Efficient Homogeneous Catalysis in the Reduction of CO to CO
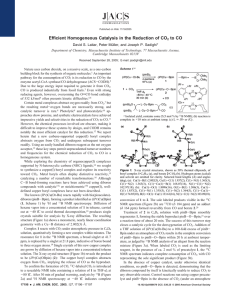
... Treatment of 2 in C6D6 solution with pinB-Bpin smoothly regenerates 1, forming the stable byproduct pinB-O-Bpin,21 over a reaction time of about 20 min. The success of this turnover step closes a catalytic cycle for the deoxygenation of CO2. Addition of a THF solution of (IPr)Cu(Ot-Bu) to a 100-fold ...
... Treatment of 2 in C6D6 solution with pinB-Bpin smoothly regenerates 1, forming the stable byproduct pinB-O-Bpin,21 over a reaction time of about 20 min. The success of this turnover step closes a catalytic cycle for the deoxygenation of CO2. Addition of a THF solution of (IPr)Cu(Ot-Bu) to a 100-fold ...
Molar Mass
... • Is the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms • Is calculated by dividing the subscripts in the molecular formula by a whole number to give the lowest ratio C5H10O5 5 = C1H2O1 = ...
... • Is the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms • Is calculated by dividing the subscripts in the molecular formula by a whole number to give the lowest ratio C5H10O5 5 = C1H2O1 = ...
TEKS 8 - UNT College of Education
... A chemical reaction, also called a chemical change, is material changing from a beginning mass to a resulting substance. The process involves one or more reactants yielding one or more products different from the reactants. The characteristic of a chemical reaction is that new material or materials ...
... A chemical reaction, also called a chemical change, is material changing from a beginning mass to a resulting substance. The process involves one or more reactants yielding one or more products different from the reactants. The characteristic of a chemical reaction is that new material or materials ...
Amount of Substance
... proton and 1 electron. Since the mass of an electron is negligible compared to that of a proton or a neutron, the hydrogen atom has only 1/12 the mass of a carbon atom; therefore the relative atomic mass of hydrogen is 1. Similarly, the relative mass of an oxygen atom, which contains 8 protons, 8 ne ...
... proton and 1 electron. Since the mass of an electron is negligible compared to that of a proton or a neutron, the hydrogen atom has only 1/12 the mass of a carbon atom; therefore the relative atomic mass of hydrogen is 1. Similarly, the relative mass of an oxygen atom, which contains 8 protons, 8 ne ...
Gr. 11 Chemistry Student Workbook (Spring 2016)
... One of the most important educational skills you can develop is how to monitor and track your own learning. Either at the end of class or at home, you will complete a daily entry in your learning log. Written Work: Use our marking scheme for daily class work (out of 5) to assess your written work. W ...
... One of the most important educational skills you can develop is how to monitor and track your own learning. Either at the end of class or at home, you will complete a daily entry in your learning log. Written Work: Use our marking scheme for daily class work (out of 5) to assess your written work. W ...
The Stereochemistry of Enzymatic Transamination“
... isotope effect in the CH bond-breaking step and a complex function of the relative rates of protonation of C, and C,, the isotope effects in this protonation, and the rate of loss of deuterium from the catalytically active group(s) at the active site. The holoenzyme reaction also exhibits a small is ...
... isotope effect in the CH bond-breaking step and a complex function of the relative rates of protonation of C, and C,, the isotope effects in this protonation, and the rate of loss of deuterium from the catalytically active group(s) at the active site. The holoenzyme reaction also exhibits a small is ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... The C atoms are balanced, one on each side of the arrow. Because CH3OH has four H atoms, we place the coefficient 2 in front of H2O to balance the H atoms: CH3OH(l) + O2(g) CO2(g) + 2 H2O(g) Adding this coefficient balances H but gives four O atoms in the products. Because there are only three O a ...
... The C atoms are balanced, one on each side of the arrow. Because CH3OH has four H atoms, we place the coefficient 2 in front of H2O to balance the H atoms: CH3OH(l) + O2(g) CO2(g) + 2 H2O(g) Adding this coefficient balances H but gives four O atoms in the products. Because there are only three O a ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas. Cations are positive and are formed by elements on the left side of the periodic chart. Anions are negative and are formed by elements on the right Atoms, Molecules, side of the periodic chart. and Ions ...
... same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas. Cations are positive and are formed by elements on the left side of the periodic chart. Anions are negative and are formed by elements on the right Atoms, Molecules, side of the periodic chart. and Ions ...
Metabolomics Reveals New Mechanisms for Pathogenesis in Barth
... mitochondria [3,4]. Cardiolipin has important roles in mitochondrial function including maintaining christae structure, supporting electron transport chain efficiency, and in apoptosis [4– 7]. Abnormalities in cardiolipin have been implicated in common human diseases including diabetes, heart failur ...
... mitochondria [3,4]. Cardiolipin has important roles in mitochondrial function including maintaining christae structure, supporting electron transport chain efficiency, and in apoptosis [4– 7]. Abnormalities in cardiolipin have been implicated in common human diseases including diabetes, heart failur ...
Formulae Boardwork
... mass of desired products × 100 atom economy = total mass of reactants Example: What is the atom economy of a reaction where the actual yield was 25 000 tonnes but the mass of the reactants was 30 000 tonnes? mass of desired products × 100 atom economy = total mass of reactants ...
... mass of desired products × 100 atom economy = total mass of reactants Example: What is the atom economy of a reaction where the actual yield was 25 000 tonnes but the mass of the reactants was 30 000 tonnes? mass of desired products × 100 atom economy = total mass of reactants ...
