Ch 8 (Student MCQs etc)
... cones are of three types, which are selective to different, if overlapping, ranges of light wavelength. The information from the cones is reorganized in the retina to give green–red and blue–yellow opponent channels (see chapter 7). There is, in addition, a group of large retinal cells alongside the ...
... cones are of three types, which are selective to different, if overlapping, ranges of light wavelength. The information from the cones is reorganized in the retina to give green–red and blue–yellow opponent channels (see chapter 7). There is, in addition, a group of large retinal cells alongside the ...
Neuro-ophthalmology
... Myasthenia Gravis (MG) Chronic auto-immune disorder characterized by presence of antibodies which block the ACH receptor sites It can affect any muscle Eye signs are the presenting signs in 50% of the patients ...
... Myasthenia Gravis (MG) Chronic auto-immune disorder characterized by presence of antibodies which block the ACH receptor sites It can affect any muscle Eye signs are the presenting signs in 50% of the patients ...
The Eye: III. Central Neurophysiology of Vision
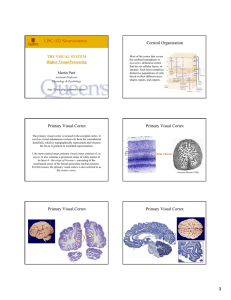
... ►large representation in visual cortex for the macula (region for highest visual acuity) ►layered structure like other cortical areas ►columnar organization as well ►receives the primary visual input ...
... ►large representation in visual cortex for the macula (region for highest visual acuity) ►layered structure like other cortical areas ►columnar organization as well ►receives the primary visual input ...
self and intrapersonal communication
... respond to stimuli. • It determines how the messages are sent to and received by ourselves. • The “result of the sum total of social, hereditary, and personal factors which have influenced your development as an individual.” ...
... respond to stimuli. • It determines how the messages are sent to and received by ourselves. • The “result of the sum total of social, hereditary, and personal factors which have influenced your development as an individual.” ...
LISC-322 Neuroscience Cortical Organization Primary Visual Cortex
... Temporal Cortex Damage Nevertheless, the visually guided behavior of patients with agnosia is preserved. Thus, agnosic patients have difficulty identifying an object, but they can grasp and manipulate it. ...
... Temporal Cortex Damage Nevertheless, the visually guided behavior of patients with agnosia is preserved. Thus, agnosic patients have difficulty identifying an object, but they can grasp and manipulate it. ...
Pattern recognition and visual word forms
... Literate adults group letters together into a single perceptual unit (visual word form). Speed of word recognition is unaffected by the number of letters for 3-6 letter words. Suggests processed in parallel ...
... Literate adults group letters together into a single perceptual unit (visual word form). Speed of word recognition is unaffected by the number of letters for 3-6 letter words. Suggests processed in parallel ...
Slide - Reza Shadmehr
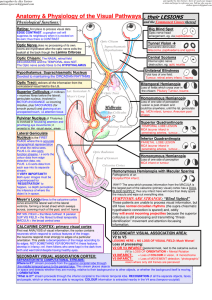
... cup in the right visual field. Information arrives in the left hemisphere. She is asked what she sees, and she answers “a cup”. She is asked to reach with the left arm towards the cup. She can reach with left arm normally. 2. Left hemisphere has very poor control over the left finger muscles: Subjec ...
... cup in the right visual field. Information arrives in the left hemisphere. She is asked what she sees, and she answers “a cup”. She is asked to reach with the left arm towards the cup. She can reach with left arm normally. 2. Left hemisphere has very poor control over the left finger muscles: Subjec ...
Literacy and Cognition - Graduateprograminliteracy
... responsibility to instruct their undergraduate and graduate students in the findings of scientific studies on brain research. Their graduates need to know the components of a balanced literacy program as well as the seven levels of brain processing that must be integrated: Phonological- the sound ...
... responsibility to instruct their undergraduate and graduate students in the findings of scientific studies on brain research. Their graduates need to know the components of a balanced literacy program as well as the seven levels of brain processing that must be integrated: Phonological- the sound ...
