ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
... Conclusions about large-scale structure In a cell or microorganism, the processes that generate mass, energy, information transfer and cell-fate specification are seamlessly integrated through a complex network of cellular constituents and reactions. A systematic comparative mathematical analysis o ...
... Conclusions about large-scale structure In a cell or microorganism, the processes that generate mass, energy, information transfer and cell-fate specification are seamlessly integrated through a complex network of cellular constituents and reactions. A systematic comparative mathematical analysis o ...
Mitochondrial Fatty Acid ß-Oxidation in the Human Eye and
... Figure 1. Immunohistochemistry of the human retinal specimen stained with mitochondrial fatty acid -oxidation (A–D and H) and control antibodies (E–G and I) without counterstain. Sections A–G are from one and sections H and I from another adult eye specimen. (A) VLCAD antibodies label strongly the ...
... Figure 1. Immunohistochemistry of the human retinal specimen stained with mitochondrial fatty acid -oxidation (A–D and H) and control antibodies (E–G and I) without counterstain. Sections A–G are from one and sections H and I from another adult eye specimen. (A) VLCAD antibodies label strongly the ...
Unit D: Quantitative Relationships in Chemical Change
... and a precipitate forms. What amount of precipitate will form if the student has reacted 0.314 mol of silver nitrate? ...
... and a precipitate forms. What amount of precipitate will form if the student has reacted 0.314 mol of silver nitrate? ...
Chemistry (English) Grade 11 and 12
... – induced dipole “bonds” to form, so that more energy is needed to break the “bonds”. “More energy” means that the substance must reach a higher boiling point before the molecules can separate into the gas phase or in ordinary language, before the substance ‘boils’. Answer to Question 1 (a): Weak Va ...
... – induced dipole “bonds” to form, so that more energy is needed to break the “bonds”. “More energy” means that the substance must reach a higher boiling point before the molecules can separate into the gas phase or in ordinary language, before the substance ‘boils’. Answer to Question 1 (a): Weak Va ...
Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach
... particles called atoms. All atoms of a g given element have the same mass and other properties that distinguish them from atoms of other elements. Atoms combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form molecules of compounds. In a chemical reaction, atoms of one element cannot change into atoms of ano ...
... particles called atoms. All atoms of a g given element have the same mass and other properties that distinguish them from atoms of other elements. Atoms combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form molecules of compounds. In a chemical reaction, atoms of one element cannot change into atoms of ano ...
L22 - Supplementary Student Notes Package
... c) What mass of sulfur must have reacted in order to produce 75 g of the compound? ...
... c) What mass of sulfur must have reacted in order to produce 75 g of the compound? ...
Derivatization reagents
... ● Purified, dried and packaged under nitrogen in convenient 50mL Hypo-Vial Sample Storage Vials ● Supplied with elastomer septa, allowing immediate access to the sample without exposure to moisture and oxygen ● Use polar solvents (acetonitrile, dimethylformamide, dimethylsulfoxide, pyridine, tetrahy ...
... ● Purified, dried and packaged under nitrogen in convenient 50mL Hypo-Vial Sample Storage Vials ● Supplied with elastomer septa, allowing immediate access to the sample without exposure to moisture and oxygen ● Use polar solvents (acetonitrile, dimethylformamide, dimethylsulfoxide, pyridine, tetrahy ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical
... • If 3.84 moles of C2H2 are burned, how many moles of O2 are needed? • How many moles of C2H2 are needed to produce 8.95 mole of H2O? • If 2.47 moles of C2H2 are burned, how many moles of CO2 are formed? ...
... • If 3.84 moles of C2H2 are burned, how many moles of O2 are needed? • How many moles of C2H2 are needed to produce 8.95 mole of H2O? • If 2.47 moles of C2H2 are burned, how many moles of CO2 are formed? ...
Nuclear Chemistry
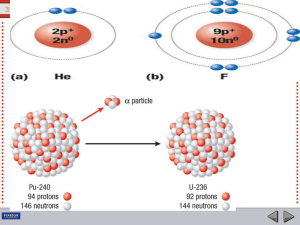
... In an α emission the parent element is displaced to a group two places to left and in β emission it will be displaced to a group one place to the right in the periodic table as illustrated in Fig.4.2. This is called Group Displacement Law. It was first stated by Fajans and Soddy (1913) and is often ...
