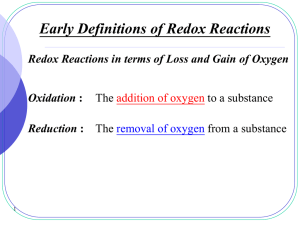
Redox reactions - SALEM-Immanuel Lutheran College
... E.g. H Cl , since Cl is more electronegative, the presumed electrical charges and thus O.N. of Cl and H are 1 and 1 respectively. ...
... E.g. H Cl , since Cl is more electronegative, the presumed electrical charges and thus O.N. of Cl and H are 1 and 1 respectively. ...
Sign of enthalpy changes Exothermic vs endothermic Acid
... If n = 0.3 mol, Hm = H/n = –2.4 x 10–3 cal / (0.3 x 10–6 mol) = –8 kcal/mol If n = 0.2 mol, Hm = H/n = –2.4 x 10–3 cal / (0.2 x 10–6 mol) = –12 kcal/mol If n = 0.1 mol, Hm = H/n = –2.4 x 10–3 cal / (0.1 x 10–6 mol) = –24 kcal/mol ...
... If n = 0.3 mol, Hm = H/n = –2.4 x 10–3 cal / (0.3 x 10–6 mol) = –8 kcal/mol If n = 0.2 mol, Hm = H/n = –2.4 x 10–3 cal / (0.2 x 10–6 mol) = –12 kcal/mol If n = 0.1 mol, Hm = H/n = –2.4 x 10–3 cal / (0.1 x 10–6 mol) = –24 kcal/mol ...
9.2 Oxidation Numbers
... phosphorus, called the furnace process, is summarized in the first equation below. The other equations show how phosphorus can be converted into ammonium phosphate. 2Ca3(PO4)2 + 6SiO2 + 10C → P4 + 10CO + 6CaSiO3 P4 + 5O2 + 6H2O → 4H3PO4 H3PO4 + NH3 → (NH4)3PO4 Are these reactions oxidation‑reduction ...
... phosphorus, called the furnace process, is summarized in the first equation below. The other equations show how phosphorus can be converted into ammonium phosphate. 2Ca3(PO4)2 + 6SiO2 + 10C → P4 + 10CO + 6CaSiO3 P4 + 5O2 + 6H2O → 4H3PO4 H3PO4 + NH3 → (NH4)3PO4 Are these reactions oxidation‑reduction ...
QualGroupB - Back To Home Page
... Some of Group B cations and reagents used are toxic. The HCl, H2SO4, NH3 and NaOH are irritants. Avoid contact and wash immediately if any is spilled or splashed on you. Wear eye protection at all times. As you perform the experiment, collect all waste solutions in a waste beaker. This mixture shoul ...
... Some of Group B cations and reagents used are toxic. The HCl, H2SO4, NH3 and NaOH are irritants. Avoid contact and wash immediately if any is spilled or splashed on you. Wear eye protection at all times. As you perform the experiment, collect all waste solutions in a waste beaker. This mixture shoul ...
Analytical Chemistry
... Calculate the molar concentration of Ag+ in a solution having a pAg of 6.372 . pAg = - log[Ag+] = 6.372 log[Ag+] = -6.372 = - 7.oo + 0.628 [Ag+] = antilog ( -7 ) * antilog ( 0.628) = 10-7*4.246 ...
... Calculate the molar concentration of Ag+ in a solution having a pAg of 6.372 . pAg = - log[Ag+] = 6.372 log[Ag+] = -6.372 = - 7.oo + 0.628 [Ag+] = antilog ( -7 ) * antilog ( 0.628) = 10-7*4.246 ...
Chem 171-2-3: Final Exam Review Multiple Choice Problems 1
... Consider a Galvanic cell represented by the following line notation: Zn(s) | Zn2+ (aq) || Cu2+ (aq) | Cu (s). Which statement about this cell is not true? a. The mass of the zinc electrode will increase as the cell discharges. b. The copper electrode is the cathode. c. Electrons will flow through th ...