PSY105 Neural Networks 2/5
... Lecture 1 recap • We can describe patterns at one level of description that emerge due to rules followed at a lower level of description. • Neural network modellers hope that we can understand behaviour by creating models of networks of artificial neurons. ...
... Lecture 1 recap • We can describe patterns at one level of description that emerge due to rules followed at a lower level of description. • Neural network modellers hope that we can understand behaviour by creating models of networks of artificial neurons. ...
Top-down influence in early visual processing: a Bayesian perspective
... Fig. 4. Temporal evolution of the normalized population average response of 30 V1 units from a monkey to the LA set (a) and the WA set (b) in a stage after the monkey had utilized the stimuli in its behavior. Each unit’s response was first smoothed by a running average within a 15-ms window and then ...
... Fig. 4. Temporal evolution of the normalized population average response of 30 V1 units from a monkey to the LA set (a) and the WA set (b) in a stage after the monkey had utilized the stimuli in its behavior. Each unit’s response was first smoothed by a running average within a 15-ms window and then ...
Visual pathways pathology
... develop in infancy; ref. them kittens who were kept in the dark from birth and went blind despite having healthy eyes. ...
... develop in infancy; ref. them kittens who were kept in the dark from birth and went blind despite having healthy eyes. ...
Danczi Csaba László - 2nd WORLD CONGRESS OF ARTS
... stimulus moving continuously across the cutaneous surface (2). The presence of extensive connections between superficial and deep regions of the colliculus in the cat supports the idea that receptive field organization in the deep layers is modulated by visual input from the overlying layers. Thus, ...
... stimulus moving continuously across the cutaneous surface (2). The presence of extensive connections between superficial and deep regions of the colliculus in the cat supports the idea that receptive field organization in the deep layers is modulated by visual input from the overlying layers. Thus, ...
Symposium Poster - uospur
... Future directions • Mice can differentiate between unilateral stimuli presented at different times in the sniff; we need to control for the possibility that they are identifying lick and no-lick trials in this way4. Therefore, it will be necessary to randomize the time position of the stimulus relat ...
... Future directions • Mice can differentiate between unilateral stimuli presented at different times in the sniff; we need to control for the possibility that they are identifying lick and no-lick trials in this way4. Therefore, it will be necessary to randomize the time position of the stimulus relat ...
Visual Coding and the Retinal Receptors
... in space from which light strikes it. • For other visual cells, receptive fields are derived from the visual field of cells that either excite or inhibit. – Example: ganglion cells converge to form the receptive field of the next level of cells. ...
... in space from which light strikes it. • For other visual cells, receptive fields are derived from the visual field of cells that either excite or inhibit. – Example: ganglion cells converge to form the receptive field of the next level of cells. ...
Chapter One: Neurological Bases for Visual Communication
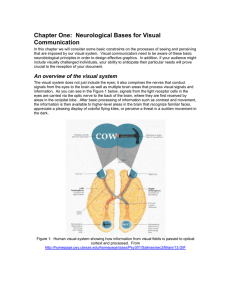
... The visual cortices The “mixed” signals from the optic chiasmus travel all the way to the back of your brain first, to a region known as the primary visual cortex, or V1. This low-level vision area is responsible for recognizing orientation of lines, contrast, and some motion. You are not consciousl ...
... The visual cortices The “mixed” signals from the optic chiasmus travel all the way to the back of your brain first, to a region known as the primary visual cortex, or V1. This low-level vision area is responsible for recognizing orientation of lines, contrast, and some motion. You are not consciousl ...
Basic Architecture of the Visual Cortex
... estimated that V1 is 400 times bigger than is needed to merely encode all the information it receives from the LGN • It also follows that the rest of the visual cortex, which is believed to perform object recognition and scene understanding, is much smaller than V1 and V2. • It has been possible to ...
... estimated that V1 is 400 times bigger than is needed to merely encode all the information it receives from the LGN • It also follows that the rest of the visual cortex, which is believed to perform object recognition and scene understanding, is much smaller than V1 and V2. • It has been possible to ...
3. Explain the basic thrust of signal-detection theory. 5. Discuss the
... The major idea behind signal detection theory is that our ability to detect signals depends not only on the initial intensity of a stimulus, but also on other sensory and decision processes as well. One factor that is particularly important here is the criterion you set for how certain you must feel ...
