The Mole Concept
... 2. determine the mass needed to provide 3. moles of hydrogen. 1 mole H2 = 2.0 grams H2; 2 mole H2 = 4.0 grams H2 3 mole H2 = 6.0 grams H2 The practical way is to multiply the molar mass by the number of moles. This converts mole to grams (3 mole H2 )(2 grams H2/ 1 mole H2 ) = 6 grams H2 Example. How ...
... 2. determine the mass needed to provide 3. moles of hydrogen. 1 mole H2 = 2.0 grams H2; 2 mole H2 = 4.0 grams H2 3 mole H2 = 6.0 grams H2 The practical way is to multiply the molar mass by the number of moles. This converts mole to grams (3 mole H2 )(2 grams H2/ 1 mole H2 ) = 6 grams H2 Example. How ...
The Mole
... We can make solutions of known concentration using volumetric flasks. The easiest way of learning this is to try an example. We need 250cm3 of 0.1 mol dm3 solution of sodium hydroxide. Use the formula to calculate the No. of moles of sodium hydroxide – No. of moles = Concentration (Mol dm3) x ...
... We can make solutions of known concentration using volumetric flasks. The easiest way of learning this is to try an example. We need 250cm3 of 0.1 mol dm3 solution of sodium hydroxide. Use the formula to calculate the No. of moles of sodium hydroxide – No. of moles = Concentration (Mol dm3) x ...
Alcohols
... -- dissolve in water to some degree -- are more polar than hydrocarbons but less polar than water ...
... -- dissolve in water to some degree -- are more polar than hydrocarbons but less polar than water ...
Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements If You Cut a Piece of Graphite • If you
... • In a chemical changes, however, atoms can lose or gain electrons and become charged particles called ions. – Positively charged ions, such as Na+, are called ...
... • In a chemical changes, however, atoms can lose or gain electrons and become charged particles called ions. – Positively charged ions, such as Na+, are called ...
Backbone sequential assigment tutorial
... find/add peaks. Now you can put peaks into the spectrum by hand. The program can also do automatic peak picking by dragging a box over the spectrum. Sparky will automatically recognise the peaks according to the current contour levels. When you put a peak by hand; the peak can be centered by the sho ...
... find/add peaks. Now you can put peaks into the spectrum by hand. The program can also do automatic peak picking by dragging a box over the spectrum. Sparky will automatically recognise the peaks according to the current contour levels. When you put a peak by hand; the peak can be centered by the sho ...
Starter S-30
... -reactants can be impure -reactions may not go to completion -may compete with smaller “side” reactions In some reactions as little as 60% yield is considered a good result ...
... -reactants can be impure -reactions may not go to completion -may compete with smaller “side” reactions In some reactions as little as 60% yield is considered a good result ...
03 Stoichiometry
... This is the most important thing you can learn as you embark upon AP Chemistry! Get good at this and you will do well all year. This NEVER goes away! It’s time to repeat my dimensional analysis disclaimer. DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS DISCLAIMER: Beginning on page 84 of the Chapter 3 text files you can find ...
... This is the most important thing you can learn as you embark upon AP Chemistry! Get good at this and you will do well all year. This NEVER goes away! It’s time to repeat my dimensional analysis disclaimer. DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS DISCLAIMER: Beginning on page 84 of the Chapter 3 text files you can find ...
Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions
... percentage can be converted directly to grams. In this sample, there will be 40.92 g of C, 4.58 g of H, and 54.50 g of O. Because the subscripts in the formula represent a mole ratio, we need to convert the grams of each element to moles. The conversion factor needed is the molar mass of each elemen ...
... percentage can be converted directly to grams. In this sample, there will be 40.92 g of C, 4.58 g of H, and 54.50 g of O. Because the subscripts in the formula represent a mole ratio, we need to convert the grams of each element to moles. The conversion factor needed is the molar mass of each elemen ...
Calculations with Chemical Reactions
... Atomic mass– the total mass of protons, neutrons and electrons in a single atom. (Note that atomic mass has no units. It is a relative measure). Molecular mass– the mass of one molecule. Molecular mass is equal to the total mass of all the elements making up a molecule. Mole –a unit of measurement w ...
