were, am, been smell, look, taste, remain, feel ...
16 Mar 09 - Pegasus @ UCF
... common and proper nouns – What are the rules for capitalizing a noun in English? count and noncount nouns – When do I use much/many, few/little? Why can’t I say much persons (In Spanish it’s "muchas personas")? Why do I say many cars but much/a lot of traffic (not many traffics)? singular and plural ...
... common and proper nouns – What are the rules for capitalizing a noun in English? count and noncount nouns – When do I use much/many, few/little? Why can’t I say much persons (In Spanish it’s "muchas personas")? Why do I say many cars but much/a lot of traffic (not many traffics)? singular and plural ...
Singular This That - Scott County, Virginia Public Schools
... The most common auxiliary verbs are the forms of be and have. They help the main verb express the various tenses. We are working in the yard. We have worked for the past two weeks. We had been working for an hour before the ...
... The most common auxiliary verbs are the forms of be and have. They help the main verb express the various tenses. We are working in the yard. We have worked for the past two weeks. We had been working for an hour before the ...
The Most Common Writing Errors
... Do not use: ya, thru, wanna, gonna Do not use: etc., & Avoid contractions: don’t, wouldn’t, can’t, it’s ...
... Do not use: ya, thru, wanna, gonna Do not use: etc., & Avoid contractions: don’t, wouldn’t, can’t, it’s ...
GLOSARIO DE INGLÉS (Educación Media) Adjective: A word that
... Adverbs of manner: They tell us how something happens. Chart or Table: An arrangement of facts or numbers in rows or columns. Clue: A sign or a piece of information that helps you to solve a problem or answer a question. Cognate: Languages and words that have the same origin, or that are related and ...
... Adverbs of manner: They tell us how something happens. Chart or Table: An arrangement of facts or numbers in rows or columns. Clue: A sign or a piece of information that helps you to solve a problem or answer a question. Cognate: Languages and words that have the same origin, or that are related and ...
parts of speech
... ADJECTIVE: An adjective is a word that describes, or tells about, a noun. Examples: pretty, old, green, plentiful, twelve, this, that, these, those, a, an, the In Sentences: The old brown dog wagged his short tail. I am very happy today. VERB: A verb is a word that tells an action or state of being. ...
... ADJECTIVE: An adjective is a word that describes, or tells about, a noun. Examples: pretty, old, green, plentiful, twelve, this, that, these, those, a, an, the In Sentences: The old brown dog wagged his short tail. I am very happy today. VERB: A verb is a word that tells an action or state of being. ...
Basic Grammar
... Points out specific persons, places, things, or ideas. This, these- point out persons or things that are near in space or time. That, those- point out persons or things that are more distant in space or time. ...
... Points out specific persons, places, things, or ideas. This, these- point out persons or things that are near in space or time. That, those- point out persons or things that are more distant in space or time. ...
Basic Grammar
... Points out specific persons, places, things, or ideas. This, these- point out persons or things that are near in space or time. That, those- point out persons or things that are more distant in space or time. ...
... Points out specific persons, places, things, or ideas. This, these- point out persons or things that are near in space or time. That, those- point out persons or things that are more distant in space or time. ...
Parts of Speech - Rocky View Schools
... Write a sentence that uses an action verb, then one that uses a verb of being. (a) ______________________________________________________________________________________ (b) ______________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... Write a sentence that uses an action verb, then one that uses a verb of being. (a) ______________________________________________________________________________________ (b) ______________________________________________________________________________________ ...
- West Point High School
... 4. A month's pay disappeared easily after paying the bills. 5. A six-year-old child should be required to make his own ...
... 4. A month's pay disappeared easily after paying the bills. 5. A six-year-old child should be required to make his own ...
writing cheat sheet
... A word that comes before a noun or pronoun, a preposition creates a phrase that modifies another word in the sentence. The noun or the pronoun is called the object of the preposition, and the phrase that is created is called a prepositional phrase. Example: She spilled the drink on him. Prepositions ...
... A word that comes before a noun or pronoun, a preposition creates a phrase that modifies another word in the sentence. The noun or the pronoun is called the object of the preposition, and the phrase that is created is called a prepositional phrase. Example: She spilled the drink on him. Prepositions ...
Parts of Speech
... to a noun or pronoun in the same sentence. Ex: No one asked the doctor herself if she needed help. ...
... to a noun or pronoun in the same sentence. Ex: No one asked the doctor herself if she needed help. ...
Chapter 1 Grammar
... ALL information as shown in book. Read through the grammar section and remember what we learned in class today. In your own words, write a summary of the grammar section. Include ALL charts shown in the grammar section. ...
... ALL information as shown in book. Read through the grammar section and remember what we learned in class today. In your own words, write a summary of the grammar section. Include ALL charts shown in the grammar section. ...
1. Lexical Categories Nouns, Verbs, Adjectives, Prepositions, Adverbs
... Morphological distribution - determined by the kind of affixes that a given word takes and other morphology. Looking at characteristic inflectional and derivational endings of words e.g.: if elements can take endings such as –s, -‘s, s’ or -ment -dom, -er, we can say they are nouns Syntactic distr ...
... Morphological distribution - determined by the kind of affixes that a given word takes and other morphology. Looking at characteristic inflectional and derivational endings of words e.g.: if elements can take endings such as –s, -‘s, s’ or -ment -dom, -er, we can say they are nouns Syntactic distr ...
NAME
... A noun is used to name a person, place, thing, quality or idea. A few examples of each are Bill, Detroit, car, beauty and justice. What is a pronoun? A pronoun is used in the place of a noun or phrase. There are many types of pronouns: personal, relative, interrogative, reflexive, intensive, demonst ...
... A noun is used to name a person, place, thing, quality or idea. A few examples of each are Bill, Detroit, car, beauty and justice. What is a pronoun? A pronoun is used in the place of a noun or phrase. There are many types of pronouns: personal, relative, interrogative, reflexive, intensive, demonst ...
A euphemism is when you make a word sound less harsh. Example
... The main clause is like a simple sentence. It must have a subject and a verb. It must also make sense. It may even be part of a bigger sentence. “I went home.” (main clause) “Because I went home.” (not a main clause-doesn’t make sense) “After the storm, the boat sank.” (the ...
... The main clause is like a simple sentence. It must have a subject and a verb. It must also make sense. It may even be part of a bigger sentence. “I went home.” (main clause) “Because I went home.” (not a main clause-doesn’t make sense) “After the storm, the boat sank.” (the ...



![Stay and write 2015 y1 [ ppt 5MB ]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003100526_1-72287210420a6e1d2b6a1ef8c9b96048-300x300.png)