'Distribution Dynamics: Stratification, Polarization and Convergence Among OECD Economies, 1870-1992'
... exception to the Ôregression schoolÕ has been the work on distribution dynamics pioneered in a series of papers by Quah (1993, 1996, 1997). He believes that only by considering the issues of growth and distribution simultaneously can we understand their underlying dynamics. He has argued, for exampl ...
... exception to the Ôregression schoolÕ has been the work on distribution dynamics pioneered in a series of papers by Quah (1993, 1996, 1997). He believes that only by considering the issues of growth and distribution simultaneously can we understand their underlying dynamics. He has argued, for exampl ...
Due Date: Friday, September 17th
... a) If both taxes and government purchases were cut by equal amounts, state and explain what the long term effects of this policy would be on private savings, public savings, and national savings. Again, we can write national savings as S = (Y – T – C) + (T –G). Clearly, public savings remains unaffe ...
... a) If both taxes and government purchases were cut by equal amounts, state and explain what the long term effects of this policy would be on private savings, public savings, and national savings. Again, we can write national savings as S = (Y – T – C) + (T –G). Clearly, public savings remains unaffe ...
Measures of economic activity and their implications for
... per cent. However, that of Luxembourg accelerated from around 1982, and Ireland’s from 1994, giving them an overall rate of nearly three per cent and four per cent per annum respectively. Despite the upward trend depicted in the figure, work by Easterlin (1995) and others suggests that this has not ...
... per cent. However, that of Luxembourg accelerated from around 1982, and Ireland’s from 1994, giving them an overall rate of nearly three per cent and four per cent per annum respectively. Despite the upward trend depicted in the figure, work by Easterlin (1995) and others suggests that this has not ...
Chapter Eight
... Note that m - m is the amount of the change in money income such that the consumer is just able to buy the original bundle of goods (i.e. purchasing power is constant) Denote ∆m = m - m and ∆pi = pi - pi ∆m = ∆pi xi (pi , m) This is the amount of money that should be given to the consumer to hold ...
... Note that m - m is the amount of the change in money income such that the consumer is just able to buy the original bundle of goods (i.e. purchasing power is constant) Denote ∆m = m - m and ∆pi = pi - pi ∆m = ∆pi xi (pi , m) This is the amount of money that should be given to the consumer to hold ...
Happiness and public policy
... 1950s – nor any significant decrease in unhappiness. Similar findings apply in Japan and the UK and in most European countries (where the series began in 1975). You might reasonably question whether such remarks mean anything, but significant new evidence from neuro-science suggests that they do. 4 ...
... 1950s – nor any significant decrease in unhappiness. Similar findings apply in Japan and the UK and in most European countries (where the series began in 1975). You might reasonably question whether such remarks mean anything, but significant new evidence from neuro-science suggests that they do. 4 ...
The Marginal Use Value
... Some people argued that water is so useful, yet its price is relatively lower than most goods. Whereas diamond is not so useful, yet its price is relatively higher than many goods. If price could reflect the value of a good, how could economists explain the paradox between water and diamond in this ...
... Some people argued that water is so useful, yet its price is relatively lower than most goods. Whereas diamond is not so useful, yet its price is relatively higher than many goods. If price could reflect the value of a good, how could economists explain the paradox between water and diamond in this ...
university of wuppertal bergische universität wuppertal
... Japan and Russia, but also from the USA and big countries with modest per capita income, such as China and India. The ambitious goals envisaged for long-term reduction of greenhouse gases will require new efforts in many fields, including innovation policy and energy policy. If one is to achieve the ...
... Japan and Russia, but also from the USA and big countries with modest per capita income, such as China and India. The ambitious goals envisaged for long-term reduction of greenhouse gases will require new efforts in many fields, including innovation policy and energy policy. If one is to achieve the ...
If Walmart Were In Charge: Sourcing CO Emissions Reductions at Least Cost
... from timber production. Deforestation of these tropical forests is a major source of global CO2 ...
... from timber production. Deforestation of these tropical forests is a major source of global CO2 ...
Chapter 2 Solow`s Neoclassical Growth Model
... from A to D because at this level actual investment exceeds breakeven investment. This means more resources are being devoted to investment than are needed to hold k constant and hence, k& is positive. An increase in capital is produced from D to ...
... from A to D because at this level actual investment exceeds breakeven investment. This means more resources are being devoted to investment than are needed to hold k constant and hence, k& is positive. An increase in capital is produced from D to ...
cm5: consumer and producer
... very important when thinking about the welfare aspects of markets, their social optimality. How much is produced of a good or service depends on demand and supply, but demands and supplies are dependent on ATP. Therefore, the socially optimal resource allocations generated by the “invisible hand”, a ...
