Indifference Curve
... budget line shifts from CD to EF and T3 is new equilibrium point. If we join the T1,T2 and T3 point we will get a curve known as INCOME CONSUMPTION CURVE(ICC).Therefore, income consumption curve is the locus of points showing the equilibrium of the consumer at different levels of income, when prices ...
... budget line shifts from CD to EF and T3 is new equilibrium point. If we join the T1,T2 and T3 point we will get a curve known as INCOME CONSUMPTION CURVE(ICC).Therefore, income consumption curve is the locus of points showing the equilibrium of the consumer at different levels of income, when prices ...
Theories of Economic Development
... net benefits of economic development, subject to maintaining the services and quality of natural resources over time” (Pearce and Turner 1990, p. 24). Its concern is about balancing the objectives of economic growth and attending to environmental considerations. In a broader sense, sustainable develo ...
... net benefits of economic development, subject to maintaining the services and quality of natural resources over time” (Pearce and Turner 1990, p. 24). Its concern is about balancing the objectives of economic growth and attending to environmental considerations. In a broader sense, sustainable develo ...
Lecture Week 12
... to be able to buy the quantities of food, shelter, and clothing that are deemed necessary. is a relative concept. In Canada, poverty is measured by using a lowincome cutoff. low-income cutoff is the income level at which a family spends 54.7 percent of its income on food, shelter, and clothing. ...
... to be able to buy the quantities of food, shelter, and clothing that are deemed necessary. is a relative concept. In Canada, poverty is measured by using a lowincome cutoff. low-income cutoff is the income level at which a family spends 54.7 percent of its income on food, shelter, and clothing. ...
1 Problem
... Assume that the long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical at Y = 3, 000 while the short-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal at P = 1.0. The aggregate demand curve is Y = 2 M P and M = 1, 500. 1. If the economy is initially in long-run equilibrium, what are the values of P and Y ? 2. What is t ...
... Assume that the long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical at Y = 3, 000 while the short-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal at P = 1.0. The aggregate demand curve is Y = 2 M P and M = 1, 500. 1. If the economy is initially in long-run equilibrium, what are the values of P and Y ? 2. What is t ...
Edgeworth-Bowley Box Diagram
... Bundle G may or may not be preferred to A, as it has more Y but less X. Bundle F may or may not be preferred to A, as it has more X but less Y. To determine how to rank A, G, and F we have to know about a specific consumer’s preferences. In other words, we have to know how much a consumer values a u ...
... Bundle G may or may not be preferred to A, as it has more Y but less X. Bundle F may or may not be preferred to A, as it has more X but less Y. To determine how to rank A, G, and F we have to know about a specific consumer’s preferences. In other words, we have to know how much a consumer values a u ...
ppt - Thomas Piketty
... • Rising aggregate wealth-income ratios might be more relevant for macro fragility than rising top income shares • See Piketty-Zucman, « Capital is Back: Wealth-Income Ratios in Rich Countries 1870-2010 », ’12: we put together new data set of national balance sheets to study long run evolution of we ...
... • Rising aggregate wealth-income ratios might be more relevant for macro fragility than rising top income shares • See Piketty-Zucman, « Capital is Back: Wealth-Income Ratios in Rich Countries 1870-2010 », ’12: we put together new data set of national balance sheets to study long run evolution of we ...
distribution of income and wealth in islam
... increasing inequality under market driven capitalist system is in distribution of income in China resulting from ‘market reforms’ implemented during past three decades. Its Gini coefficient, together with a very high GDP growth, according to China’s National Bureau of Statistics, is currently 0.474 ...
... increasing inequality under market driven capitalist system is in distribution of income in China resulting from ‘market reforms’ implemented during past three decades. Its Gini coefficient, together with a very high GDP growth, according to China’s National Bureau of Statistics, is currently 0.474 ...
Chapter Eight Effects of a Price Change Effects of a Price Change
... Slutsky’s Effects for Giffen Goods • Slutsky’s decomposition of the effect of a price change into a pure substitution effect and an income effect thus explains why the Law of Downward-Sloping Demand is violated for extremely income-inferior goods. ...
... Slutsky’s Effects for Giffen Goods • Slutsky’s decomposition of the effect of a price change into a pure substitution effect and an income effect thus explains why the Law of Downward-Sloping Demand is violated for extremely income-inferior goods. ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES SECOND-BEST INSTITUTIONS Dani Rodrik Working Paper 14050
... Christopher Woodruff (1999) found that there was little confidence in the courts and very little resort to them. Firms relied instead on relational contracting, just as in Africa. The strategies were in fact quite similar: build long-term relationships based on trust, demand immediate payment, scree ...
