Slide ()
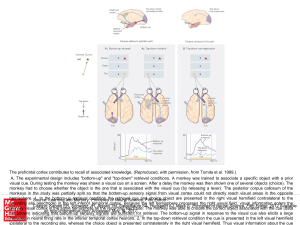
... visual cue. During testing the monkey was shown a visual cue on a screen. After a delay the monkey was then shown one of several objects (choice). The monkey had to choose whether the object is the one that is associated with the visual cue (by releasing a lever). The posterior corpus callosum of th ...
... visual cue. During testing the monkey was shown a visual cue on a screen. After a delay the monkey was then shown one of several objects (choice). The monkey had to choose whether the object is the one that is associated with the visual cue (by releasing a lever). The posterior corpus callosum of th ...
Slide ()
... visual cue. During testing the monkey was shown a visual cue on a screen. After a delay the monkey was then shown one of several objects (choice). The monkey had to choose whether the object is the one that is associated with the visual cue (by releasing a lever). The posterior corpus callosum of th ...
... visual cue. During testing the monkey was shown a visual cue on a screen. After a delay the monkey was then shown one of several objects (choice). The monkey had to choose whether the object is the one that is associated with the visual cue (by releasing a lever). The posterior corpus callosum of th ...
view - Scan. Vet. Press
... cell in the primary visual cortex. The cell receives synaptic input from many neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus. The neurons connected to a particular cortical cell have circular receptive fields that are linearly arranged and of the same type. This gives the cortical cell an oblong receptiv ...
... cell in the primary visual cortex. The cell receives synaptic input from many neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus. The neurons connected to a particular cortical cell have circular receptive fields that are linearly arranged and of the same type. This gives the cortical cell an oblong receptiv ...
Dorsal Column * Medial Lemniscal System (DC-ML)
... Non-dominant hemisphere (Brodmann’s area 5 & 7) • Unilateral negligence • Asomatognosia ...
... Non-dominant hemisphere (Brodmann’s area 5 & 7) • Unilateral negligence • Asomatognosia ...
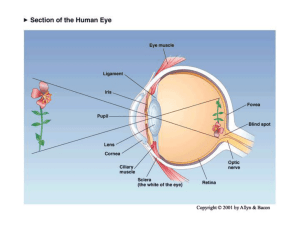
Vision
... Cortical cells have receptive fields too Receptive field in cortex relates to much bigger area that receptive field in retina, so , many ganglion cells Only adjacent areas of visual field in centre have colossal connections ...
... Cortical cells have receptive fields too Receptive field in cortex relates to much bigger area that receptive field in retina, so , many ganglion cells Only adjacent areas of visual field in centre have colossal connections ...
Vision - Dave Brodbeck
... • Cortical cells have receptive fields too • Receptive field in cortex relates to much bigger area that receptive field in retina, so , many ganglion cells • Only adjacent areas of visual field in centre have colossal connections ...
... • Cortical cells have receptive fields too • Receptive field in cortex relates to much bigger area that receptive field in retina, so , many ganglion cells • Only adjacent areas of visual field in centre have colossal connections ...
LSU Seminar Neuroscience Center of Excellence
... Arianna Maffei, Ph.D. Research Associate Brandeis University, Waltham, MA The fine-tuning of circuits in sensory cortex requires sensory experience during an early critical period. Visual deprivation (VD) during the critical period has atastrophic effects on visual function, including loss of visual ...
... Arianna Maffei, Ph.D. Research Associate Brandeis University, Waltham, MA The fine-tuning of circuits in sensory cortex requires sensory experience during an early critical period. Visual deprivation (VD) during the critical period has atastrophic effects on visual function, including loss of visual ...
Chapter 7 part two
... One theory that brings together all of the reviewed attention effects (top-down biases, gain modulation, enhancement and suppression) is Desimone and Duncan’s ‘biased competition’model of attention. The theory rests on three assumptions. First, given the limits on our ability to process several stim ...
