Experimental
... the volume. Keeping to overnight, the crystals of Cu(ClO4)2 were formed. [Precaution- Cu(ClO4)2 is explosive in nature so it should not be too concentrate]. Step II: 20 ml distilled acetonitrile was taken with metallic Cu pieces, 1 spatula of blue crystals Cu(ClO4)2 was added and the solution was re ...
... the volume. Keeping to overnight, the crystals of Cu(ClO4)2 were formed. [Precaution- Cu(ClO4)2 is explosive in nature so it should not be too concentrate]. Step II: 20 ml distilled acetonitrile was taken with metallic Cu pieces, 1 spatula of blue crystals Cu(ClO4)2 was added and the solution was re ...
Answers pg 233 #4,5
... Answers pg 229 #1,2 1 a) Why is the following equation not balanced? N2 + H2 → NH3 Because there are 2 nitrogen atoms on the left side (reactants) and only one nitrogen atom on the right side (products). Also there are 2 hydrogen atoms on the left side (reactants) and 3 hydrogen atoms on the right s ...
... Answers pg 229 #1,2 1 a) Why is the following equation not balanced? N2 + H2 → NH3 Because there are 2 nitrogen atoms on the left side (reactants) and only one nitrogen atom on the right side (products). Also there are 2 hydrogen atoms on the left side (reactants) and 3 hydrogen atoms on the right s ...
ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS 1. How are minerals and rocks related? 2
... four common characteristics. •Formed through natural processes •NONLIVING: Not alive and never was EXAMPLE: diamonds vs. coal •SOLIDS: Objects with a definite size and shape •Elements or compounds with a unique chemical composition or CRYSTAL (a solid in which the atoms are arranged in a repeating p ...
... four common characteristics. •Formed through natural processes •NONLIVING: Not alive and never was EXAMPLE: diamonds vs. coal •SOLIDS: Objects with a definite size and shape •Elements or compounds with a unique chemical composition or CRYSTAL (a solid in which the atoms are arranged in a repeating p ...
Differentiation of Igneous Rocks: Crystal Fractionation and Layered
... intrusion, Greenland), a chain of volcanoes (the Cascades) ...
... intrusion, Greenland), a chain of volcanoes (the Cascades) ...
the music of molecules: novel approaches for stem education
... concepts as complex as molecular order/disorder, and crystal symmetry. Being the “universal language of mankind” (H.W. Longfellow), music has the potential to provide an effective support to science communication. Historically, music and mathematics have always been strongly related, from Pythagoras ...
... concepts as complex as molecular order/disorder, and crystal symmetry. Being the “universal language of mankind” (H.W. Longfellow), music has the potential to provide an effective support to science communication. Historically, music and mathematics have always been strongly related, from Pythagoras ...
SPATIALLY RESOLVED SECOND HARMONIC GENERATION AND
... For testing the described methods a Li-outdiffused tayer was prepared by annealing a LiNb03 crystal in an oxygen atmosphere at llOO"C for 24 hours. Li outdiffusion causes an increase of the extraordinary refractive index in the surface tayer of the crystal. This can be visuaiized by Macb-Zehnder int ...
... For testing the described methods a Li-outdiffused tayer was prepared by annealing a LiNb03 crystal in an oxygen atmosphere at llOO"C for 24 hours. Li outdiffusion causes an increase of the extraordinary refractive index in the surface tayer of the crystal. This can be visuaiized by Macb-Zehnder int ...
Chemistry Vocab for Quiz 12/21 or 12/22 Atom – The smallest
... Physical change – A change that alters the form or appearance of a material but does not make the material into a different substance. Chemical change – A change in matter that produces a new substance. Solution – A well mixed mixture. Solubility – A measure of how well a solute can be dissolved at ...
... Physical change – A change that alters the form or appearance of a material but does not make the material into a different substance. Chemical change – A change in matter that produces a new substance. Solution – A well mixed mixture. Solubility – A measure of how well a solute can be dissolved at ...
F Santina Russo/Expose
... → in the morning the industry crystallographers browse though the new sets of compound structures → just-in-time production → Data collection service provides a time gain → Acceleration of the structure-based drug discovery cycle ...
