Why the Euro Failed and How It Will Survive
... stocks, were not watched, as they cannot easily be included in a consumer price index. We now realize that nominal GDP grew excessively over the whole period and that a tighter interest rate policy would have been called for. Automatic Payments Clearance—The ECB manages an automatic system called TA ...
... stocks, were not watched, as they cannot easily be included in a consumer price index. We now realize that nominal GDP grew excessively over the whole period and that a tighter interest rate policy would have been called for. Automatic Payments Clearance—The ECB manages an automatic system called TA ...
Exchange rates and the transmission of global liquidity
... To be sure, there are some mitigating factors. For one thing, much of the recent increase in dollar debt in EMEs has been in the form of debt securities issued by emerging market corporates. These debt securities have long maturities. The average maturity of international debt securities issued by E ...
... To be sure, there are some mitigating factors. For one thing, much of the recent increase in dollar debt in EMEs has been in the form of debt securities issued by emerging market corporates. These debt securities have long maturities. The average maturity of international debt securities issued by E ...
Presentation
... possible, even allowing some “sacrifice”. • System arrangement – The control of capital account – The control of exchange rate (fixed or manageable floating exchange regime for the purpose to devaluating domestic currency) – No debt, but accumulating hard currency or its denominated assets. ...
... possible, even allowing some “sacrifice”. • System arrangement – The control of capital account – The control of exchange rate (fixed or manageable floating exchange regime for the purpose to devaluating domestic currency) – No debt, but accumulating hard currency or its denominated assets. ...
The Price Competitiveness of U.S. Exports: An Update
... But in foreign currency terms, prices have been relatively ...
... But in foreign currency terms, prices have been relatively ...
Exchange rates
... MK, U 26, p 128 and match with a heading The Bretton-Woods Agreement of 1944 established ______ exchange rates, defined in terms of ______ and the US dollar. Between 1944 and 1971 many currencies were _______ ______ the US dollar, i.e. their parities with the US dolar were fixed. One US dollar was ...
... MK, U 26, p 128 and match with a heading The Bretton-Woods Agreement of 1944 established ______ exchange rates, defined in terms of ______ and the US dollar. Between 1944 and 1971 many currencies were _______ ______ the US dollar, i.e. their parities with the US dolar were fixed. One US dollar was ...
File - MCNEIL ECONOMICS
... Established a free trade zone between the countries Trade has increased in all countries Enhanced standard of living ...
... Established a free trade zone between the countries Trade has increased in all countries Enhanced standard of living ...
China`s Renminbi Will Not Threaten The Dollar`s Reserve
... without having to create additional U.S. dollars, which had the byproduct of driving up the market price for gold and making it increasingly difficult to maintain the $35 an ounce dollar peg. The SDR was intended to play a significant role in foreign exchange reserves, but with the collapse of the d ...
... without having to create additional U.S. dollars, which had the byproduct of driving up the market price for gold and making it increasingly difficult to maintain the $35 an ounce dollar peg. The SDR was intended to play a significant role in foreign exchange reserves, but with the collapse of the d ...
operating_exposure
... The effect of hedging on exporters When an arrangement exists to export a stated quantity at a price fixed in home currency, devaluation can temporarily hurt an exporter’s profit. This is true in both dollar and foreigncurrency units. This is because costs are still susceptible to exchange rate ...
... The effect of hedging on exporters When an arrangement exists to export a stated quantity at a price fixed in home currency, devaluation can temporarily hurt an exporter’s profit. This is true in both dollar and foreigncurrency units. This is because costs are still susceptible to exchange rate ...
Economy: Undo Jonathan`s Sealed Failure (2)
... accounts and foreign exchange sales by oil companies). Although the inflow more than offset the entire import cost of $57.66 billion (C&F unadjusted for balance of payments), there was unexpected drop in foreign reserves from their end-year 2009 level. Expenditure on imported invisibles was dispropo ...
... accounts and foreign exchange sales by oil companies). Although the inflow more than offset the entire import cost of $57.66 billion (C&F unadjusted for balance of payments), there was unexpected drop in foreign reserves from their end-year 2009 level. Expenditure on imported invisibles was dispropo ...
