Document
... Reversible Reactions (KC or P = > 10-10 and < 1010); Quasi Non-Reversible Reactions (KC or P = < 10-10 and > 1010); The large value of K does not imply that the reaction proceeds at a given temperature. Why? S. Holger Eichhorn; University of Windsor; General Chemistry II 59-141; © 2005 ...
... Reversible Reactions (KC or P = > 10-10 and < 1010); Quasi Non-Reversible Reactions (KC or P = < 10-10 and > 1010); The large value of K does not imply that the reaction proceeds at a given temperature. Why? S. Holger Eichhorn; University of Windsor; General Chemistry II 59-141; © 2005 ...
Chemical Kinetics
... Study at a point soon after they are mixed before product builds up. Reaction rate will depend only on concentration of the reactants. ...
... Study at a point soon after they are mixed before product builds up. Reaction rate will depend only on concentration of the reactants. ...
Chapter 4: Reaction Stoichiometry Reaction Stoichiometry
... CaCO3(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + H2CO3(aq) → H2O(l) + CO2(g) CaCO3(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) K2CO3(s) + 2 HBr(aq) → 2 KBr(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) ...
... CaCO3(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + H2CO3(aq) → H2O(l) + CO2(g) CaCO3(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) K2CO3(s) + 2 HBr(aq) → 2 KBr(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) ...
IChO 2012
... whereas aluminum fluoride, AlF 3, has a very high melting point (m.p. = 1291 °C). Is the structure and bonding in aluminum fluoride and aluminum bromide likely to be similar to aluminum chloride? B. An Organoaluminum Halide If [(C2H5)2AlCl]2 is treated with NaF, the air-sensitive fluorine analog, [( ...
... whereas aluminum fluoride, AlF 3, has a very high melting point (m.p. = 1291 °C). Is the structure and bonding in aluminum fluoride and aluminum bromide likely to be similar to aluminum chloride? B. An Organoaluminum Halide If [(C2H5)2AlCl]2 is treated with NaF, the air-sensitive fluorine analog, [( ...
Chemistry 120
... Ionic Solutions In an ionic solution, there are therefore charged particles – the ions – and as the compound is electrically neutral, then the solution is neutral. When a voltage is applied to the solution, the ions can move and a current flows through the solution. ...
... Ionic Solutions In an ionic solution, there are therefore charged particles – the ions – and as the compound is electrically neutral, then the solution is neutral. When a voltage is applied to the solution, the ions can move and a current flows through the solution. ...
KINETICS questions
... (a) Addition of hydrogen gas at constant temperature and volume (b) Increase in volume of the reaction vessel at constant temperature (c) Addition of catalyst. In your explanation, include a diagram of potential energy versus reaction coordinate. (d) Increase in temperature. In your explanation, inc ...
... (a) Addition of hydrogen gas at constant temperature and volume (b) Increase in volume of the reaction vessel at constant temperature (c) Addition of catalyst. In your explanation, include a diagram of potential energy versus reaction coordinate. (d) Increase in temperature. In your explanation, inc ...
Unit 5: Chemical Equations and Reactions
... To Predict Products and Balance Chemical Equations: 1. Write the correct chemical formulas for all products and reactants with proper subscripts. The presence of metals or ionic compounds indicates that we will need to use ions and charges to form any products. 2. For hydrocarbon combustion, balance ...
... To Predict Products and Balance Chemical Equations: 1. Write the correct chemical formulas for all products and reactants with proper subscripts. The presence of metals or ionic compounds indicates that we will need to use ions and charges to form any products. 2. For hydrocarbon combustion, balance ...
AL Chemistry Past paper essay questions
... Write an essay on amino acids, polypeptides and proteins. Your essay should include the properties of amino acids in aqueous solutions and a method of separation for a mixture of amino acids, as well as the constitution of polypeptides and proteins and their hydrolysis. ...
... Write an essay on amino acids, polypeptides and proteins. Your essay should include the properties of amino acids in aqueous solutions and a method of separation for a mixture of amino acids, as well as the constitution of polypeptides and proteins and their hydrolysis. ...
Undergraduate Chemistry Major Handbook - JHU Chemistry
... 030.404: Electrochemical Systems for Energy Conversion and Storage. This course will be focused on the fundamentals and applications of electrochemical methods in catalysis, charge transport, and energy conversion and storage. Topics that will be covered are basic electrochemical techniques, homogen ...
... 030.404: Electrochemical Systems for Energy Conversion and Storage. This course will be focused on the fundamentals and applications of electrochemical methods in catalysis, charge transport, and energy conversion and storage. Topics that will be covered are basic electrochemical techniques, homogen ...
