What are the general types of reactions?
... – Mass is not created or destroyed in a chemical reaction – For practical purposes • Same types of atoms before and after a reaction • Same number of each type of atom before and after ...
... – Mass is not created or destroyed in a chemical reaction – For practical purposes • Same types of atoms before and after a reaction • Same number of each type of atom before and after ...
Name
... Name the parts of an atom. Give the charge and amu for each. Proton + 1 amu, Neutron 0 1 amu, electron - 1/1,826amu ...
... Name the parts of an atom. Give the charge and amu for each. Proton + 1 amu, Neutron 0 1 amu, electron - 1/1,826amu ...
Unit Description - Honors Chemistry
... Define physical change and list several common physical changes. Define chemical change and list several indications that a chemical change has taken place. Apply the law of conservation of mass to chemical reactions. Contrast mixtures and substances. Classify mixtures as homogeneous or he ...
... Define physical change and list several common physical changes. Define chemical change and list several indications that a chemical change has taken place. Apply the law of conservation of mass to chemical reactions. Contrast mixtures and substances. Classify mixtures as homogeneous or he ...
Entropy, Carnot Engine and Thermoelectric Effect
... Thermal Equilibrium : Two systems placed in contact with each other are said to be in thermal equilibrium if no net transfer of heat takes place between them. Mechanical Equilibrium : Two mechanically connected systems are said to be mechanical equilibrium if they exert equal and opposite mechanical ...
... Thermal Equilibrium : Two systems placed in contact with each other are said to be in thermal equilibrium if no net transfer of heat takes place between them. Mechanical Equilibrium : Two mechanically connected systems are said to be mechanical equilibrium if they exert equal and opposite mechanical ...
View
... relationships among variables between systems and their components in the natural and designed worlds. Develop a model based on evidence to illustrate the relationships between systems or between components of a system. ...
... relationships among variables between systems and their components in the natural and designed worlds. Develop a model based on evidence to illustrate the relationships between systems or between components of a system. ...
1 - College of Arts and Sciences
... A mass of 4.0 g indicates that the uncertainty is in the first decimal place of the measurement. Thus, the mass might be anything between 3.9 and 4.1 ...
... A mass of 4.0 g indicates that the uncertainty is in the first decimal place of the measurement. Thus, the mass might be anything between 3.9 and 4.1 ...
The Atomic Theory, and the Structure of Matter
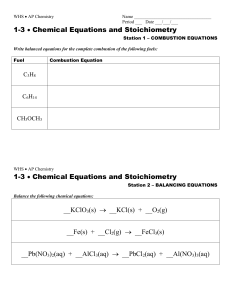
... 1. Write the chemical formula for each reactant and product followed by the state of each: solid (s); liquid (l); gas (g); aqueous(aq) 2. Adjust the numbers of molecules until there are the same number of atoms of each type on both sides of the equation. This balances the mass of both the reactants ...
... 1. Write the chemical formula for each reactant and product followed by the state of each: solid (s); liquid (l); gas (g); aqueous(aq) 2. Adjust the numbers of molecules until there are the same number of atoms of each type on both sides of the equation. This balances the mass of both the reactants ...
Viju B - IS MU
... Chiral auxiliaries are optically active groups, temporarily covalently attached to the prochiral substrate, that induce a selective formation of one of the enantiomeric products during a stereoselective reaction. When the reaction stereochemistry is achieved, the auxiliary is removed. The benzoin gr ...
... Chiral auxiliaries are optically active groups, temporarily covalently attached to the prochiral substrate, that induce a selective formation of one of the enantiomeric products during a stereoselective reaction. When the reaction stereochemistry is achieved, the auxiliary is removed. The benzoin gr ...
Thermo Chemistry Ch 9 Notes
... kilojoules (kJ) m-mass of substance undergoing the change measured in units of grams (g) or kilograms (kg) c=heat capacity -heat required to change the temp of 1 g of substance ...
... kilojoules (kJ) m-mass of substance undergoing the change measured in units of grams (g) or kilograms (kg) c=heat capacity -heat required to change the temp of 1 g of substance ...
Unit 5 Study Guide
... Unit 5 Study Guide: Chemical Reactions 1. What are the 7 diatomic molecules? ...
... Unit 5 Study Guide: Chemical Reactions 1. What are the 7 diatomic molecules? ...
Thermodynamics
... of any first-law energy that is available to perform thermodynamic work; i.e., work mediated by thermal energy. Free energy is subject to irreversible loss in the course of such work. Since a first-law energy is always conserved, it is evident that free energy is an expendable, second-law kind of en ...
