Food Security - The Foundation for Democracy in Africa
... Other scholars argues that those who resisted wanted to maintained their distinct linguistic, cultural and social characteristics didn’t fit in the pattern of ether gathers or herders dichotomy hence spitted out in their own community. Ladies and gentlemen, with the penetration of colonialism, their ...
... Other scholars argues that those who resisted wanted to maintained their distinct linguistic, cultural and social characteristics didn’t fit in the pattern of ether gathers or herders dichotomy hence spitted out in their own community. Ladies and gentlemen, with the penetration of colonialism, their ...
HST560: AP® World History
... (c. 1750 C.E. to c. 1900 C.E.) Students explore African trading empires along with the moral pressure and global economic changes that resulted in the end of the trans-Atlantic slave trade. They investigate the dual role of industrialization and nationalism and the transformation of European, Africa ...
... (c. 1750 C.E. to c. 1900 C.E.) Students explore African trading empires along with the moral pressure and global economic changes that resulted in the end of the trans-Atlantic slave trade. They investigate the dual role of industrialization and nationalism and the transformation of European, Africa ...
England and France in the High Middle Ages
... open sea. Navigation was done by both dead reckoning and the astrolabe, an instrument perfected by the Arabs that allowed navigation by the sun and stars by measuring the angle from the horizon, enabling latitude to be calculated. 3. Leading in the revival of trade in the eleventh century were the I ...
... open sea. Navigation was done by both dead reckoning and the astrolabe, an instrument perfected by the Arabs that allowed navigation by the sun and stars by measuring the angle from the horizon, enabling latitude to be calculated. 3. Leading in the revival of trade in the eleventh century were the I ...
Navya Janga Trade Liberalization: A World With No Borders
... United States is able to make better use of its resources, more jobs are created and the cost of products is reduced, allowing low and middle-class families are able to live higher quality lives. With more FTAs, the United States is able to reap more of these benefits. With international free trade ...
... United States is able to make better use of its resources, more jobs are created and the cost of products is reduced, allowing low and middle-class families are able to live higher quality lives. With more FTAs, the United States is able to reap more of these benefits. With international free trade ...
Era Overview: The First Global Age, 1400-1800
... their European rivals. Exploration also offered these states the chance to form overseas empires, thus adding to their wealth and power. A third reason for sea travel had to do with ideas. European rulers, supported by the Catholic Church, wanted to spread their religious beliefs and win converts to ...
... their European rivals. Exploration also offered these states the chance to form overseas empires, thus adding to their wealth and power. A third reason for sea travel had to do with ideas. European rulers, supported by the Catholic Church, wanted to spread their religious beliefs and win converts to ...
AP World History Review Session 4: 1750-1914
... a) the rise of social and political reform movements. b) increased foreign investment in less-industrialized nations. c) a manufacturing system based on division of labor. d) an increased demand for African slaves in North America. e) an increase in the number of independent nations. ...
... a) the rise of social and political reform movements. b) increased foreign investment in less-industrialized nations. c) a manufacturing system based on division of labor. d) an increased demand for African slaves in North America. e) an increase in the number of independent nations. ...
Period 5 Practice MC
... a) the rise of social and political reform movements. b) increased foreign investment in less-industrialized nations. c) a manufacturing system based on division of labor. d) an increased demand for African slaves in North America. e) an increase in the number of independent nations. ...
... a) the rise of social and political reform movements. b) increased foreign investment in less-industrialized nations. c) a manufacturing system based on division of labor. d) an increased demand for African slaves in North America. e) an increase in the number of independent nations. ...
Section 1: The Renaissance in Italy
... Indies. Columbus’ first meeting with Native Americans there began a recurring cycle of encounter, conquest, and death across the Western Hemisphere. Columbus first encountered the Taíno people and claimed their land for Spain, taking prisoners back with him. A wave of Spanish conquistadors, or conq ...
... Indies. Columbus’ first meeting with Native Americans there began a recurring cycle of encounter, conquest, and death across the Western Hemisphere. Columbus first encountered the Taíno people and claimed their land for Spain, taking prisoners back with him. A wave of Spanish conquistadors, or conq ...
The First Global Age: Europe and Asia.
... 1793. Lord Macartney refuses kowtow (touch head to ground) to emperor. 1800s. China would realize it could learn from the West, the hard way. Korea and Isolation. Korea (Chosen dynasty) buys into Confucianism. Low status for merchants. Koreans thus look down on foreign trade. Imitate Chinese. Korea ...
