Chapter 4: Energy Analysis of Closed Systems
... Heat in the amount of 1072.42 kJ is added to the water. Specific Heats and Changes in Internal Energy and Enthalpy for Ideal Gases Before the first law of thermodynamics can be applied to systems, ways to calculate the change in internal energy of the substance enclosed by the system boundary must b ...
... Heat in the amount of 1072.42 kJ is added to the water. Specific Heats and Changes in Internal Energy and Enthalpy for Ideal Gases Before the first law of thermodynamics can be applied to systems, ways to calculate the change in internal energy of the substance enclosed by the system boundary must b ...
C2 Additional Chemistry Thursday 14 May
... Describe what electrolysis is and what it does. State the type of compound that can be used as an electrolyte Explain why the electrolyte must been molten or in solution for electrolysis to work Describe which ions move to which electrode. Explain what then happens to ions at that electrode, in term ...
... Describe what electrolysis is and what it does. State the type of compound that can be used as an electrolyte Explain why the electrolyte must been molten or in solution for electrolysis to work Describe which ions move to which electrode. Explain what then happens to ions at that electrode, in term ...
Thermodynamics and Equilibrium
... to conclude that processes should be spontaneous if they are exothermic. However, there are many examples of spontaneous endothermic processes, the most common being evaporation in which liquid molecules spontaneously break their intermolecular forces to pass into the gas phase. Thus, the enthalpy c ...
... to conclude that processes should be spontaneous if they are exothermic. However, there are many examples of spontaneous endothermic processes, the most common being evaporation in which liquid molecules spontaneously break their intermolecular forces to pass into the gas phase. Thus, the enthalpy c ...
Balancing Equations (A visual aid)
... I. Obtain a container of colored beads. If your container of beads does not have enough, get them from the reserve stockpile at the teacher’s desk. The numbers shown below are the minimum for you to be able to do the equation balancing. II. For equations (1) - (7) below, complete the following steps ...
... I. Obtain a container of colored beads. If your container of beads does not have enough, get them from the reserve stockpile at the teacher’s desk. The numbers shown below are the minimum for you to be able to do the equation balancing. II. For equations (1) - (7) below, complete the following steps ...
Chapter 2 Classical Thermodynamics: The Second Law 2.1 Heat
... Also, from 1st law, dE = d̄Q + d̄W = d̄Qrev + d̄W rev = d̄Qirrev + d̄W irrev and, by definition of reversibility, for a given change of the system (e.g., given dV for a gas), d̄W irrev > d̄W rev (to overcome friction, etc.), we have d̄Qirrev < d̄Qrev , or d̄Q ≤ T dS ...
... Also, from 1st law, dE = d̄Q + d̄W = d̄Qrev + d̄W rev = d̄Qirrev + d̄W irrev and, by definition of reversibility, for a given change of the system (e.g., given dV for a gas), d̄W irrev > d̄W rev (to overcome friction, etc.), we have d̄Qirrev < d̄Qrev , or d̄Q ≤ T dS ...
Part I - American Chemical Society
... ! When you have selected your answer to each question, blacken the corresponding space on the answer sheet using a soft, #2 pencil. Make a heavy, full mark, but no stray marks. If you decide to change an answer, erase the unwanted mark very carefully. ! There is only one correct answer to each quest ...
... ! When you have selected your answer to each question, blacken the corresponding space on the answer sheet using a soft, #2 pencil. Make a heavy, full mark, but no stray marks. If you decide to change an answer, erase the unwanted mark very carefully. ! There is only one correct answer to each quest ...
Chemical Reactions
... (BrINClHOF) For example, Oxygen is O2 as an element. In a compound, it can’t be a diatomic element because it’s not an element anymore, it’s a compound! ...
... (BrINClHOF) For example, Oxygen is O2 as an element. In a compound, it can’t be a diatomic element because it’s not an element anymore, it’s a compound! ...
Test - Regents
... 59 At constant temperature, the relationship between the volume (V) of a given mass of gas and its pressure (P) is (1) V = kP (3) PV = k (2) P = kV (4) V = k P ...
... 59 At constant temperature, the relationship between the volume (V) of a given mass of gas and its pressure (P) is (1) V = kP (3) PV = k (2) P = kV (4) V = k P ...
Discussion 9, Mahaffy et al., Chapter 15
... Oxidation Reduction Reactions a. Oxidation is loss of electrons (acts as a reducing agent) b.Reduction is gain of electrons (acts as a oxidizing agent) Assigning Oxidation numbers c. Oxidation number is 0 for atoms in an element. d.The sum of all oxidation numbers in a molecule or ion must add up to ...
... Oxidation Reduction Reactions a. Oxidation is loss of electrons (acts as a reducing agent) b.Reduction is gain of electrons (acts as a oxidizing agent) Assigning Oxidation numbers c. Oxidation number is 0 for atoms in an element. d.The sum of all oxidation numbers in a molecule or ion must add up to ...
chm5423chapter5notes..
... At wavelengths longer than 310. nm the quantum yield for the production of O(1D) atoms was expected to quickly drop to zero. In fact, while the quantum yield decreases, it remains in the region 0.1-0.2 (Fig 3.3, Chapter 3). This is because a second, spin forbidden process that forms an O( 1D) atom a ...
... At wavelengths longer than 310. nm the quantum yield for the production of O(1D) atoms was expected to quickly drop to zero. In fact, while the quantum yield decreases, it remains in the region 0.1-0.2 (Fig 3.3, Chapter 3). This is because a second, spin forbidden process that forms an O( 1D) atom a ...
cbse class – x science solutions
... What will be the observed colour of the sky on a planet where there is no atmosphere? Why? Dark, because no light would be scattered to the observer’s eye Name the component of white light that deviates the least and the component that deviates the most while passing through a glass prism. Least – R ...