... Consider a Galvanic cell represented by the following line notation: Zn(s) | Zn2+ (aq) || Cu2+ (aq) | Cu (s). Which statement about this cell is not true? a. The mass of the zinc electrode will increase as the cell discharges. b. The copper electrode is the cathode. c. Electrons will flow through th ...
Thermochemistry Chem 2/H
... There are two kinds of coffeecup calorimetry problems. 2nd kind: Two volumes of a solution are given. What to do: Add them and plug into m (the density of most solutions = 1g/mL, so the mL = the grams) DT, Final temperature minus Initial temperature. Solve for q and change joules to kJ. Pick one of ...
... There are two kinds of coffeecup calorimetry problems. 2nd kind: Two volumes of a solution are given. What to do: Add them and plug into m (the density of most solutions = 1g/mL, so the mL = the grams) DT, Final temperature minus Initial temperature. Solve for q and change joules to kJ. Pick one of ...
Document
... Plan: We will use Hess’s law. In doing so, we first note the numbers of moles of substances among the reactants and products in the target equation, (3). We then manipulate equations (1) and (2) to give the same number of moles of these substances, so that when the resulting equations are added, we ...
... Plan: We will use Hess’s law. In doing so, we first note the numbers of moles of substances among the reactants and products in the target equation, (3). We then manipulate equations (1) and (2) to give the same number of moles of these substances, so that when the resulting equations are added, we ...
solliqsol - chemmybear.com
... (a) Distinction or correctly implied distinction between the structures of graphite and diamond. Freedom of movement of electrons in graphite resulting from the structure. (b) The rock salt forms a concentrated solution with very little water from the ice. The solution now has a freezing point lower ...
... (a) Distinction or correctly implied distinction between the structures of graphite and diamond. Freedom of movement of electrons in graphite resulting from the structure. (b) The rock salt forms a concentrated solution with very little water from the ice. The solution now has a freezing point lower ...
Chemistry 30 - SharpSchool
... 30-D1.3k predict, qualitatively, using Le Chatelier’s principle, shifts in equilibrium caused by changes in temperature, pressure, volume, concentration or the addition of a catalyst and describe how these changes affect the equilibrium constant ...
... 30-D1.3k predict, qualitatively, using Le Chatelier’s principle, shifts in equilibrium caused by changes in temperature, pressure, volume, concentration or the addition of a catalyst and describe how these changes affect the equilibrium constant ...
Chemistry Transition Information
... a) How many moles of water are needed to react with 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? b) How many moles of glucose can you make from 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? c) How many moles of oxygen can you make from 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? ...
... a) How many moles of water are needed to react with 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? b) How many moles of glucose can you make from 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? c) How many moles of oxygen can you make from 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? ...
chem - CBSE Guess
... two or more compounds combine to produce only one product. Decomposition reactions: In these reactions, a compound breaks down or decomposes to form two or more substances. These reactions are exactly opposite to combination reactions. We know that there is only one product in combination reactions. ...
... two or more compounds combine to produce only one product. Decomposition reactions: In these reactions, a compound breaks down or decomposes to form two or more substances. These reactions are exactly opposite to combination reactions. We know that there is only one product in combination reactions. ...
Final Exam Review Notes
... Some numbers are very large or very small difficult to express. For example, Avogadro’s number = 602,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 an electron’s mass = 0.000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 91 kg Also, it's not clear how many sig figs there are in some measurements. For example, Express 100.0 g to 3 ...
... Some numbers are very large or very small difficult to express. For example, Avogadro’s number = 602,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 an electron’s mass = 0.000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 91 kg Also, it's not clear how many sig figs there are in some measurements. For example, Express 100.0 g to 3 ...
Chemistry
... law of conservation of mass. These equations make it possible to predict the masses of reactants and products involved in chemical reactions. In this section, the idea of atoms and chemical bonding being the most important fundamental concept in chemistry is introduced. The knowledge of atomic struc ...
... law of conservation of mass. These equations make it possible to predict the masses of reactants and products involved in chemical reactions. In this section, the idea of atoms and chemical bonding being the most important fundamental concept in chemistry is introduced. The knowledge of atomic struc ...