... One theory that brings together all of the reviewed attention effects (top-down biases, gain modulation, enhancement and suppression) is Desimone and Duncan’s ‘biased competition’model of attention. The theory rests on three assumptions. First, given the limits on our ability to process several stim ...
Blue= rods Green = Cones
... one small part of the visual field • Input from each eye is separated into “ocular dominance columns” within the module • CO Blobs: color and low spatial frequency • Outside of CO Blobs: orientation, movement, spatial frequency, texture, binocular disparity ...
... one small part of the visual field • Input from each eye is separated into “ocular dominance columns” within the module • CO Blobs: color and low spatial frequency • Outside of CO Blobs: orientation, movement, spatial frequency, texture, binocular disparity ...
SENSATION - Ms. Kelly's AP Psychology Website
... is used to predict when a weak signal will be detected. A new theory that assumes there is no absolute threshold. Detection of a stimulus depends on a combination of actors: stimulus intensity, background noise, a person’s level of experience, motivation & physical condition. ...
... is used to predict when a weak signal will be detected. A new theory that assumes there is no absolute threshold. Detection of a stimulus depends on a combination of actors: stimulus intensity, background noise, a person’s level of experience, motivation & physical condition. ...
Accumulative evidence indicates that microglial cells influence the
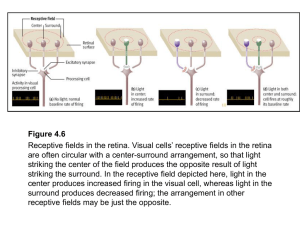
... with electrophysiological recordings. Neurons in the visual cortex have a receptive field like a keyhole through which they look at the scenery in front of the eyes. Visual input from the area surrounding the receptive field fails to induce neuronal firing but can modulate the neuronal responses to ...
... with electrophysiological recordings. Neurons in the visual cortex have a receptive field like a keyhole through which they look at the scenery in front of the eyes. Visual input from the area surrounding the receptive field fails to induce neuronal firing but can modulate the neuronal responses to ...
Nature Reviews Neuroscience Highlight
... same side of the boundary but were far apart could appear to be dissimilar. This type of sharp boundary is a classic feature of perceptual categorization and allows for the dissociation of physical similarity and category membership. Two monkeys were trained to categorize the stimuli set as either c ...
... same side of the boundary but were far apart could appear to be dissimilar. This type of sharp boundary is a classic feature of perceptual categorization and allows for the dissociation of physical similarity and category membership. Two monkeys were trained to categorize the stimuli set as either c ...
Introduction
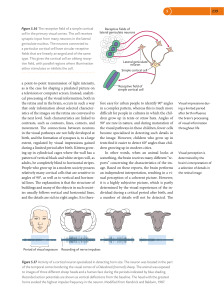
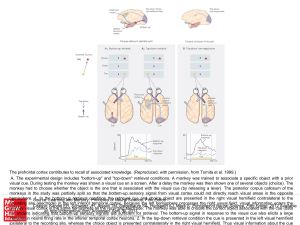
... (a) Input from the right half of the visual field strikes the left side of each retina and is transmitted to the left hemisphere (shown in red). Input from the left half of the visual field strikes the right side of each retina and is transmitted to the right hemisphere (shown in green). The nerve f ...
... (a) Input from the right half of the visual field strikes the left side of each retina and is transmitted to the left hemisphere (shown in red). Input from the left half of the visual field strikes the right side of each retina and is transmitted to the right hemisphere (shown in green). The nerve f ...
Visual extinction

Visual extinction is a neurological disorder which occurs following damage to the parietal lobe of the brain. It is similar to, but distinct from, hemispatial neglect. Visual extinction has the characteristic symptom of difficulty to perceive contralesional stimuli when presented simultaneously with an ipsilesional stimulus, but the ability to correctly identify them when not presented simultaneously. Under simultaneous presentation, the contralesional stimulus is apparently ignored by the patient, or extinguished. This deficiency may lead to difficulty on behalf of the patient with processing the stimuli’s 3D position.