... very important when thinking about the welfare aspects of markets, their social optimality. How much is produced of a good or service depends on demand and supply, but demands and supplies are dependent on ATP. Therefore, the socially optimal resource allocations generated by the “invisible hand”, a ...
Market demand is simply a horizontal summation
... According to Alfred Marshall, demand schedule shows the amounts of a good that consumers are willing to purchase at various prices. Later, the term “demand schedule’ was changed to “demand curve.” It is not a single number. It depends on many variables. However, we focus on relevant economic variabl ...
... According to Alfred Marshall, demand schedule shows the amounts of a good that consumers are willing to purchase at various prices. Later, the term “demand schedule’ was changed to “demand curve.” It is not a single number. It depends on many variables. However, we focus on relevant economic variabl ...
Globalisation and the Western Australian Economy
... world have been converging slowly towards those of the developed world (Commonwealth Treasury 2001). Despite these benefits, concerns have been raised in Australia and many other countries about the effects of freer global markets in trade and investment. Globalisation is a controversial issue as se ...
... world have been converging slowly towards those of the developed world (Commonwealth Treasury 2001). Despite these benefits, concerns have been raised in Australia and many other countries about the effects of freer global markets in trade and investment. Globalisation is a controversial issue as se ...
CAPITAL AND WEALTH TAXATION IN THE 21sT
... This approach successfully brings together many of the existing scattered results from the literature. In addition, if we introduce capital market imperfections into our basic inheritance tax model, then we find that one needs to supplement inheritance taxes with annual taxation of wealth and capita ...
... This approach successfully brings together many of the existing scattered results from the literature. In addition, if we introduce capital market imperfections into our basic inheritance tax model, then we find that one needs to supplement inheritance taxes with annual taxation of wealth and capita ...
x 2
... goods are income-inferior (i.e. demand is reduced by higher income). The substitution and income effects oppose each other when an incomeinferior good’s own price changes. ...
... goods are income-inferior (i.e. demand is reduced by higher income). The substitution and income effects oppose each other when an incomeinferior good’s own price changes. ...
Wk10
... • When pollution is unregulated, all consumers bear the consequences of pollution. • When cap-and-trade is enacted, the cost of pollution is borne directly by firms. Polluting firms tend to be able to organize better lobbying efforts, because consumers feel the cost of pollution diffusely. • This il ...
... • When pollution is unregulated, all consumers bear the consequences of pollution. • When cap-and-trade is enacted, the cost of pollution is borne directly by firms. Polluting firms tend to be able to organize better lobbying efforts, because consumers feel the cost of pollution diffusely. • This il ...
Chapter 8 8 Slutsky Equation
... normal good. But, the income effect is in the opposite direction. Good 1 is ( 1’’’,x (x ’’’ 2’’’) income-inferior f because an x 2’ i increase to income i x2’’ causes demand to f ll fall. x2 ...
... normal good. But, the income effect is in the opposite direction. Good 1 is ( 1’’’,x (x ’’’ 2’’’) income-inferior f because an x 2’ i increase to income i x2’’ causes demand to f ll fall. x2 ...
Beyond IPAT and Kuznets Curves: Globalization as a Vital Factor in
... tion for trees), or in the case of synergism of different effects. The authors cite the example of cities which because of population increases push out into farmland, resulting in humans' lungs being afflicted by a mixture of and traffic effluents and suffering disproportionate agrochemicals damage ...
... tion for trees), or in the case of synergism of different effects. The authors cite the example of cities which because of population increases push out into farmland, resulting in humans' lungs being afflicted by a mixture of and traffic effluents and suffering disproportionate agrochemicals damage ...
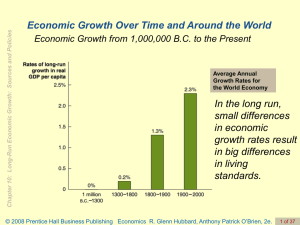
Economics R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O`Brien, 2e.
... Failure to Enforce the Rule of Law Property rights The rights individuals or firms have to the exclusive use of their property, including the right to buy or sell it. Rule of law The ability of a government to enforce the laws of the country, particularly with respect to protecting private property ...
... Failure to Enforce the Rule of Law Property rights The rights individuals or firms have to the exclusive use of their property, including the right to buy or sell it. Rule of law The ability of a government to enforce the laws of the country, particularly with respect to protecting private property ...