Ben S Bernanke: Money, gold and the Great Depression
... decade, full recovery arriving only with the advent of World War II. Moreover, as I will discuss later, the Depression was international in scope, affecting most countries around the world not only the United States. What caused the Depression? This question is a difficult one, but answering it is ...
... decade, full recovery arriving only with the advent of World War II. Moreover, as I will discuss later, the Depression was international in scope, affecting most countries around the world not only the United States. What caused the Depression? This question is a difficult one, but answering it is ...
Economics 3500 Introduction to International Economics
... exchange one, three, or six months after the contract in agreed upon. Foreign exchange futures. -A forward contract for standardized currency amounts and selected calendar Dates traded on an organized market (exchange). Gold standard. A monetary system in which governments or central banks maintain ...
... exchange one, three, or six months after the contract in agreed upon. Foreign exchange futures. -A forward contract for standardized currency amounts and selected calendar Dates traded on an organized market (exchange). Gold standard. A monetary system in which governments or central banks maintain ...
Mr. Tietmeyer discusses the benefits, opportunities and pitfalls of
... stable. Only then will the euro lead to full price transparency, reduce costs and become an attractive investment currency. Secondly, monetary union must not trigger or exacerbate economic tensions. Broadly speaking, an essential requirement that must be met is: one size fits all. And, thirdly, mone ...
... stable. Only then will the euro lead to full price transparency, reduce costs and become an attractive investment currency. Secondly, monetary union must not trigger or exacerbate economic tensions. Broadly speaking, an essential requirement that must be met is: one size fits all. And, thirdly, mone ...
Currency Crisis Models - Kellogg School of Management
... An important policy question is: what is the optimal nature of interest rate policy during and after a currency crisis? There has been relatively little formal work on this topic. Christiano, Braggion and Roldos (2006) take an important first step in this direction. They argue that it is optimal to ...
... An important policy question is: what is the optimal nature of interest rate policy during and after a currency crisis? There has been relatively little formal work on this topic. Christiano, Braggion and Roldos (2006) take an important first step in this direction. They argue that it is optimal to ...
Currency Crisis in Thailand: The Leading Indicators
... attacks (Sussangkarn, 1998). On July 2, 1997, after draining its foreign exchange reserves, the world market forced the Bank of Thailand to give up its defense of the baht. The government sought aid from the IMF (International Monetary Fund) and central banks in Japan and Asia (Alexander and Guthrie ...
... attacks (Sussangkarn, 1998). On July 2, 1997, after draining its foreign exchange reserves, the world market forced the Bank of Thailand to give up its defense of the baht. The government sought aid from the IMF (International Monetary Fund) and central banks in Japan and Asia (Alexander and Guthrie ...
The Costs of a Single Currency
... 2. . . . causes output to rise in the short run . . . A rise in aggregate demand is represented with a rightward shift in the aggregate-demand curve from AD1 to AD2. In the short run, the economy moves from point A to point B. Output rises from Y1 to Y2, and the price level rises from P1 to P2. Over ...
... 2. . . . causes output to rise in the short run . . . A rise in aggregate demand is represented with a rightward shift in the aggregate-demand curve from AD1 to AD2. In the short run, the economy moves from point A to point B. Output rises from Y1 to Y2, and the price level rises from P1 to P2. Over ...
Ch. 26 Section 1
... resources to produce those things that they produce better than any other country When a country produces more than their people can actually use, they sell the extra amount abroad. Countries can have comparative advantage in particular resources such as Saudi Arabia (oil deposits), or the U.S. ...
... resources to produce those things that they produce better than any other country When a country produces more than their people can actually use, they sell the extra amount abroad. Countries can have comparative advantage in particular resources such as Saudi Arabia (oil deposits), or the U.S. ...
China
... lots of short-term money has flowed in. Controls are likely to become even more porous as China becomes more integrated into the global economy. Thus, waiting for speculative and other inflows to ease before changing the exchange-rate regime might not be a fruitful strategy. China ought to move to a ...
