General Chemistry
... The mole is defined so that one mole of a substance has a mass equal to its AW or MW in grams Basically, you are replacing amu with grams, e.g. The mass of a P atom is 31 amu. The molar mass of P is 31 grams. The mass of a Ca atom is 40 amu The molar mass of Ca is 40 grams ...
... The mole is defined so that one mole of a substance has a mass equal to its AW or MW in grams Basically, you are replacing amu with grams, e.g. The mass of a P atom is 31 amu. The molar mass of P is 31 grams. The mass of a Ca atom is 40 amu The molar mass of Ca is 40 grams ...
General Chemistry
... The mole is defined so that one mole of a substance has a mass equal to its AW or MW in grams Basically, you are replacing amu with grams, e.g. The mass of a P atom is 31 amu. The molar mass of P is 31 grams. The mass of a Ca atom is 40 amu The molar mass of Ca is 40 grams ...
... The mole is defined so that one mole of a substance has a mass equal to its AW or MW in grams Basically, you are replacing amu with grams, e.g. The mass of a P atom is 31 amu. The molar mass of P is 31 grams. The mass of a Ca atom is 40 amu The molar mass of Ca is 40 grams ...
Practice Test 11 - U of L Class Index
... There are multiple methods used for the industrial production of sulfur. In the southern United States, the Frasch process is the main method used. In western Canada, the Claus process is the main method used. Describe one of these methods, including any relevant balanced chemical equations. Make su ...
... There are multiple methods used for the industrial production of sulfur. In the southern United States, the Frasch process is the main method used. In western Canada, the Claus process is the main method used. Describe one of these methods, including any relevant balanced chemical equations. Make su ...
Chapter 13 Notes
... A chemical property of wood or paper is that it undergoes the chemical reaction of burning. A chemical property of water is that it does not. Iron rusts but gold does not. Physical changes in a substance do not alter its chemical composition, just its appearance. Water turns to ice. A pencil may be ...
... A chemical property of wood or paper is that it undergoes the chemical reaction of burning. A chemical property of water is that it does not. Iron rusts but gold does not. Physical changes in a substance do not alter its chemical composition, just its appearance. Water turns to ice. A pencil may be ...
+ H 2 O(g)
... First, the oxidation number of each atom have to be calculated and check if any of them changed. None of the oxidation numbers changes. CaO is a basic oxide as well as NH4+ is the protonated ammonia, then it can deliver H+ as an acid, then this reaction might be an acid base reaction. It occurs in h ...
... First, the oxidation number of each atom have to be calculated and check if any of them changed. None of the oxidation numbers changes. CaO is a basic oxide as well as NH4+ is the protonated ammonia, then it can deliver H+ as an acid, then this reaction might be an acid base reaction. It occurs in h ...
Chapter 3: Introduction to chemical formulas and reactivity
... much product you can get. The limiting reactant is entirely used up in the reaction. • Back to the sandwich example: if I have 6 slices of bread and 4 slices of cheese, which is the limiting reactant? • Note: it doesn’t matter if I start with the bread or the cheese, I’ll still be able to determine ...
... much product you can get. The limiting reactant is entirely used up in the reaction. • Back to the sandwich example: if I have 6 slices of bread and 4 slices of cheese, which is the limiting reactant? • Note: it doesn’t matter if I start with the bread or the cheese, I’ll still be able to determine ...
Honors Chemistry II Review 1. Express the following in scientific
... Which reactant is limiting if there are 80kg of water to be removed and 65kg of Li2O available? How many kg of the excess reactant remain? 20. After lithium hydroxide is produced aboard the space shuttle, it is used to remove exhaled carbon dioxide from the air supply according to the following equa ...
... Which reactant is limiting if there are 80kg of water to be removed and 65kg of Li2O available? How many kg of the excess reactant remain? 20. After lithium hydroxide is produced aboard the space shuttle, it is used to remove exhaled carbon dioxide from the air supply according to the following equa ...
Types of Reactions notes 02 Types of chemical reactions
... H2O(l) - the water is liquid H2O(s) - the water is solid (ice) H2O(g)- the water is a gas (steam) NaCl(aq) – means that the chemical is disolved in water. In this case it would be salt dissolved in water. ...