... In an α emission the parent element is displaced to a group two places to left and in β emission it will be displaced to a group one place to the right in the periodic table as illustrated in Fig.4.2. This is called Group Displacement Law. It was first stated by Fajans and Soddy (1913) and is often ...
Document
... Comparison of T1 and T2 rapid motion (small molecule non-viscous liquids), T1 and T2 are equal ...
... Comparison of T1 and T2 rapid motion (small molecule non-viscous liquids), T1 and T2 are equal ...
Chem 11 Notes Booklet (pdf version)
... Remember that the unit for energy is the Joule (J). b) Physical State - Chemical reactions often depend on the physical state of the chemicals involved. This information can be included in an equation by using these symbols: (s) = solid (l) = liquid (g) = gas (a) = aqueous (dissolved in water) For e ...
... Remember that the unit for energy is the Joule (J). b) Physical State - Chemical reactions often depend on the physical state of the chemicals involved. This information can be included in an equation by using these symbols: (s) = solid (l) = liquid (g) = gas (a) = aqueous (dissolved in water) For e ...
Experimental and Computational Evidence of Metal‑O2 Activation
... on the initial concentration of O2 and whether the CoAGAO was pretreated with excess H2O2. Oxygen isotope fractionation was analyzed as previously described38−47,49 using a specially constructed apparatus.64 Samples were prepared by isolating O2 before and after treatment of O2 saturated solutions c ...
... on the initial concentration of O2 and whether the CoAGAO was pretreated with excess H2O2. Oxygen isotope fractionation was analyzed as previously described38−47,49 using a specially constructed apparatus.64 Samples were prepared by isolating O2 before and after treatment of O2 saturated solutions c ...
Solid-State and High-Resolution Liquid 119Sn NMR Spectroscopy
... downfield and upfield edges of the observed NMR spectrum in the solid state whereas δ22 represents the frequency that corresponds to a singularity in the powder pattern where the spectral amplitude tends to infinity. Physically, these δnn values describe the shape of an ellipsoid in three dimensions ...
... downfield and upfield edges of the observed NMR spectrum in the solid state whereas δ22 represents the frequency that corresponds to a singularity in the powder pattern where the spectral amplitude tends to infinity. Physically, these δnn values describe the shape of an ellipsoid in three dimensions ...
`Metabolic Pool` and the Use of 15N-Labelled
... Jeevanandam agrees that the concept of a single metabolic pool of nitrogen is an oversimplification. To what extent does this oversimplification limit our understanding? There are at least three different aspects of amino acid metabolism; each may require a different definition of the metabolic nitr ...
... Jeevanandam agrees that the concept of a single metabolic pool of nitrogen is an oversimplification. To what extent does this oversimplification limit our understanding? There are at least three different aspects of amino acid metabolism; each may require a different definition of the metabolic nitr ...
Sampling techniques and comparative extraction procedures for
... amounts of metabolites were recovered when the extraction was carried out by thawing-freezing in HClO4 or 0.1 M HCl, followed by a 8 min incubation at 50³C (not shown). Similar loss of alkalinestable metabolites was observed after extraction in 0.25 M KOH for 10 min at 80³C. In contrast, the recover ...
... amounts of metabolites were recovered when the extraction was carried out by thawing-freezing in HClO4 or 0.1 M HCl, followed by a 8 min incubation at 50³C (not shown). Similar loss of alkalinestable metabolites was observed after extraction in 0.25 M KOH for 10 min at 80³C. In contrast, the recover ...
Slide 1
... Chemical Shift a) Small local magnetic fields (Bloc) are generated by electrons as they circulate nuclei. 1) Current in a circular coil generates a magnetic field b) These local magnetic fields can either oppose or augment the external magnetic field 1) Typically oppose external magnetic field 2) Nu ...
... Chemical Shift a) Small local magnetic fields (Bloc) are generated by electrons as they circulate nuclei. 1) Current in a circular coil generates a magnetic field b) These local magnetic fields can either oppose or augment the external magnetic field 1) Typically oppose external magnetic field 2) Nu ...
1 mole
... Calculate the number of moles in a given mass of an element and the mass of a given number of moles of an element Calculate the number of moles of an element when given the number of atoms of the element Calculate the number of atoms of an element when given the number of moles of the element ...
