Chapter 5HW_Ans
... One molecules of Al2(SO4)3 has 2 aluminum ions , 3 sulfur atoms, 12 oxygen atoms, and it has 3 sulfate ions. Therefore one mole of Al2(SO4)3 will have as 2 moles of aluminum ions, 3 moles of sulfur, 12 moles of oxygen, and 3 moles of SO42- ions. ...
... One molecules of Al2(SO4)3 has 2 aluminum ions , 3 sulfur atoms, 12 oxygen atoms, and it has 3 sulfate ions. Therefore one mole of Al2(SO4)3 will have as 2 moles of aluminum ions, 3 moles of sulfur, 12 moles of oxygen, and 3 moles of SO42- ions. ...
physical setting chemistry
... heat of reaction for a chemical reaction? (1) (the heat of fusion) – (the heat of vaporization) (2) (the heat of vaporization) – (the heat of fusion) (3) (the potential energy of the products) – (the potential energy of the reactants) (4) (the potential energy of the reactants) – (the potential ener ...
... heat of reaction for a chemical reaction? (1) (the heat of fusion) – (the heat of vaporization) (2) (the heat of vaporization) – (the heat of fusion) (3) (the potential energy of the products) – (the potential energy of the reactants) (4) (the potential energy of the reactants) – (the potential ener ...
Chemistry
... subject or as part of a balanced science course. This syllabus is designed to place less emphasis on factual material and greater emphasis on the understanding and application of scientific concepts and principles. This approach has been adopted in recognition of the need for students to develop ski ...
... subject or as part of a balanced science course. This syllabus is designed to place less emphasis on factual material and greater emphasis on the understanding and application of scientific concepts and principles. This approach has been adopted in recognition of the need for students to develop ski ...
Analyze
... Octane at –57˚C is a solid just about to melt. As energy is added the solid octane melts and its temperature does not change until all the solid is melted. Only when octane is entirely liquid does added energy increase the temperature of the liquid until the boiling point of octane is reached. Durin ...
... Octane at –57˚C is a solid just about to melt. As energy is added the solid octane melts and its temperature does not change until all the solid is melted. Only when octane is entirely liquid does added energy increase the temperature of the liquid until the boiling point of octane is reached. Durin ...
Chapter 2
... • Atoms with incomplete valence shells can share or transfer valence electrons with certain other atoms • These interactions usually result in atoms staying close together, held by attractions called chemical bonds ...
... • Atoms with incomplete valence shells can share or transfer valence electrons with certain other atoms • These interactions usually result in atoms staying close together, held by attractions called chemical bonds ...
Code: I1 Title: Heterogeneous Catalysis Lecturer: Prof S D Jackson
... The course builds upon the knowledge gained in years 1 and 2. It will expand on the ideas of bonding through the use of examples from main group chemistry. The student will also learn about some of the general chemistry of these elements (particularly groups 13 – 16) in addition to some detailed stu ...
... The course builds upon the knowledge gained in years 1 and 2. It will expand on the ideas of bonding through the use of examples from main group chemistry. The student will also learn about some of the general chemistry of these elements (particularly groups 13 – 16) in addition to some detailed stu ...
1999 Free-Response Questions
... Explanations should be clear and well organized. Examples and equations may be included in your responses where appropriate. Specific answers are preferable to broad, diffuse responses. Answer BOTH Question 5 AND Question 6. Both of these questions will be graded. The Section II score weighting for ...
... Explanations should be clear and well organized. Examples and equations may be included in your responses where appropriate. Specific answers are preferable to broad, diffuse responses. Answer BOTH Question 5 AND Question 6. Both of these questions will be graded. The Section II score weighting for ...
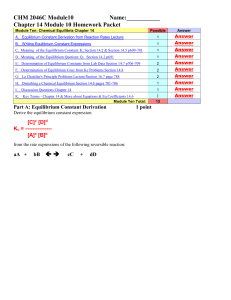
CHEM 1212 Module Ten-Chapter 16 Name
... __________________ 1. If all the reactants and the products are in the same phase (such as gases), then the we say the system is in _______________equilibrium. __________________ 2. If at least one of the reactants or one of the products is not in the same phase, then we say the system is in _______ ...
... __________________ 1. If all the reactants and the products are in the same phase (such as gases), then the we say the system is in _______________equilibrium. __________________ 2. If at least one of the reactants or one of the products is not in the same phase, then we say the system is in _______ ...
