Chap 1-3 Review
... Atomic number = 117 Atomic mass = 290 Describe this element in terms of number of each subatomic particle and predict the most likely ionic charge. ...
... Atomic number = 117 Atomic mass = 290 Describe this element in terms of number of each subatomic particle and predict the most likely ionic charge. ...
Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life
... Thibodeau: Anatomy and Physiology, 5/e Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life It would be difficult to appreciate fully the characteristics of living matter and its functions without looking at the basic principles of chemistry as they apply to life processes. In fact, it is almost impossible to speak of ...
... Thibodeau: Anatomy and Physiology, 5/e Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life It would be difficult to appreciate fully the characteristics of living matter and its functions without looking at the basic principles of chemistry as they apply to life processes. In fact, it is almost impossible to speak of ...
STARBASE Challenge: Polishing Pennies – Change Your Change
... they often tarnish, and become a darker, duller color. This color change happens due to a chemical change as the copper slowly reacts with oxygen in the air over time to create copper oxide. The Statue of Liberty and many other landmarks and historical artifacts started out copper brown and have cha ...
... they often tarnish, and become a darker, duller color. This color change happens due to a chemical change as the copper slowly reacts with oxygen in the air over time to create copper oxide. The Statue of Liberty and many other landmarks and historical artifacts started out copper brown and have cha ...
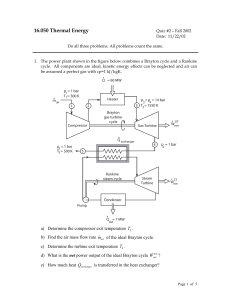
revision - metc instructors collab site
... dependent only on thermodynamic temperature and is energy stored in the molecules States that the total energy stored in a body, or system, is termed enthalpy (H) Defines total stored energy the sum of internal energy and the product of pressure(P) and volume (V), i.e. H = U + PV Defines potential e ...
... dependent only on thermodynamic temperature and is energy stored in the molecules States that the total energy stored in a body, or system, is termed enthalpy (H) Defines total stored energy the sum of internal energy and the product of pressure(P) and volume (V), i.e. H = U + PV Defines potential e ...
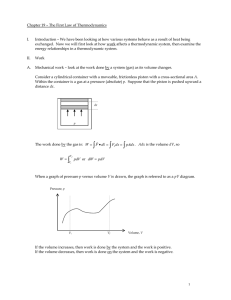
Chapter 19 – The First Law of Thermodynamics
... Interesting Note: If a system changes from an initial state i to a final state f along different paths (e.g., Path A and Path B), the change in internal energy will be the same along those paths. And, in fact, all paths that go from i to f. That is, U = Uf - Ui . From the first law, that means that ...
... Interesting Note: If a system changes from an initial state i to a final state f along different paths (e.g., Path A and Path B), the change in internal energy will be the same along those paths. And, in fact, all paths that go from i to f. That is, U = Uf - Ui . From the first law, that means that ...
Thermochemistry - Piedra Vista High School
... First Law of Thermodynamics Energy can be converted from one form to another but energy cannot be created or destroyed. Second Law of Thermodynamics The entropy of the universe increases in a spontaneous process and remains unchanged in an equilibrium process. ...
... First Law of Thermodynamics Energy can be converted from one form to another but energy cannot be created or destroyed. Second Law of Thermodynamics The entropy of the universe increases in a spontaneous process and remains unchanged in an equilibrium process. ...
10-4 Enthalpy (Section 10.6)
... • System absorbs KE from surroundings as PE in the bonds. Surroundings will feel cold. • ∆H = P – R = positive value (heat absorbed) ...
... • System absorbs KE from surroundings as PE in the bonds. Surroundings will feel cold. • ∆H = P – R = positive value (heat absorbed) ...
Ionic Compounds 1. What is the formula for aluminum phosphate
... Use the following to answer questions 1-2: Consider three 1-L flasks at STP. Flask A contains NH3 gas, flask B contains NO2 gas, and flask C contains N2 gas. 1. Which contains the largest number of molecules? 2. In which flask do the molecules have the highest average velocity, speed? 3. A gas sampl ...
... Use the following to answer questions 1-2: Consider three 1-L flasks at STP. Flask A contains NH3 gas, flask B contains NO2 gas, and flask C contains N2 gas. 1. Which contains the largest number of molecules? 2. In which flask do the molecules have the highest average velocity, speed? 3. A gas sampl ...
ISP203A – Global Change Energy Objectives Indentify types of
... B. Label the phases or phase changes that occur at each component and between components of the water cycle. C. Finally, label the types of energy and use arrows to indicate when one type of energy is transforming into another. For example: Water vapor turning into a cloud. Chemical potential energy ...
... B. Label the phases or phase changes that occur at each component and between components of the water cycle. C. Finally, label the types of energy and use arrows to indicate when one type of energy is transforming into another. For example: Water vapor turning into a cloud. Chemical potential energy ...
Atomic Structure
... (2) decrease, producing an increase in reaction rate. (3) increase, producing an decrease in reaction rate. (4) decrease, producing a decrease in reaction rate. 5. From the reactions below which of the following would have the fastest rate of reaction? (1) CO2 (g) --> C (s) + O2 (g) (2) Al(s) + O2 ( ...
... (2) decrease, producing an increase in reaction rate. (3) increase, producing an decrease in reaction rate. (4) decrease, producing a decrease in reaction rate. 5. From the reactions below which of the following would have the fastest rate of reaction? (1) CO2 (g) --> C (s) + O2 (g) (2) Al(s) + O2 ( ...
CHAPTER 1-MATTER AND ITS PROPERTIES The
... 13. The device working under constant pressure and used to measure the quantity of heat in an isolated system composed of a styrofoam cup is called ___coffee cup calorimeter____ 14. In thermodynamics __ work____ means the transfer of energy between the system and its surroundings due to an external ...
... 13. The device working under constant pressure and used to measure the quantity of heat in an isolated system composed of a styrofoam cup is called ___coffee cup calorimeter____ 14. In thermodynamics __ work____ means the transfer of energy between the system and its surroundings due to an external ...
Chemical Thermodynamics - Winona State University
... • Standard molar entropy, S: entropy of a substance in its standard state. Similar in concept to H. • Units: J/mol-K. Note units of H: kJ/mol. • Standard molar entropies of elements are not zero. • For a chemical reaction which produces n moles of products from m moles of reactants: S nS ...
... • Standard molar entropy, S: entropy of a substance in its standard state. Similar in concept to H. • Units: J/mol-K. Note units of H: kJ/mol. • Standard molar entropies of elements are not zero. • For a chemical reaction which produces n moles of products from m moles of reactants: S nS ...
Questions - TTU Physics
... equilibrium at absolute temperature T. Consider an infinitesimal, quasi-static process in which the magnetic field is changed by dB. Recall that, in such a situation, the mechanical work done is - μdB. For this system, use the following definitions (E is the internal energy, S is the entropy): Entha ...
... equilibrium at absolute temperature T. Consider an infinitesimal, quasi-static process in which the magnetic field is changed by dB. Recall that, in such a situation, the mechanical work done is - μdB. For this system, use the following definitions (E is the internal energy, S is the entropy): Entha ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.