Chapter 5
... What is not apparent in the preceding equation is the role of energy in a reaction. For many reactions, energy, often in the form of heat, is absorbed—that is, it acts somewhat like a reactant. You might write an equation for those reactions that looks like this: energy + reactants S products In oth ...
... What is not apparent in the preceding equation is the role of energy in a reaction. For many reactions, energy, often in the form of heat, is absorbed—that is, it acts somewhat like a reactant. You might write an equation for those reactions that looks like this: energy + reactants S products In oth ...
Chemistry 2008 Multiple Choice
... [OH-] = ½(0.002 M) = 0.001 M pOH = -log(1 x 10-3) = 3 pH = 14 – 3 = 11 At the same temperature both gases have the same kinetic energy (K = 3/2RT). Amino acids: NH2–C(R)H–COOH (I hope you remember your biology). CO32- + 2 H+ CO2(g) + H2O Zn + 2 H+ H2(g) + Zn2+ Ba2+ + SO42- BaSO4(s) ...
... [OH-] = ½(0.002 M) = 0.001 M pOH = -log(1 x 10-3) = 3 pH = 14 – 3 = 11 At the same temperature both gases have the same kinetic energy (K = 3/2RT). Amino acids: NH2–C(R)H–COOH (I hope you remember your biology). CO32- + 2 H+ CO2(g) + H2O Zn + 2 H+ H2(g) + Zn2+ Ba2+ + SO42- BaSO4(s) ...
Stoichiometry
... To be able to determine amounts of products and reactants…moles and grams….for ANY chemical reaction. 2 CH3OH (l) + 3 O2 (g) --> 2 CO2 (g) + 4 H2O (l) ...
... To be able to determine amounts of products and reactants…moles and grams….for ANY chemical reaction. 2 CH3OH (l) + 3 O2 (g) --> 2 CO2 (g) + 4 H2O (l) ...
sample problem - KFUPM Resources
... How does the value of ΔG change when the pressures of the H2, Cl2 and HCl gases are changed to 0.25 atm, 0.45 atm and 0.30 atm, respectively, at 25C? (ΔGf for HCl(g) is ‒ 95.27 kJ/mol) ...
... How does the value of ΔG change when the pressures of the H2, Cl2 and HCl gases are changed to 0.25 atm, 0.45 atm and 0.30 atm, respectively, at 25C? (ΔGf for HCl(g) is ‒ 95.27 kJ/mol) ...
Mock Examination (2016/2017) CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 SECTION B
... Given the following materials and apparatus, briefly describe how a 0.10 M hydrochloric acid can be prepared. (You are NOT required to use all apparatus.) 200 cm3 of 0.4 M hydrochloric acid, 100.0 cm3 volumetric flask, 250.0 cm3 volumetric flask, 25.0 cm3 pipette, 50.0 cm3 burette, distilled water T ...
... Given the following materials and apparatus, briefly describe how a 0.10 M hydrochloric acid can be prepared. (You are NOT required to use all apparatus.) 200 cm3 of 0.4 M hydrochloric acid, 100.0 cm3 volumetric flask, 250.0 cm3 volumetric flask, 25.0 cm3 pipette, 50.0 cm3 burette, distilled water T ...
ΔH - GCC
... g of water originally at 25.1°C. The final temperature of both pellet and the water is 31.3°C. Calculate the heat capacity C (in J/°C) of the pellet. Strategy Water constitutes the surroundings; the pellet is the system. Use qsurr = msΔT to determine the heat absorbed by the water; then use q = CΔT ...
... g of water originally at 25.1°C. The final temperature of both pellet and the water is 31.3°C. Calculate the heat capacity C (in J/°C) of the pellet. Strategy Water constitutes the surroundings; the pellet is the system. Use qsurr = msΔT to determine the heat absorbed by the water; then use q = CΔT ...
Electrolysis of water
Electrolysis of water is the decomposition of water (H2O) into oxygen (O2) and hydrogen gas (H2) due to an electric current being passed through the water.This technique can be used to make hydrogen fuel (hydrogen gas) and breathable oxygen; though currently most industrial methods make hydrogen fuel from natural gas instead.