... Christopher Woodruff (1999) found that there was little confidence in the courts and very little resort to them. Firms relied instead on relational contracting, just as in Africa. The strategies were in fact quite similar: build long-term relationships based on trust, demand immediate payment, scree ...
PDF (view with Acrobat)
... c. Describe the three theories of how income should be distributed and what each theory implies about how the government should use taxes and transfer programs. Perfect equality suggests that everyone should have the same amount of income. This would imply a very progressive tax system and a lot of ...
... c. Describe the three theories of how income should be distributed and what each theory implies about how the government should use taxes and transfer programs. Perfect equality suggests that everyone should have the same amount of income. This would imply a very progressive tax system and a lot of ...
Eligibility revised - Rosenberg Housing Authority
... The Disaster Housing Assistance program (DHAP) is entering the second portion of the program. The U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development’s Disaster Housing Assistance Program requires clients to re-qualify for continued assistance within six months of the lease-up date or July 31st, whiche ...
... The Disaster Housing Assistance program (DHAP) is entering the second portion of the program. The U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development’s Disaster Housing Assistance Program requires clients to re-qualify for continued assistance within six months of the lease-up date or July 31st, whiche ...
1. Market Failure and Economic Efficiency
... one more unit of a good or service. Marginal Benefit Curve = Demand Curve ...
... one more unit of a good or service. Marginal Benefit Curve = Demand Curve ...
The Impact of Formal and Informal Institutions on - Beck-Shop
... realize the equilibrium growth rate – that is to say the growth rate of technological progress.3 This argument is based on the assumption of diminishing returns to scale. Accordingly, less developed countries exhibit a relatively low capital stock. Therefore, every additional unit of capital causes ...
... realize the equilibrium growth rate – that is to say the growth rate of technological progress.3 This argument is based on the assumption of diminishing returns to scale. Accordingly, less developed countries exhibit a relatively low capital stock. Therefore, every additional unit of capital causes ...
Learning for a New Economy - Initiative for Policy Dialogue
... Markedly different perspective than standard question, which focuses on static efficiency, moving countries to “frontier” or moving out frontier through the accumulation of more resources Question is especially salient because the two policies may be in conflict − Intellectual property restricts use ...
... Markedly different perspective than standard question, which focuses on static efficiency, moving countries to “frontier” or moving out frontier through the accumulation of more resources Question is especially salient because the two policies may be in conflict − Intellectual property restricts use ...
Slides
... i. All agents gain from trade, although these gains are not proportionally distributed; ii. Inequality of relative revenues and utilities is higher in an open economy than in autarky given that some agents do not export; iii. Falling trade costs first increase and then decrease inequality. • Replica ...
... i. All agents gain from trade, although these gains are not proportionally distributed; ii. Inequality of relative revenues and utilities is higher in an open economy than in autarky given that some agents do not export; iii. Falling trade costs first increase and then decrease inequality. • Replica ...
CHAPTER 2: AN UNEQUAL WORLD - Indus Valley School of Art
... countries have more people and more workers, so therefore produce more. If we simply compared countries in terms of the total production, we would find that highly populated countries have higher production, but we would not know whether the living standards of the larger countries are really higher ...
... countries have more people and more workers, so therefore produce more. If we simply compared countries in terms of the total production, we would find that highly populated countries have higher production, but we would not know whether the living standards of the larger countries are really higher ...
Theorem of Exchange
... ~ John will have more X, so his MUVx decreases ~ Mary will have fewer X ,so her MUVx for the remaining X rises Trade goes on as long as their MUVx are not equal. ...
... ~ John will have more X, so his MUVx decreases ~ Mary will have fewer X ,so her MUVx for the remaining X rises Trade goes on as long as their MUVx are not equal. ...
The Sources of Economic Inequality
... which a family normally spends 63.6 percent or more of its income on food, shelter, and clothing. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Canada Inc., Toronto, Ontario ...
... which a family normally spends 63.6 percent or more of its income on food, shelter, and clothing. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Canada Inc., Toronto, Ontario ...
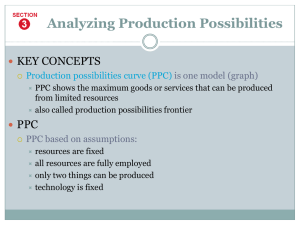
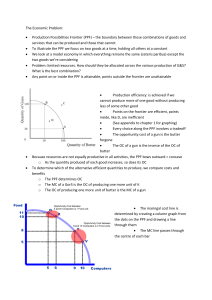
The Economic Problem: • Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF
... Preferences are a description of a person’s likes and dislikes To describe rpeferences, economists use the concepts of MB and the MB curve The MB of a GorS is the benefit received from consuming one more unit of it o Measured by the amount a person is willing to pay for an additional unit of a GorS ...