... lots of short-term money has flowed in. Controls are likely to become even more porous as China becomes more integrated into the global economy. Thus, waiting for speculative and other inflows to ease before changing the exchange-rate regime might not be a fruitful strategy. China ought to move to a ...
ToP of the BoPs
... stress, both in the emerging and developed markets, by which we could make investment and trading decisions. They are the thermometer by which we can first observe the very real signs of a monetary system in turmoil. In keeping with our musical theme, we wanted to make reference to another iconic UK ...
... stress, both in the emerging and developed markets, by which we could make investment and trading decisions. They are the thermometer by which we can first observe the very real signs of a monetary system in turmoil. In keeping with our musical theme, we wanted to make reference to another iconic UK ...
The Global Financial Crisis
... alone. Almost three quarters of this amount went into short-term portfolio investment, that is, purchase of bonds and non-controlling shares. This kind of investment created very few jobs as about half of it went to purchase government bonds. Unlike in Asia where bank loans were the predominant form ...
... alone. Almost three quarters of this amount went into short-term portfolio investment, that is, purchase of bonds and non-controlling shares. This kind of investment created very few jobs as about half of it went to purchase government bonds. Unlike in Asia where bank loans were the predominant form ...
www.uri.edu
... 1970s International The 70s opened with the US running out of gold, which forced president Nixon to abandon the Bretton Woods system and adopt a flexible exchange rate. The US $’s value would now be determined in a market rather than by the government. We begin with a brief overview of the “Books” ...
... 1970s International The 70s opened with the US running out of gold, which forced president Nixon to abandon the Bretton Woods system and adopt a flexible exchange rate. The US $’s value would now be determined in a market rather than by the government. We begin with a brief overview of the “Books” ...
A Common Sense Vision for Canada
... confidence in the future value of money and bring corresponding gains in efficiency. The idea that a positive rate of inflation is needed to facilitate labor market adjustments when nominal wages are rigid is an obsolete leftover of Keynesian doctrine for the following two reasons. Labor market rigi ...
... confidence in the future value of money and bring corresponding gains in efficiency. The idea that a positive rate of inflation is needed to facilitate labor market adjustments when nominal wages are rigid is an obsolete leftover of Keynesian doctrine for the following two reasons. Labor market rigi ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿 - Tulane University
... • The firm was founded in 1969 by George Soros and in 2010 was reported to be one of the most profitable firms in the hedge fund industry, averaging a 20% annual rate of return over four decades. • It is headquartered in New York City. • In July, 2011, The Quantum fund announced that they would be e ...
... • The firm was founded in 1969 by George Soros and in 2010 was reported to be one of the most profitable firms in the hedge fund industry, averaging a 20% annual rate of return over four decades. • It is headquartered in New York City. • In July, 2011, The Quantum fund announced that they would be e ...
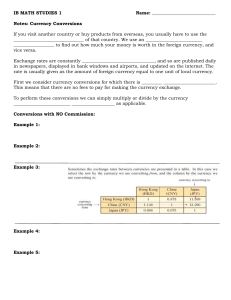
Commission on Currency Exchange
... rates instead. Suppose you live in the U.S. The table below shows how much one American dollar (USD) is worth in some other currencies: ...
... rates instead. Suppose you live in the U.S. The table below shows how much one American dollar (USD) is worth in some other currencies: ...
China and the United States should stabilize the yuan/dollar
... ity shows that both the renminbi and dollar exchange rates (trade) surplus could actually increase! are, as of early 2009, aligned more or less correctly with each Instead of being an exchange rate question, the huge other (at 6.85 yuan/dollar), and with the average exchange trade imbalance between ...
... ity shows that both the renminbi and dollar exchange rates (trade) surplus could actually increase! are, as of early 2009, aligned more or less correctly with each Instead of being an exchange rate question, the huge other (at 6.85 yuan/dollar), and with the average exchange trade imbalance between ...
Chapter 13 The Global Economy
... foreign direct investment (FDI) flexible (floating) exchange rate system ...
... foreign direct investment (FDI) flexible (floating) exchange rate system ...