... The major idea behind signal detection theory is that our ability to detect signals depends not only on the initial intensity of a stimulus, but also on other sensory and decision processes as well. One factor that is particularly important here is the criterion you set for how certain you must feel ...
Eagleman Ch 5. Vision
... Most activity within the brain is produced on the inside and is only modified by sensory input. Patients who lose their vision hallucinate that they still see objects around them. ...
... Most activity within the brain is produced on the inside and is only modified by sensory input. Patients who lose their vision hallucinate that they still see objects around them. ...
Visual vs. Language-based Thinking
... effectiveness of dynamic compared to static visualizations. However, this remains an hypothesis to be tested, for which interdisciplinary research is required. Such research might also shed light on the relation between the mirror neuron system and working memory. We assume that visualizations depic ...
... effectiveness of dynamic compared to static visualizations. However, this remains an hypothesis to be tested, for which interdisciplinary research is required. Such research might also shed light on the relation between the mirror neuron system and working memory. We assume that visualizations depic ...
Studying the impact on vision of silencing cells - Find a team
... Studying the impact on vision of silencing cells in the retina Context. The process of vision begins in the retina. This thin neural tissue, located at the back of the eye, is able to convert light from different parts of the visual scene into a «code » sent to the brain. This code is composed of el ...
... Studying the impact on vision of silencing cells in the retina Context. The process of vision begins in the retina. This thin neural tissue, located at the back of the eye, is able to convert light from different parts of the visual scene into a «code » sent to the brain. This code is composed of el ...
Newsletter 5 - Eye vs. Camera - California Training Institute
... of the eye ensures that a similar HD version of acuity is only available within the 1‐2 degree angle of the fovea, with vision sharply decreasing towards the periphery 2. Visual perception must occur before reaction can take place, and the analysis of what an officer perceives or does not percei ...
... of the eye ensures that a similar HD version of acuity is only available within the 1‐2 degree angle of the fovea, with vision sharply decreasing towards the periphery 2. Visual perception must occur before reaction can take place, and the analysis of what an officer perceives or does not percei ...
Lecture 13A
... the classes of biologically relevant stimuli (prey vs. predator) at or shortly after birth. • In some phylogenetically ancient species (frogs) visual object recognition even in adulthood is exclusively innate. • In rodent species the innate sensory recognition systems function throughout ontogeny. I ...
... the classes of biologically relevant stimuli (prey vs. predator) at or shortly after birth. • In some phylogenetically ancient species (frogs) visual object recognition even in adulthood is exclusively innate. • In rodent species the innate sensory recognition systems function throughout ontogeny. I ...
Object recognition in clutter: selectivity and invariance
... object recognition in cluttered conditions, typical of natural visual scenes, where objects of interest do not appear in isolation but together with background objects. Object recognition in primates is thought to depend on neuronal activity in the inferotemporal cortex (IT) [1], which is the last s ...
... object recognition in cluttered conditions, typical of natural visual scenes, where objects of interest do not appear in isolation but together with background objects. Object recognition in primates is thought to depend on neuronal activity in the inferotemporal cortex (IT) [1], which is the last s ...
Visual Field Defects - Northwestern Medical Review
... the location of lesions. As we will see later this unique pattern also holds true for the oculomotor muscles. In this case either of the eyes will have difficulty in moving to the contralateral position. Left ...
... the location of lesions. As we will see later this unique pattern also holds true for the oculomotor muscles. In this case either of the eyes will have difficulty in moving to the contralateral position. Left ...
Visual extinction

Visual extinction is a neurological disorder which occurs following damage to the parietal lobe of the brain. It is similar to, but distinct from, hemispatial neglect. Visual extinction has the characteristic symptom of difficulty to perceive contralesional stimuli when presented simultaneously with an ipsilesional stimulus, but the ability to correctly identify them when not presented simultaneously. Under simultaneous presentation, the contralesional stimulus is apparently ignored by the patient, or extinguished. This deficiency may lead to difficulty on behalf of the patient with processing the stimuli’s 3D position.