... Preferences are a description of a person’s likes and dislikes To describe rpeferences, economists use the concepts of MB and the MB curve The MB of a GorS is the benefit received from consuming one more unit of it o Measured by the amount a person is willing to pay for an additional unit of a GorS ...
1 - people.vcu.edu
... e. What would the compensated demand curve for X look like in this situation? The products are perfect substitutes. So when X is being purchased, any further price reduction results in an increase in X solely due to income effects. Abstracting out this income effect would leave the quantity of X unc ...
... e. What would the compensated demand curve for X look like in this situation? The products are perfect substitutes. So when X is being purchased, any further price reduction results in an increase in X solely due to income effects. Abstracting out this income effect would leave the quantity of X unc ...
qqch12as - Harper College
... D. presumes that changes in wages and other resource prices match changes in the price level. 2. The aggregate supply curve (short-run) is upsloping because: A. wages and other resource prices match changes in the price level. B. the price level is flexible upward but inflexible downward. C. per-uni ...
... D. presumes that changes in wages and other resource prices match changes in the price level. 2. The aggregate supply curve (short-run) is upsloping because: A. wages and other resource prices match changes in the price level. B. the price level is flexible upward but inflexible downward. C. per-uni ...
qqch12asanswers
... D. presumes that changes in wages and other resource prices match changes in the price level. 2. The aggregate supply curve (short-run) is upsloping because: A. wages and other resource prices match changes in the price level. B. the price level is flexible upward but inflexible downward. C. per-uni ...
... D. presumes that changes in wages and other resource prices match changes in the price level. 2. The aggregate supply curve (short-run) is upsloping because: A. wages and other resource prices match changes in the price level. B. the price level is flexible upward but inflexible downward. C. per-uni ...
V - Institute for Research on Poverty
... The purpose of this paper is to provide an exegesis of this literature. Our reasons for doing this are several. ...
... The purpose of this paper is to provide an exegesis of this literature. Our reasons for doing this are several. ...
PROBLEM SET 3 SOLUTIONS 14.02 Introductory Macroeconomics March 16, 2005
... I. Answer each as True, False, or Uncertain, providing some explanation for your choice. 1. The aggregate demand curve is downward sloping because people demand fewer goods at higher prices. FALSE. The AD curve is downward sloping because an increase in prices reduces real money supply, which induce ...
... I. Answer each as True, False, or Uncertain, providing some explanation for your choice. 1. The aggregate demand curve is downward sloping because people demand fewer goods at higher prices. FALSE. The AD curve is downward sloping because an increase in prices reduces real money supply, which induce ...
Kuznets curve

In economics, a Kuznets curve graphs the hypothesis that as an economy develops, market forces first increase and then decrease economic inequality. The hypothesis was first advanced by economist Simon Kuznets in the 1950s and '60s.One explanation of such a progression suggests that early in development investment opportunities for those who have money multiply, while an influx of cheap rural labor to the cities holds down wages. Whereas in mature economies, human capital accrual, or an estimate of cost that has been incurred but not yet paid, takes the place of physical capital accrual as the main source of growth; and inequality slows growth by lowering education levels because poorer, disadvantaged people lack finance for their education in imperfect credit-markets.The Kuznets curve implies that as a nation undergoes industrialization – and especially the mechanization of agriculture – the center of the nation’s economy will shift to the cities. As internal migration by farmers looking for better-paying jobs in urban hubs causes a significant rural-urban inequality gap (the owners of firms would be profiting, while laborers from those industries would see their incomes rise at a much slower rate and agricultural workers would possibly see their incomes decrease), rural populations decrease as urban populations increase. Inequality is then expected to decrease when a certain level of average income is reached and the processes of industrialization – democratization and the rise of the welfare state – allow for the trickle-down of the benefits from rapid growth, and increase the per-capita income. Kuznets believed that inequality would follow an inverted “U” shape as it rises and then falls again with the increase of income per-capita.Kuznets curve diagrams show an inverted U curve, although variables along the axes are often mixed and matched, with inequality or the Gini coefficient on the Y axis and economic development, time or per-capita incomes on the X axis.Since 1991 the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) has become a standard feature in the technical literature of environmental policy, though its application there has been strongly contested.