... Atomic mass– the total mass of protons, neutrons and electrons in a single atom. (Note that atomic mass has no units. It is a relative measure). Molecular mass– the mass of one molecule. Molecular mass is equal to the total mass of all the elements making up a molecule. Mole –a unit of measurement w ...
Slides
... (prot) Returns a list of rxns this protein catalyzes Transcription-units-of-proteins(prot) Returns a list of TU’s activated/inhibited by the given protein Transporter? (prot) Is this protein a transporter? Polypeptide-or-homomultimer?(prot) Transcription-factor? (prot) Obtain ...
... (prot) Returns a list of rxns this protein catalyzes Transcription-units-of-proteins(prot) Returns a list of TU’s activated/inhibited by the given protein Transporter? (prot) Is this protein a transporter? Polypeptide-or-homomultimer?(prot) Transcription-factor? (prot) Obtain ...
2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules
... • A Catalyst: is a substance that speeds up chemical reactions. 1. decreases activation energy 2. increases reaction rate ...
... • A Catalyst: is a substance that speeds up chemical reactions. 1. decreases activation energy 2. increases reaction rate ...
2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules
... • A Catalyst: is a substance that speeds up chemical reactions. 1. decreases activation energy 2. increases reaction rate ...
... • A Catalyst: is a substance that speeds up chemical reactions. 1. decreases activation energy 2. increases reaction rate ...
Chapter 5 ppt
... Individual products and reactants are separated by a plus sign Chemical Equation: A written statement using symbols and formulas to describe the changes that occur in a reaction Example: 2H2(g) + O2 (g) 2H2O (l) Letter in parentheses indicates the state of the substance: gas (g), liquid (l), solid ...
... Individual products and reactants are separated by a plus sign Chemical Equation: A written statement using symbols and formulas to describe the changes that occur in a reaction Example: 2H2(g) + O2 (g) 2H2O (l) Letter in parentheses indicates the state of the substance: gas (g), liquid (l), solid ...
Chemical Equations Chemical Reaction: Interaction between
... The arrow points towards the products formed by the reaction Individual products and reactants are separated by a plus sign Chemical Equation: A written statement using symbols and formulas to describe the changes that occur in a reaction Example: 2H2(g) + O2 (g) Æ 2H2O (l) Letter in parentheses ind ...
... The arrow points towards the products formed by the reaction Individual products and reactants are separated by a plus sign Chemical Equation: A written statement using symbols and formulas to describe the changes that occur in a reaction Example: 2H2(g) + O2 (g) Æ 2H2O (l) Letter in parentheses ind ...
Metabolic Engineering for Fuels and Chemicals
... Global regulators for carbon metabolism (mutations in mlc, crp, csrA) Global regulators for redox control (mutations in fnr, arcA) Prolonging the growth phase and metabolism (comparing ethanol/lactic acid) ...
... Global regulators for carbon metabolism (mutations in mlc, crp, csrA) Global regulators for redox control (mutations in fnr, arcA) Prolonging the growth phase and metabolism (comparing ethanol/lactic acid) ...
The Mole - Piscataway High School
... composition? Percent composition – percent by mass of each element in the compound Percent by mass of an element in a compound is the number of grams of the element divided by the mass in grams of the compound multiplied by 100% Equation: Percent composition from Chemical formula ...
... composition? Percent composition – percent by mass of each element in the compound Percent by mass of an element in a compound is the number of grams of the element divided by the mass in grams of the compound multiplied by 100% Equation: Percent composition from Chemical formula ...
Isotopic fractionation in proteins as a measure of hydrogen bond
... We calculate the H/D zero-point energies, and hence Φ, with the electronic ground state potential of a twodiabatic state model.17 For X and Y as donor and acceptor, the two diabatic states of the model are X–H · · · Y and X · · · H–Y, which are modelled as Morse oscillators. The coupling between the ...
... We calculate the H/D zero-point energies, and hence Φ, with the electronic ground state potential of a twodiabatic state model.17 For X and Y as donor and acceptor, the two diabatic states of the model are X–H · · · Y and X · · · H–Y, which are modelled as Morse oscillators. The coupling between the ...
Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements Modern Atomic theory
... Dalton explained these laws with his atomic theory which included the following concepts; Each element is composed of tiny, indestructible particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element have the same mass and other properties that distinguish them from atoms of other elements Atoms combine in ...
... Dalton explained these laws with his atomic theory which included the following concepts; Each element is composed of tiny, indestructible particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element have the same mass and other properties that distinguish them from atoms of other elements Atoms combine in ...
C 4 The Atomic Theory
... does. Similarly, E always required exactly four times as much oxygen as C does. Once again, Dalton noticed that small whole numbers (2 and 4) seemed to be the rule. Dalton used his experimental results to propose the law of multiple proportions: When two elements react to form more than one substanc ...
... does. Similarly, E always required exactly four times as much oxygen as C does. Once again, Dalton noticed that small whole numbers (2 and 4) seemed to be the rule. Dalton used his experimental results to propose the law of multiple proportions: When two elements react to form more than one substanc ...
AP Chemistry - cloudfront.net
... 8.37 Which group in the periodic table has elements with high IE1 and very negative first electron affinities (EA1)? What is the charge on the ions that these atoms form? 8.59 Write the charge and full ground-state electron configuration of the monatomic ion most likely to be formed by each of the f ...
... 8.37 Which group in the periodic table has elements with high IE1 and very negative first electron affinities (EA1)? What is the charge on the ions that these atoms form? 8.59 Write the charge and full ground-state electron configuration of the monatomic ion most likely to be formed by each of the f ...
Atomic Structure
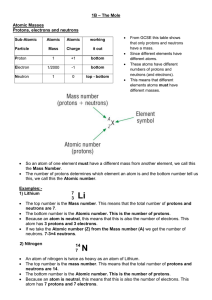
... What is the atomic number (Z) and the mass number (A) of an isotope of lithium containing 4 neutrons? A lithium atom contains 3 protons in its nucleus. atomic number Z = number of protons = 3 number of neutrons = 4 mass number A = (number of protons) + (number of neutrons) mass number A = (3) + (4) ...
... What is the atomic number (Z) and the mass number (A) of an isotope of lithium containing 4 neutrons? A lithium atom contains 3 protons in its nucleus. atomic number Z = number of protons = 3 number of neutrons = 4 mass number A = (number of protons) + (number of neutrons) mass number A = (3) + (4) ...
Physicists realize an atom laser, a source of coherent matter waves
... suggested: optical transitions which eject atoms from the cavity due to the absorbed photon recoil, and tunneling through thin barriers of light. The gain process in an atom laser. An atom laser is only possible for bosonic atoms. The accumulation of atoms in a single quantum state is based on Bose- ...
... suggested: optical transitions which eject atoms from the cavity due to the absorbed photon recoil, and tunneling through thin barriers of light. The gain process in an atom laser. An atom laser is only possible for bosonic atoms. The accumulation of atoms in a single quantum state is based on Bose- ...
Chapter 3 PowerPoint
... Atomic Mass Atoms are so small, it is difficult to discuss how much they weigh in grams. Use atomic mass units. an atomic mass unit (amu) is one twelth the mass of a carbon-12 atom. This gives us a basis for comparison. The decimal numbers on the table are atomic masses in amu. ...
... Atomic Mass Atoms are so small, it is difficult to discuss how much they weigh in grams. Use atomic mass units. an atomic mass unit (amu) is one twelth the mass of a carbon-12 atom. This gives us a basis for comparison. The decimal numbers on the table are atomic masses in amu. ...
Ingenuity Pathway Analysis of metabolomics data including cross
... Two distinct philosophies are applied to metabolomic studies depending on whether an existing hypothesis is being tested (targeted) or a more open investigation is on-going (non-targeted). Targeted approaches typically usually use standard clinical chemistry platforms or chromatography (either gas ( ...
... Two distinct philosophies are applied to metabolomic studies depending on whether an existing hypothesis is being tested (targeted) or a more open investigation is on-going (non-targeted). Targeted approaches typically usually use standard clinical chemistry platforms or chromatography (either gas ( ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.