The American University in Cairo
... widening the inequality gaps not only among the different countries but within each country depending on where that country stands from the development ladder. As a result, various theoretical and empirical researches in different social science disciplines were directed to study the factors of prod ...
... widening the inequality gaps not only among the different countries but within each country depending on where that country stands from the development ladder. As a result, various theoretical and empirical researches in different social science disciplines were directed to study the factors of prod ...
PDF Download
... scientific investigation. Thus, very little is yet known about the human brain, and even less has been communicated to the general public. Once we combine this fact with our innate tendency towards comparisons, and modern levels of income being a recent phenomenon, it is hardly surprising that the m ...
... scientific investigation. Thus, very little is yet known about the human brain, and even less has been communicated to the general public. Once we combine this fact with our innate tendency towards comparisons, and modern levels of income being a recent phenomenon, it is hardly surprising that the m ...
Evaluating Alternatives to GDP as Measures of
... informal activities that take place outside markets even though these may contribute to individual welfare. This is relevant to both developed (child care, voluntary work) and developing (substance agriculture) countries. GDP thus tends to overestimate the welfare impact of fundamental changes invol ...
... informal activities that take place outside markets even though these may contribute to individual welfare. This is relevant to both developed (child care, voluntary work) and developing (substance agriculture) countries. GDP thus tends to overestimate the welfare impact of fundamental changes invol ...
Evaluating Alternatives to GDP as Measures of Social Welfare
... informal activities that take place outside markets even though these may contribute to individual welfare. This is relevant to both developed (child care, voluntary work) and developing (substance agriculture) countries. GDP thus tends to overestimate the welfare impact of fundamental changes invol ...
... informal activities that take place outside markets even though these may contribute to individual welfare. This is relevant to both developed (child care, voluntary work) and developing (substance agriculture) countries. GDP thus tends to overestimate the welfare impact of fundamental changes invol ...
Growth, Productivity, and the Wealth Of Nations
... None of these are perfect solutions since they come with large strings attached. ...
... None of these are perfect solutions since they come with large strings attached. ...
Equity, Sustainable Development and Environmental Economics
... High levels of affluence are perhaps even more damaging to the environment as they are accompanied by high levels of consumption, which lead to resource depletion and waste accumulation. Many environmental problems—such as global warming and chemical contamination—are the result of affluence rather ...
... High levels of affluence are perhaps even more damaging to the environment as they are accompanied by high levels of consumption, which lead to resource depletion and waste accumulation. Many environmental problems—such as global warming and chemical contamination—are the result of affluence rather ...
PDF Download
... emerges. Countries found high up along the vertical axis include both those with large ICT-producing sectors, such as Finland and the United States, and those with almost no such production, notably Australia. As illustrated by Figure 2, however, there is a positive relationship also between R&D and ...
... emerges. Countries found high up along the vertical axis include both those with large ICT-producing sectors, such as Finland and the United States, and those with almost no such production, notably Australia. As illustrated by Figure 2, however, there is a positive relationship also between R&D and ...
Kuznets curve

In economics, a Kuznets curve graphs the hypothesis that as an economy develops, market forces first increase and then decrease economic inequality. The hypothesis was first advanced by economist Simon Kuznets in the 1950s and '60s.One explanation of such a progression suggests that early in development investment opportunities for those who have money multiply, while an influx of cheap rural labor to the cities holds down wages. Whereas in mature economies, human capital accrual, or an estimate of cost that has been incurred but not yet paid, takes the place of physical capital accrual as the main source of growth; and inequality slows growth by lowering education levels because poorer, disadvantaged people lack finance for their education in imperfect credit-markets.The Kuznets curve implies that as a nation undergoes industrialization – and especially the mechanization of agriculture – the center of the nation’s economy will shift to the cities. As internal migration by farmers looking for better-paying jobs in urban hubs causes a significant rural-urban inequality gap (the owners of firms would be profiting, while laborers from those industries would see their incomes rise at a much slower rate and agricultural workers would possibly see their incomes decrease), rural populations decrease as urban populations increase. Inequality is then expected to decrease when a certain level of average income is reached and the processes of industrialization – democratization and the rise of the welfare state – allow for the trickle-down of the benefits from rapid growth, and increase the per-capita income. Kuznets believed that inequality would follow an inverted “U” shape as it rises and then falls again with the increase of income per-capita.Kuznets curve diagrams show an inverted U curve, although variables along the axes are often mixed and matched, with inequality or the Gini coefficient on the Y axis and economic development, time or per-capita incomes on the X axis.Since 1991 the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) has become a standard feature in the technical literature of environmental policy, though its application there has been strongly contested.