... What will be the observed colour of the sky on a planet where there is no atmosphere? Why? Dark, because no light would be scattered to the observer’s eye Name the component of white light that deviates the least and the component that deviates the most while passing through a glass prism. Least – R ...
MIDTERM REVIEW UNIT 1: Mass/Measurement
... 11. In a reaction between lead (II) nitrate and copper (II) bromide, do the following: a) write the formulas for the reactants and the products and balance the equation b) If 0.67 moles of copper (II) ...
... 11. In a reaction between lead (II) nitrate and copper (II) bromide, do the following: a) write the formulas for the reactants and the products and balance the equation b) If 0.67 moles of copper (II) ...
H + H–H H∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙ H∙∙∙∙∙∙H H∙∙∙∙∙∙H∙∙∙∙∙∙H
... This process can be generalized as: A + B-C [ABC] A-B + C Activated complex Transition state ...
... This process can be generalized as: A + B-C [ABC] A-B + C Activated complex Transition state ...
Problems - Department of Chemistry HKU
... What is the order and rate constant for the reaction under these conditions? 21.10 The addition of hydrogen halides to alkenes has played a fundamental role in the investigation of organic reaction mechanisms. In one study (M.J. Haugh and D.R. Dalton, J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 97, 5674 (1975)), high press ...
... What is the order and rate constant for the reaction under these conditions? 21.10 The addition of hydrogen halides to alkenes has played a fundamental role in the investigation of organic reaction mechanisms. In one study (M.J. Haugh and D.R. Dalton, J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 97, 5674 (1975)), high press ...
unit (4) calculations and chemical reactions
... Consider the reaction in which magnesium oxide reacts with carbon dioxide to form magnesium carbonate. We can represent the above “word description” by a “chemical equation”. Chemical equation: MgO + CO2 → MgCO3 Reactants Product We often indicate the physical state of reactants and products using t ...
... Consider the reaction in which magnesium oxide reacts with carbon dioxide to form magnesium carbonate. We can represent the above “word description” by a “chemical equation”. Chemical equation: MgO + CO2 → MgCO3 Reactants Product We often indicate the physical state of reactants and products using t ...
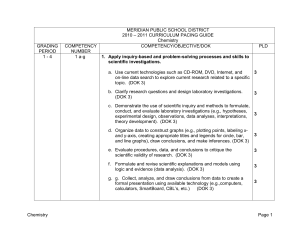
MERIDIAN PUBLIC SCHOOL DISTRICT
... b. Use the ideal gas laws to explain the relationships between volume, temperature, pressure, and quantity in moles. (DOK 2) ...
... b. Use the ideal gas laws to explain the relationships between volume, temperature, pressure, and quantity in moles. (DOK 2) ...
50 Forgotten Facts
... 26) Molecular compounds tend to be soft, have low melting points and high vapor pressures. Hydrogen bonds are the strongest of the intermolecular forces (when the H of one polar molecule attracts the N, O or F of another polar molecule), followed by dipole (where the more electronegative end of one ...
... 26) Molecular compounds tend to be soft, have low melting points and high vapor pressures. Hydrogen bonds are the strongest of the intermolecular forces (when the H of one polar molecule attracts the N, O or F of another polar molecule), followed by dipole (where the more electronegative end of one ...
Unit 4
... Consider the reaction in which magnesium oxide reacts with carbon dioxide to form magnesium carbonate. We can represent the above “word description” by a “chemical equation”. Chemical equation: MgO + CO2 → MgCO3 Reactants Product We often indicate the physical state of reactants and products using t ...
... Consider the reaction in which magnesium oxide reacts with carbon dioxide to form magnesium carbonate. We can represent the above “word description” by a “chemical equation”. Chemical equation: MgO + CO2 → MgCO3 Reactants Product We often indicate the physical state of reactants and products using t ...
Chapter 12: Thermodynamic Property Relations
... Some thermodynamic properties can be measured directly, but many others cannot. Therefore, it is necessary to develop some relations between these two groups so that the properties that cannot be measured directly can be evaluated. The derivations are based on the fact that properties are point fun ...
... Some thermodynamic properties can be measured directly, but many others cannot. Therefore, it is necessary to develop some relations between these two groups so that the properties that cannot be measured directly can be evaluated. The derivations are based on the fact that properties are point fun ...
Document
... Some thermodynamic properties can be measured directly, but many others cannot. Therefore, it is necessary to develop some relations between these two groups so that the properties that cannot be measured directly can be evaluated. The derivations are based on the fact that properties are point fun ...
... Some thermodynamic properties can be measured directly, but many others cannot. Therefore, it is necessary to develop some relations between these two groups so that the properties that cannot be measured directly can be evaluated. The derivations are based on the fact that properties are point fun ...
Chapter 1 Chemistry: The Study of Matter
... Chromatography is a method of separating mixtures that uses a stationary phase and a mobile phase. Paper chromatography can be used to separate pigments because they move at different rates on the paper. ...
... Chromatography is a method of separating mixtures that uses a stationary phase and a mobile phase. Paper chromatography can be used to separate pigments because they move at different rates on the paper. ...
Hein and Arena - faculty at Chemeketa
... In 1888, the French chemist Henri LeChatelier This generalization, known as set forth a far-reaching generalization on the LeChatelier’s Principle, states behavior of equilibrium systems. If a stress or strain is applied to a system in equilibrium, the system will respond in such a way as to reliev ...
... In 1888, the French chemist Henri LeChatelier This generalization, known as set forth a far-reaching generalization on the LeChatelier’s Principle, states behavior of equilibrium systems. If a stress or strain is applied to a system in equilibrium, the system will respond in such a way as to reliev ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.