... of any first-law energy that is available to perform thermodynamic work; i.e., work mediated by thermal energy. Free energy is subject to irreversible loss in the course of such work. Since a first-law energy is always conserved, it is evident that free energy is an expendable, second-law kind of en ...
Review Chemistry KEY - cms16-17
... The substances will have a new identity and new and different chemical and physical properties will form. 31. Explain the difference between reactants and products. Include where in the equation they would be found. Reactants form products. The reactants are what you start with and the product is th ...
... The substances will have a new identity and new and different chemical and physical properties will form. 31. Explain the difference between reactants and products. Include where in the equation they would be found. Reactants form products. The reactants are what you start with and the product is th ...
Physical Chemistry–I (CHEM-3411-A) Term
... background in these subjects may want to consider the use of Thermodynamics and Kinetics for the Biological Sciences, by G. G. Hammes, (Wiley, ISBN 0-471-37491-1). Course description: This is part of a two-semester sequence of courses in physical chemistry for students of science and engineering. Th ...
... background in these subjects may want to consider the use of Thermodynamics and Kinetics for the Biological Sciences, by G. G. Hammes, (Wiley, ISBN 0-471-37491-1). Course description: This is part of a two-semester sequence of courses in physical chemistry for students of science and engineering. Th ...
Ch. 3 9-Station Review
... A student is assigned the task of determining the number of moles of water in one mole of MgCl2 · n H2O. The student collects the data shown in the following table. Mass of empty container Initial mass of sample and container Mass of sample and container after first heating Mass of sample and contai ...
... A student is assigned the task of determining the number of moles of water in one mole of MgCl2 · n H2O. The student collects the data shown in the following table. Mass of empty container Initial mass of sample and container Mass of sample and container after first heating Mass of sample and contai ...
Section 7.1 Describing Reactions
... headings, vocabulary, and figures in this section. List two things you expect to learn. After reading, state what you learned about each item you listed. For more information on this Reading Strategy, see the Reading and Study Skills in the Skills and Reference Handbook at the end of your textbook. ...
... headings, vocabulary, and figures in this section. List two things you expect to learn. After reading, state what you learned about each item you listed. For more information on this Reading Strategy, see the Reading and Study Skills in the Skills and Reference Handbook at the end of your textbook. ...
Johnny Xie Period 5 Chapter 6 Thermochemistry 6.1 The Nature of
... Temperature is a property that reflects motions of particles in the object. Heat involves the transfer of energy due to difference in temperature. ...
... Temperature is a property that reflects motions of particles in the object. Heat involves the transfer of energy due to difference in temperature. ...
Thermodynamics
... A steady decrease in the car’s total mechanical energy occurs because of work being done against the friction between the car’s axles and its bearings and between the car’s wheels and the coaster track. If the internal energy for the roller coaster (the system) and the energy dissipated to the surro ...
... A steady decrease in the car’s total mechanical energy occurs because of work being done against the friction between the car’s axles and its bearings and between the car’s wheels and the coaster track. If the internal energy for the roller coaster (the system) and the energy dissipated to the surro ...
Document
... q is energy liberated or added to the system while w is the work done on or by the system The change in energy depends on the amount of heat added or released from the system and the amount of work done on or from the system When heat is added or work is done to the system the energy increases ...
... q is energy liberated or added to the system while w is the work done on or by the system The change in energy depends on the amount of heat added or released from the system and the amount of work done on or from the system When heat is added or work is done to the system the energy increases ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... Introduction: The equation H2 + O2 H2O is unbalanced because there are two oxygen atoms on the reactants side of the equation, and only one on the products side of the equation. To balance the equation, you cannot change the structure of any of the molecules, but you can change the number of molec ...
... Introduction: The equation H2 + O2 H2O is unbalanced because there are two oxygen atoms on the reactants side of the equation, and only one on the products side of the equation. To balance the equation, you cannot change the structure of any of the molecules, but you can change the number of molec ...
MCQ plus answers
... Use a dark lead pencil so that you can use an eraser if you make an error. Errors made in ink cannot be corrected – you will need to ask the examination supervisor for another sheet. Boxes with faint or incomplete lines or not completed in the prescribed manner may not be read. Be sure to complete t ...
... Use a dark lead pencil so that you can use an eraser if you make an error. Errors made in ink cannot be corrected – you will need to ask the examination supervisor for another sheet. Boxes with faint or incomplete lines or not completed in the prescribed manner may not be read. Be sure to complete t ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.