Catalysis
... 5. The activity of certain enzymes depend upon certain non-protein substances called Co-enzymes. For each enzyme, there is only one co-enzyme 6. Enzymes lose their activity when exposed to ultravoilet radiations or in presence of electrolytes 7. Even a small amounts of an enzyme can be highly effici ...
... 5. The activity of certain enzymes depend upon certain non-protein substances called Co-enzymes. For each enzyme, there is only one co-enzyme 6. Enzymes lose their activity when exposed to ultravoilet radiations or in presence of electrolytes 7. Even a small amounts of an enzyme can be highly effici ...
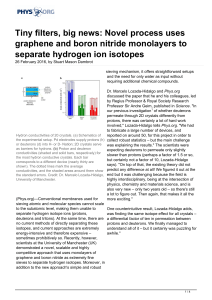
Full circle: Years in Industry informs Al Weimer`s work in fuels
... temperature required to split water to make hydrogen from about 1,600 degrees Celsius to about 1,000 degrees, low enough that standard materials no longer melt into glowing puddles on the floor. For an encore, they focused sunlight on grass clippings and fallen leaves – known more formally as source ...
... temperature required to split water to make hydrogen from about 1,600 degrees Celsius to about 1,000 degrees, low enough that standard materials no longer melt into glowing puddles on the floor. For an encore, they focused sunlight on grass clippings and fallen leaves – known more formally as source ...
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
... SAMPLE EXERCISE 5.2 Relating heat and work to changes of internal energy Two gases, A(g) and B(g), are confined in a cylinder-and-piston arrangement like that in Figure 5.3. Substances A and B react to form a solid product: As the reactions occurs, the system loses 1150 J of heat to the surrounding. ...
... SAMPLE EXERCISE 5.2 Relating heat and work to changes of internal energy Two gases, A(g) and B(g), are confined in a cylinder-and-piston arrangement like that in Figure 5.3. Substances A and B react to form a solid product: As the reactions occurs, the system loses 1150 J of heat to the surrounding. ...
Chapter 4
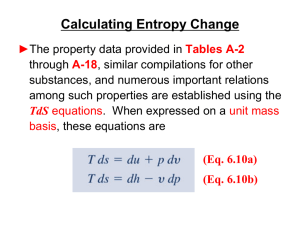
... Calculating Entropy Change of an Ideal Gas Example: Air undergoes a process from T1 = 620 K, p1 = 12 bar to a final state where s2 = s1, p2 = 1.4 bar. Employing the ideal gas model, determine the final temperature T2, in K. Solve using (a) pr data from Table A-22 and (b) a constant specific heat ra ...
... Calculating Entropy Change of an Ideal Gas Example: Air undergoes a process from T1 = 620 K, p1 = 12 bar to a final state where s2 = s1, p2 = 1.4 bar. Employing the ideal gas model, determine the final temperature T2, in K. Solve using (a) pr data from Table A-22 and (b) a constant specific heat ra ...
Explaining organisational change - ANU Press
... and without referring to external factors, a purposive system will perform in an efficient and effective manner. This belief has become the foundation of the machine metaphor or the mechanistic organisation (Morgan, 1997). A prevalent example of a management system built on a closed system model is ...
... and without referring to external factors, a purposive system will perform in an efficient and effective manner. This belief has become the foundation of the machine metaphor or the mechanistic organisation (Morgan, 1997). A prevalent example of a management system built on a closed system model is ...
chapter 16
... absorb energy overall as it takes place. If this energy comes from the motion (kinetic energy) of the reactants, the particles in the system will be moving more slowly after the reaction than before. The system will have less thermal energy, and the temperature will decrease. Because the system is a ...
... absorb energy overall as it takes place. If this energy comes from the motion (kinetic energy) of the reactants, the particles in the system will be moving more slowly after the reaction than before. The system will have less thermal energy, and the temperature will decrease. Because the system is a ...
Document
... system. Thermodynamics deals only with the large scale response of a system which we can observe and measure in experiments. Gases have various properties that we can observe with our senses, including the gas pressure p, temperature T, mass n, and volume V that contains the gas. Careful, scientific ...
... system. Thermodynamics deals only with the large scale response of a system which we can observe and measure in experiments. Gases have various properties that we can observe with our senses, including the gas pressure p, temperature T, mass n, and volume V that contains the gas. Careful, scientific ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.