... → in the morning the industry crystallographers browse though the new sets of compound structures → just-in-time production → Data collection service provides a time gain → Acceleration of the structure-based drug discovery cycle ...
CHAPTER 2: MATTER
... physical properties depend on the quantity of the sample. Such as: mass, length, volume Intensive physical properties do not vary with the quantity of the sample. Such as: density, color, boiling point ...
... physical properties depend on the quantity of the sample. Such as: mass, length, volume Intensive physical properties do not vary with the quantity of the sample. Such as: density, color, boiling point ...
Yamanashi Prefecture
... In 2005, the company relocated its head office to Hokuto City, thus increasing its production capacity greatly. With the growth of optical communication demand, the high-performance, high-quality single crystals are getting important key materials. Although the market is still in its early stage, th ...
... In 2005, the company relocated its head office to Hokuto City, thus increasing its production capacity greatly. With the growth of optical communication demand, the high-performance, high-quality single crystals are getting important key materials. Although the market is still in its early stage, th ...
Rocks_and_the_Rock_Cycle_
... Contains the same elements/compounds of earth’s crust Therefore silica & oxygen most abundant Categorized by the amount of silica & oxygen content ...
... Contains the same elements/compounds of earth’s crust Therefore silica & oxygen most abundant Categorized by the amount of silica & oxygen content ...
Organization Brochure - Contract
... substances and excipients is the measurement of intrinsic dissolution rates. Its determination can be in some cases important since bioavailability of an API is influenced by the dissolution rate. Furthermore, intrinsic dissolution tests are a way to prove chemical purity, batch-to-batch consistency ...
... substances and excipients is the measurement of intrinsic dissolution rates. Its determination can be in some cases important since bioavailability of an API is influenced by the dissolution rate. Furthermore, intrinsic dissolution tests are a way to prove chemical purity, batch-to-batch consistency ...
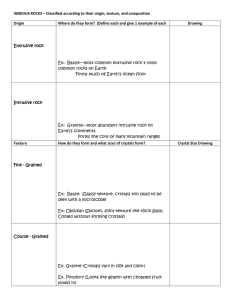
IGNEOUS ROCKS – Classified according to their origin, texture, and
... Ex: Granite—most abundant intrusive rock on Earth’s continents Forms the core of many mountain ranges Texture ...
... Ex: Granite—most abundant intrusive rock on Earth’s continents Forms the core of many mountain ranges Texture ...
L-Val and Cu(II)-L-Ile - Scientific Research Publishing
... cis- and trans-isomers (red and green lines, respectively), the measured blue line is almost agreed with cis-isomer. This means cis-isomer was mainly precipitated. Small peaks at around 7 is appeared which has the same peak of green (trans) line. This means small amount of trans-isomer was included ...
... cis- and trans-isomers (red and green lines, respectively), the measured blue line is almost agreed with cis-isomer. This means cis-isomer was mainly precipitated. Small peaks at around 7 is appeared which has the same peak of green (trans) line. This means small amount of trans-isomer was included ...
Rocks_and_the_Rock_Cycle_mod
... Contains the same elements/compounds of earth’s crust Therefore silica & oxygen most abundant Categorized by the amount of silica & oxygen content ...
... Contains the same elements/compounds of earth’s crust Therefore silica & oxygen most abundant Categorized by the amount of silica & oxygen content ...
1641
... technique, in which mass transfer of a solute from the liquid solution to a pure solid crystalline phase occurs. It is beneficial over other separation techniques, which can help in the formulation of drug chemicals into capsules; the dissolution of crystals can be well characterized and thus allows ...
... technique, in which mass transfer of a solute from the liquid solution to a pure solid crystalline phase occurs. It is beneficial over other separation techniques, which can help in the formulation of drug chemicals into capsules; the dissolution of crystals can be well characterized and thus allows ...
ADVANCED TEM TECHNIQUES FOR ASSESSING ... METEORITIC MAGNETITE CRYSTALS. , P. A. Midgley
... Figure 1. a) STEM HAADF image of magnetite chains in a coccus. b) Tomographic reconstruction of the crystal arrowed in a) obtained from a tilt series of 57 STEM HAADF images in a Philips CM300 field emission gun combined TEM/ STEM. The tableau shows the three-dimensional morphology of the crystal fr ...