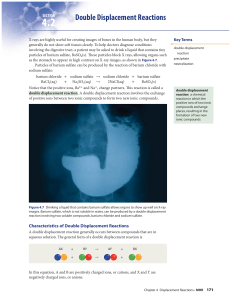
Section 1 Describing Chemical Reactions Chapter 8
... • One of the compounds formed is usually a precipitate, an insoluble gas that bubbles out of the solution, or a molecular compound, usually water. • The other compound is often soluble and remains dissolved in solution. ...
... • One of the compounds formed is usually a precipitate, an insoluble gas that bubbles out of the solution, or a molecular compound, usually water. • The other compound is often soluble and remains dissolved in solution. ...
Electrochemistry Oxidation – Reduction and Oxidation Numbers
... 5. Oxygen in a compound or ion usually has an oxidation state of –2. (Peroxides are the exception, in which case the oxidation number is –1.) 6. Hydrogen in a compound or ion usually has an oxidation state of +1. (Hydrides are the exception, in which case the oxidation number is –1.) 7. For covalent ...
... 5. Oxygen in a compound or ion usually has an oxidation state of –2. (Peroxides are the exception, in which case the oxidation number is –1.) 6. Hydrogen in a compound or ion usually has an oxidation state of +1. (Hydrides are the exception, in which case the oxidation number is –1.) 7. For covalent ...
Bk2P06EE
... The positive value indicates that the reaction is feasible but it gives no information about the rate. Nevertheless, the activation energy for the reaction in (a)(ii) is likely to be small since it involves simple electron transfer without involving breaking of covalent bonds. Therefore, the reactio ...
... The positive value indicates that the reaction is feasible but it gives no information about the rate. Nevertheless, the activation energy for the reaction in (a)(ii) is likely to be small since it involves simple electron transfer without involving breaking of covalent bonds. Therefore, the reactio ...
Chemical Equations - Salem Community Schools
... Chemical Equations It may also be important to know the physical state of each reactant and product. How can we indicate the bubbles we see during this reaction are CO2? Symbols in the parentheses are put after formulas to indicate the state of the substance. Solids, liquids, gases, and water (aqueo ...
... Chemical Equations It may also be important to know the physical state of each reactant and product. How can we indicate the bubbles we see during this reaction are CO2? Symbols in the parentheses are put after formulas to indicate the state of the substance. Solids, liquids, gases, and water (aqueo ...
CIS Exam Questions
... Which of the following would have been different for the two reactions? A The pH of the final solution B The volume of gas produced C The mass of water formed D The mass of copper(II) carbonate dissolved 29. Which of the following is the best description of a feedstock? A A consumer product such as ...
... Which of the following would have been different for the two reactions? A The pH of the final solution B The volume of gas produced C The mass of water formed D The mass of copper(II) carbonate dissolved 29. Which of the following is the best description of a feedstock? A A consumer product such as ...
Review on N acylation reaction
... organic synthesis, the methods of amide synthesis have been significantly advanced. But the two step acylation, activation of carboxylic acid and reaction with amines have been often used in non-peptide chemistry. Acid chlorides are generally recognized as key intermediate for acylation, for convers ...
... organic synthesis, the methods of amide synthesis have been significantly advanced. But the two step acylation, activation of carboxylic acid and reaction with amines have been often used in non-peptide chemistry. Acid chlorides are generally recognized as key intermediate for acylation, for convers ...
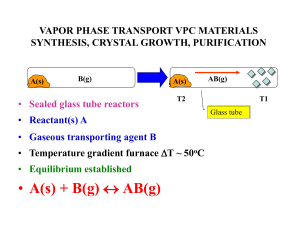
vapor phase transport vpc materials synthesis, crystal growth
... The reactor consists of three inner quartz tubes, which supply the reactive gases, InCl3, GaCl3 (N2 carrier) and NH3, and an outer quartz tube, which supplies inert gas (N2) and houses the reaction in a horizontal tube furnace. Two independently controlled heating tapes were used to tune the vapour ...
... The reactor consists of three inner quartz tubes, which supply the reactive gases, InCl3, GaCl3 (N2 carrier) and NH3, and an outer quartz tube, which supplies inert gas (N2) and houses the reaction in a horizontal tube furnace. Two independently controlled heating tapes were used to tune the vapour ...
4.2- Reaction Stoichiometry Reaction Stoichiometry
... ions and their solutions are good conductor of electricity ionic compounds and strong acids ...
... ions and their solutions are good conductor of electricity ionic compounds and strong acids ...
Stoichiometry File
... requires detailed and quantitative understanding of the reactions involved. The economics of any chemical process obviously depend on the amounts of each reactant needed to produce a given amount of product. For processes carried out on an industrial scale, even very small changes in efficiency can ...
... requires detailed and quantitative understanding of the reactions involved. The economics of any chemical process obviously depend on the amounts of each reactant needed to produce a given amount of product. For processes carried out on an industrial scale, even very small changes in efficiency can ...