... 1793. Lord Macartney refuses kowtow (touch head to ground) to emperor. 1800s. China would realize it could learn from the West, the hard way. Korea and Isolation. Korea (Chosen dynasty) buys into Confucianism. Low status for merchants. Koreans thus look down on foreign trade. Imitate Chinese. Korea ...
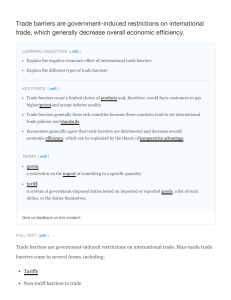
Trade barriers are government-induced restrictions on
... Economists generally agree that trade barriers are detrimental and decrease overall economic efficiency. This can be explained by the theory of comparative advantage. In theory, free tradeinvolves the removal of all such barriers, except perhaps those considered necessary for health or national secu ...
... Economists generally agree that trade barriers are detrimental and decrease overall economic efficiency. This can be explained by the theory of comparative advantage. In theory, free tradeinvolves the removal of all such barriers, except perhaps those considered necessary for health or national secu ...
Chap007
... 5. Furthering the goals of foreign policy preferential trade terms can be granted to countries that a government wants to build strong relations with trade policy can also be used to punish rogue states the Helms-Burton Act and the D’Amato Act, have been passed to protect American companies from ...
... 5. Furthering the goals of foreign policy preferential trade terms can be granted to countries that a government wants to build strong relations with trade policy can also be used to punish rogue states the Helms-Burton Act and the D’Amato Act, have been passed to protect American companies from ...
A Brief Economic History of Britain from circa 1600
... enter circulation and ships started to leave for exotic parts. Their cargoes brought the raw materials that would fuel the move to an industrial age. The British entered an age, which championed the deliberate search for knowledge, and the profit that might go with it. Joseph Banks, who sailed with ...
... enter circulation and ships started to leave for exotic parts. Their cargoes brought the raw materials that would fuel the move to an industrial age. The British entered an age, which championed the deliberate search for knowledge, and the profit that might go with it. Joseph Banks, who sailed with ...
CAPITALISM AND GLOBALIZATION SINCE 1492 (MODEL
... Attendance: Students are expected to participate in class and complete the assigned readings each week. Much of the material in the lectures may not be covered in the readings but will be on the exams, and so students should obtain notes for any missed classes. Honor Code: All course work is govern ...
... Attendance: Students are expected to participate in class and complete the assigned readings each week. Much of the material in the lectures may not be covered in the readings but will be on the exams, and so students should obtain notes for any missed classes. Honor Code: All course work is govern ...
Unit 4 Notes
... After the Opium Wars, Britain and other European nations began carving China up into their own “_____spheres____________ __of_______ ________influence_________________” where they controlled special trading and economic rights within their designated area or section of China. The United States, want ...
... After the Opium Wars, Britain and other European nations began carving China up into their own “_____spheres____________ __of_______ ________influence_________________” where they controlled special trading and economic rights within their designated area or section of China. The United States, want ...
Overview of the First Americans
... The exchange, however, was not evenly balanced. Killer diseases killed millions of Indians. The survivors were drawn into European trading networks that disrupted earlier patterns of life. European Colonization There were three distinct forms of European colonization in the New World: empires of co ...
... The exchange, however, was not evenly balanced. Killer diseases killed millions of Indians. The survivors were drawn into European trading networks that disrupted earlier patterns of life. European Colonization There were three distinct forms of European colonization in the New World: empires of co ...
Foundationrev
... As sedentary civilizations developed, social structures and gender roles cemented. Major world religions developed during this period and spread with along trade routes. Civilizations became more complex and structured as time moved on. ...
... As sedentary civilizations developed, social structures and gender roles cemented. Major world religions developed during this period and spread with along trade routes. Civilizations became more complex and structured as time moved on. ...
Foundation
... As sedentary civilizations developed, social structures and gender roles cemented. Major world religions developed during this period and spread with along trade routes. Civilizations became more complex and structured as time moved on. ...
... As sedentary civilizations developed, social structures and gender roles cemented. Major world religions developed during this period and spread with along trade routes. Civilizations became more complex and structured as time moved on. ...
Five Major World Religions
... The European nations established a trade pattern known as the triangular trade and exported precious metals from the Americas. European maritime nations competed for overseas markets, colonies, and resources, creating new economic practices, such as mercantilism, linking European nations with their ...
... The European nations established a trade pattern known as the triangular trade and exported precious metals from the Americas. European maritime nations competed for overseas markets, colonies, and resources, creating new economic practices, such as mercantilism, linking European nations with their ...