... H2O(l) - the water is liquid H2O(s) - the water is solid (ice) H2O(g)- the water is a gas (steam) NaCl(aq) – means that the chemical is disolved in water. In this case it would be salt dissolved in water. ...
chemical reaction
... (aq) – aqueous (dissolved in water, exists as ions) ↓ - a precipitate has formed ...
... (aq) – aqueous (dissolved in water, exists as ions) ↓ - a precipitate has formed ...
Arts and Sciences Program Chemistry Department Chemistry Placement Test
... 15. How many silicon atoms are there in 1.00 g of silicon? A ...
... 15. How many silicon atoms are there in 1.00 g of silicon? A ...
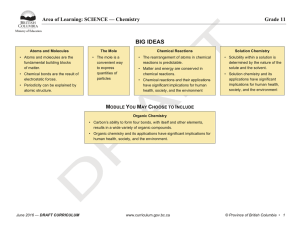
BIG IDEAS - BC Curriculum - Province of British Columbia
... Planning and conducting • Collaboratively and individually plan, select, and use appropriate investigation methods, including field work and lab experiments, to collect reliable data (qualitative and quantitative) • Assess risks and address ethical, cultural, and/or environmental issues associated w ...
... Planning and conducting • Collaboratively and individually plan, select, and use appropriate investigation methods, including field work and lab experiments, to collect reliable data (qualitative and quantitative) • Assess risks and address ethical, cultural, and/or environmental issues associated w ...
Chemical Reaction
... Chemical Reaction Beginning & ending substances have different properties Atoms are rearranged, chemical bonds are broken and new bonds are formed All reactions involve energy changes ...
... Chemical Reaction Beginning & ending substances have different properties Atoms are rearranged, chemical bonds are broken and new bonds are formed All reactions involve energy changes ...
Chemical Reactions are…
... appear to have less mass as ashes; where is the rest? Gases and smoke. ...
... appear to have less mass as ashes; where is the rest? Gases and smoke. ...
Notes for Matter Packet- Balancing equations (PDF
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
Chemistry 20H
... Note that the only way to increase the number of iodine atoms on the reactant side is to add another NaI molecule, thus increasing both the number of sodium and iodine atoms. This causes the number of sodium atoms to become unbalanced, so the number of sodium atoms on the product side must be increa ...
... Note that the only way to increase the number of iodine atoms on the reactant side is to add another NaI molecule, thus increasing both the number of sodium and iodine atoms. This causes the number of sodium atoms to become unbalanced, so the number of sodium atoms on the product side must be increa ...
Please use your NUMERICAL RESPONSE SHEET to answer the
... While examining a section of the periodic table, Zarley noticed that Hg and Br were written in blue print while the other elements were written in black or red print. How did he explain this? a. Hg and Br are the heaviest element. b. Hg and Br are the most reactive element. c. Hg and Br are the most ...
... While examining a section of the periodic table, Zarley noticed that Hg and Br were written in blue print while the other elements were written in black or red print. How did he explain this? a. Hg and Br are the heaviest element. b. Hg and Br are the most reactive element. c. Hg and Br are the most ...
Chapter 3
... • In the previous example, say that only 32.0 g of CH4 were produced due to side reactions and waste. • We define the percent or reaction yield as [actual yield/theoretical yield]x100 • This gives % yield = [32.0/40.0] x 100 = ...
... • In the previous example, say that only 32.0 g of CH4 were produced due to side reactions and waste. • We define the percent or reaction yield as [actual yield/theoretical yield]x100 • This gives % yield = [32.0/40.0] x 100 = ...
Chemical Reactions and Stoichiometry
... other reactant is used up in the creation of the product. You must compare the given quantity to the required quantity of each reactant. b. COOKIES: The cookie recipe says that I need 1 cup of sugar and 2 cups of flour to make 1 batch of cookies. What the ratio of sugar to flour? If I had 5 cups of ...
... other reactant is used up in the creation of the product. You must compare the given quantity to the required quantity of each reactant. b. COOKIES: The cookie recipe says that I need 1 cup of sugar and 2 cups of flour to make 1 batch of cookies. What the ratio of sugar to flour? If I had 5 cups of ...