... Figure 1. a) STEM HAADF image of magnetite chains in a coccus. b) Tomographic reconstruction of the crystal arrowed in a) obtained from a tilt series of 57 STEM HAADF images in a Philips CM300 field emission gun combined TEM/ STEM. The tableau shows the three-dimensional morphology of the crystal fr ...
silicates-2 - Fred Haynes
... Framework silicates - QUARTZ Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in the erath’s continental crust, after feldspar. Its crystal structure is a continuous framework of SiO4 (silicon tetratehdra) with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of SiO2. T ...
... Framework silicates - QUARTZ Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in the erath’s continental crust, after feldspar. Its crystal structure is a continuous framework of SiO4 (silicon tetratehdra) with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of SiO2. T ...
Here - Liquid Crystals and Photonics Group
... Liquid crystals are widely used in display devices but their electro-optical properties can also be used in many other applications. In smart phones the autofocus is based on a small lens that can move with respect to the camera, and it would be more reliable to use an electronic component without m ...
... Liquid crystals are widely used in display devices but their electro-optical properties can also be used in many other applications. In smart phones the autofocus is based on a small lens that can move with respect to the camera, and it would be more reliable to use an electronic component without m ...
Section-B
... d. Anionic polymerization 16. A water soluble polymer displays a Lower Critical Solution Temperature at 37°C. What happens when the polymer solution is heated to 40°C? a. The polymer solution is more homogeneous at the higher temperature b. The polymer forms large single crystals c. Some polymer pre ...
... d. Anionic polymerization 16. A water soluble polymer displays a Lower Critical Solution Temperature at 37°C. What happens when the polymer solution is heated to 40°C? a. The polymer solution is more homogeneous at the higher temperature b. The polymer forms large single crystals c. Some polymer pre ...
Part 2 1. In a crystalline solid, which of the following diffusion paths
... d. Anionic polymerization 16. A water soluble polymer displays a Lower Critical Solution Temperature at 37°C. What happens when the polymer solution is heated to 40°C? a. The polymer solution is more homogeneous at the higher temperature b. The polymer forms large single crystals c. Some polymer pre ...
... d. Anionic polymerization 16. A water soluble polymer displays a Lower Critical Solution Temperature at 37°C. What happens when the polymer solution is heated to 40°C? a. The polymer solution is more homogeneous at the higher temperature b. The polymer forms large single crystals c. Some polymer pre ...
Solid State - The Gurukul Institute
... 6. Name the crystal defect which lowers the density of an ionic crystal. 7. What is the effect of Schottky and Frenkel defects on the density of crystalline solids? 8. Give reasons for the following: Copper is conducting as such while copper sulphate is conducting only in molten state or in aqueous ...
... 6. Name the crystal defect which lowers the density of an ionic crystal. 7. What is the effect of Schottky and Frenkel defects on the density of crystalline solids? 8. Give reasons for the following: Copper is conducting as such while copper sulphate is conducting only in molten state or in aqueous ...
Manual JBS Magic Triangle
... Small molecules such as I3C may also be added to the crystallization drop to allow for incorporation in the crystal lattice during crystallization [1]. For cocrystallization, centrifugation of the I3C solution is recommended. When setting up crystallization drops by mixing a small volume of the rese ...
... Small molecules such as I3C may also be added to the crystallization drop to allow for incorporation in the crystal lattice during crystallization [1]. For cocrystallization, centrifugation of the I3C solution is recommended. When setting up crystallization drops by mixing a small volume of the rese ...
Crystallization

Crystallization is the (natural or artificial) process of formation of solid crystals precipitating from a solution, melt or more rarely deposited directly from a gas. Crystallization is also a chemical solid–liquid separation technique, in which mass transfer of a solute from the liquid solution to a pure solid crystalline phase occurs. In chemical engineering crystallization occurs in a crystallizer. Crystallization is therefore an aspect of precipitation, obtained through a variation of the solubility conditions of the solute in the solvent, as compared to precipitation due to chemical reaction.