Columbian Exchange PP from class
... Printing technology spread from China to Europe. European and Korean artisans invented printing with moveable metal type at about the same time. • Gutenberg’s printing press with moveable ...
... Printing technology spread from China to Europe. European and Korean artisans invented printing with moveable metal type at about the same time. • Gutenberg’s printing press with moveable ...
Globalization in World History
... - C. Bayly - Up to 1600 - Ideology: underpinned by cosmic kingship, universal religion, humoural understandings of the body and land - Long-range circulation of goods but not about modern ‘consumption’ - Agents: warriors, ...
... - C. Bayly - Up to 1600 - Ideology: underpinned by cosmic kingship, universal religion, humoural understandings of the body and land - Long-range circulation of goods but not about modern ‘consumption’ - Agents: warriors, ...
Development and interaction of cultures
... Around the mid 1300’s plague, also known as the black death caused drastic population decline that took 150 years to rebuild. It was also a factor for the backwardness of medieval Europe. Magna Carta in England limited the King’s power. This also allowed a more representative government. ...
... Around the mid 1300’s plague, also known as the black death caused drastic population decline that took 150 years to rebuild. It was also a factor for the backwardness of medieval Europe. Magna Carta in England limited the King’s power. This also allowed a more representative government. ...
1750-1914: The Age of European Hegemony
... Joint Stock Companies Also known as corporations Formed with support from national governments Allowed investors to share in profits and earn dividends from industry and colonization Sometimes granted monopoly power over certain regions or products ...
... Joint Stock Companies Also known as corporations Formed with support from national governments Allowed investors to share in profits and earn dividends from industry and colonization Sometimes granted monopoly power over certain regions or products ...
WHAP Teacher Copy Western Christendom after the fall of Rome
... D. Yet More Reasons for Europe’s Rise Like Technological Borrowing 1. Gunpowder from China, but Europeansfirst to use it in cannons, in early fourteenth centuryby 1500, had most advanced arsenals in world 2. A three-way struggle for powerkings, warrior aristocrats, and church leaders enabled urb ...
... D. Yet More Reasons for Europe’s Rise Like Technological Borrowing 1. Gunpowder from China, but Europeansfirst to use it in cannons, in early fourteenth centuryby 1500, had most advanced arsenals in world 2. A three-way struggle for powerkings, warrior aristocrats, and church leaders enabled urb ...
Chapter 14 - msjacksonapworld
... their lives for the chance to gain great wealth through trade goods from the Far East and South America. European impact on the world as a result of the Age of Exploration has been much debated; while some scholars view it as a positive, others see a decidedly negative result. Some native societies ...
... their lives for the chance to gain great wealth through trade goods from the Far East and South America. European impact on the world as a result of the Age of Exploration has been much debated; while some scholars view it as a positive, others see a decidedly negative result. Some native societies ...
Introduction-Review-Conclusion
... framework of historical understanding. Politically, belief systems helped to justify authority and maintain a social order where everyone would know what was expected of them, belief systems would spread across trade routes through missionaries and merchants and culturally would inspire architects a ...
... framework of historical understanding. Politically, belief systems helped to justify authority and maintain a social order where everyone would know what was expected of them, belief systems would spread across trade routes through missionaries and merchants and culturally would inspire architects a ...
Proto-globalization

Proto-globalization or early modern globalization is a period of the history of globalization roughly spanning the years between 1600 and 1800, following the period of archaic globalization. First introduced by historians A. G. Hopkins and Christopher Bayly, the term describes the phase of increasing trade links and cultural exchange that characterized the period immediately preceding the advent of so-called 'modern globalization' in the 19th century.Proto-globalization distinguished itself from modern globalization on the basis of expansionism, the method of managing global trade, and the level of information exchange. The period of proto-globalization is marked by such trade arrangements as the East India Company, the shift of hegemony to Western Europe, the rise of larger-scale conflicts between powerful nations such as the Thirty Year War, and a rise of new commodities—most particularly slave trade. The Triangular Trade made it possible for Europe to take advantage of resources within the western hemisphere. The transfer of plant and animal crops and epidemic diseases associated with Alfred Crosby's concept of The Columbian Exchange also played a central role in this process. Proto-globalization trade and communications involved a vast group including European, Muslim, Indian, Southeast Asian and Chinese merchants, particularly in the Indian Ocean region.The transition from proto-globalization to modern globalization was marked with a more complex global network based on both capitalistic and technological exchange; however, it led to a significant collapse in cultural exchange.