... Calculate the number of moles in a given mass of an element and the mass of a given number of moles of an element Calculate the number of moles of an element when given the number of atoms of the element Calculate the number of atoms of an element when given the number of moles of the element ...
Stoichiometry Notes
... We use ratios to set up equations. For example, if we knew the number of moles of CH 4 that undergoes a chemical reaction and we needed to find out information regarding the water, we would use the following ratio: 1 mole CH4 -------------------------2 moles of H2O ...
... We use ratios to set up equations. For example, if we knew the number of moles of CH 4 that undergoes a chemical reaction and we needed to find out information regarding the water, we would use the following ratio: 1 mole CH4 -------------------------2 moles of H2O ...
5.7 Quantity Relationships in Chemical Reactions
... reagent that runs out first the limiting reagent. The one that does not run out is called the excess reagent. If the reagents are mixed in nonstoichiometric quantities, one must calculate the amount of product that each could theoretically produce to determine which reagent is limiting. The maximum ...
... reagent that runs out first the limiting reagent. The one that does not run out is called the excess reagent. If the reagents are mixed in nonstoichiometric quantities, one must calculate the amount of product that each could theoretically produce to determine which reagent is limiting. The maximum ...
Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging Activity of Flavone Glycosides from Melilotus neapolitana
... metabolites from plants having a strong antioxidant and radical scavenging activities [5, 6]. In this study, one new and six known flavone glycosides were isolated from Melilotus neapolitana and the radical scavenging and antioxidant activities of these compounds were evaluated. Results and Discussi ...
... metabolites from plants having a strong antioxidant and radical scavenging activities [5, 6]. In this study, one new and six known flavone glycosides were isolated from Melilotus neapolitana and the radical scavenging and antioxidant activities of these compounds were evaluated. Results and Discussi ...
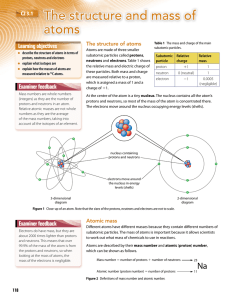
The structure and mass of atoms - Brentwood Ursuline Convent
... Examiner feedback Electrons do have mass, but they are about 2000 times lighter than protons and neutrons. This means that over 99.9% of the mass of the atom is from the protons and neutrons, so when looking at the mass of atoms, the mass of the electrons is negligible. ...
... Examiner feedback Electrons do have mass, but they are about 2000 times lighter than protons and neutrons. This means that over 99.9% of the mass of the atom is from the protons and neutrons, so when looking at the mass of atoms, the mass of the electrons is negligible. ...
Biochemistry
... • Recovers the carbon skeleton from phosphoglycolate • Chloroplast Phosphotase • Peroxisome (aka microsome) • Mitochondria Glycolate oxidase ...
... • Recovers the carbon skeleton from phosphoglycolate • Chloroplast Phosphotase • Peroxisome (aka microsome) • Mitochondria Glycolate oxidase ...
Slide 1
... The positively charged protons in the nucleus hold the negatively charged electrons in their orbits. The number of protons in the nucleus therefore determines the chemical properties of that atom. The positive nuclear charge determines the possible structures of electron orbits that can occur. The n ...
... The positively charged protons in the nucleus hold the negatively charged electrons in their orbits. The number of protons in the nucleus therefore determines the chemical properties of that atom. The positive nuclear charge determines the possible structures of electron orbits that can occur. The n ...
The Mole Concept
... 2. determine the mass needed to provide 3. moles of hydrogen. 1 mole H2 = 2.0 grams H2; 2 mole H2 = 4.0 grams H2 3 mole H2 = 6.0 grams H2 The practical way is to multiply the molar mass by the number of moles. This converts mole to grams (3 mole H2 )(2 grams H2/ 1 mole H2 ) = 6 grams H2 Example. How ...
... 2. determine the mass needed to provide 3. moles of hydrogen. 1 mole H2 = 2.0 grams H2; 2 mole H2 = 4.0 grams H2 3 mole H2 = 6.0 grams H2 The practical way is to multiply the molar mass by the number of moles. This converts mole to grams (3 mole H2 )(2 grams H2/ 1 mole H2 ) = 6 grams H2 Example. How ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.