PDF w - ACS Publications - American Chemical Society
... relative to their BDEs. This finding suggests that there are other factors in addition to the BDE of the C−H bond influencing the rate constant of the reaction. For example, a mechanistic study of HAT by an iron(III) imido complex revealed a strong dependence of the rate constants on the size and ster ...
... relative to their BDEs. This finding suggests that there are other factors in addition to the BDE of the C−H bond influencing the rate constant of the reaction. For example, a mechanistic study of HAT by an iron(III) imido complex revealed a strong dependence of the rate constants on the size and ster ...
Can atoms be counted or measured
... 1. If you were cooking _______________– you would need 1 cup of rice and 2 cups of water. 2. This is the basic recipe for cooking rice. 3. If you wanted to cook ______________ the amount of rice, you would use this recipe and multiply all ingredients by 2. Therefore adding 2 cups of rice and 4 cups ...
... 1. If you were cooking _______________– you would need 1 cup of rice and 2 cups of water. 2. This is the basic recipe for cooking rice. 3. If you wanted to cook ______________ the amount of rice, you would use this recipe and multiply all ingredients by 2. Therefore adding 2 cups of rice and 4 cups ...
Mittenthal, J.E., Clarke, B., Waddell, T., and Fawcett, G.
... (4A) The inputs must not be the same as the outputs, because such a g-reaction does not accomplish any transformation. (4A1) One input must not be the same as one output, because the other input must then be the same as the other output. (4A2) (0, 0) and (0, 1) are not allowed as inputs or outputs. ...
... (4A) The inputs must not be the same as the outputs, because such a g-reaction does not accomplish any transformation. (4A1) One input must not be the same as one output, because the other input must then be the same as the other output. (4A2) (0, 0) and (0, 1) are not allowed as inputs or outputs. ...
Four Amino Acids Are Converted to Succinyl
... Seven amino acids form acetyl CoA and/or acetoacetyl-CoA. These amino acids are lysine, leucine,tryptophan, phenylalanine, tyrosine,, isoleucine, and threonine. Leucine is ketogenic, forming acetyl CoA and acetoacetate. Lysine is exclusively ketogenic amino acid, converted to acetoacetyl CoA. Trypto ...
... Seven amino acids form acetyl CoA and/or acetoacetyl-CoA. These amino acids are lysine, leucine,tryptophan, phenylalanine, tyrosine,, isoleucine, and threonine. Leucine is ketogenic, forming acetyl CoA and acetoacetate. Lysine is exclusively ketogenic amino acid, converted to acetoacetyl CoA. Trypto ...
Unit 13 Stoichiometry (Theoretical)
... b. How many grams of acetylene (C2H2) are produced by adding water to 5.00 grams of CaC2? (ans. 2.03 g C2H2) ...
... b. How many grams of acetylene (C2H2) are produced by adding water to 5.00 grams of CaC2? (ans. 2.03 g C2H2) ...
File
... A sample of a compound contains 30.46% Nitrogen and 69.54% Oxygen by mass In a separate experiment, the molar mass of the compound is estimated to be between 90 g and 95 g. Determine the molecular formula and the accurate molar mass of the compound. ...
... A sample of a compound contains 30.46% Nitrogen and 69.54% Oxygen by mass In a separate experiment, the molar mass of the compound is estimated to be between 90 g and 95 g. Determine the molecular formula and the accurate molar mass of the compound. ...
fahad h. ahmad - Fahad`s Academy
... We can know the charge of elements by looking at groups of periodic table. Group I to group III elements has charge of +1, increasing to +3, going to the right. Group V to group VII elements has charge of -3, decreasing to -1, going to the right. E.g. Aluminium sulfate We have to balance the charges ...
... We can know the charge of elements by looking at groups of periodic table. Group I to group III elements has charge of +1, increasing to +3, going to the right. Group V to group VII elements has charge of -3, decreasing to -1, going to the right. E.g. Aluminium sulfate We have to balance the charges ...
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry
... building block, organic compounds usually have hydrogen atoms as well. Oxygen and nitrogen are also common, but almost any other element can be found in organic compounds. In this section, we deal with the class of compounds known as hydrocarbons, which are compounds that contain only carbon and hyd ...
... building block, organic compounds usually have hydrogen atoms as well. Oxygen and nitrogen are also common, but almost any other element can be found in organic compounds. In this section, we deal with the class of compounds known as hydrocarbons, which are compounds that contain only carbon and hyd ...
Stoichiometry - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Note: I am not sure how the units work out for this. It would appear that the grams cancel each other out leaving no value, but for some reason you are left with moles. This may be something to ask your teacher about. 1.2.5. Define the terms empirical formula and molecular formula. The molecular for ...
... Note: I am not sure how the units work out for this. It would appear that the grams cancel each other out leaving no value, but for some reason you are left with moles. This may be something to ask your teacher about. 1.2.5. Define the terms empirical formula and molecular formula. The molecular for ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... true in general. That is, samples that have the same mass ratio are not necessarily the same substance. For example, there are many compounds other than isooctane that also have a carbon-to-hydrogen mass ratio of 5.33:1.00. Dalton also used data from Proust, as well as results from his own experimen ...
... true in general. That is, samples that have the same mass ratio are not necessarily the same substance. For example, there are many compounds other than isooctane that also have a carbon-to-hydrogen mass ratio of 5.33:1.00. Dalton also used data from Proust, as well as results from his own experimen ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... true in general. That is, samples that have the same mass ratio are not necessarily the same substance. For example, there are many compounds other than isooctane that also have a carbon-to-hydrogen mass ratio of 5.33:1.00. Dalton also used data from Proust, as well as results from his own experimen ...
... true in general. That is, samples that have the same mass ratio are not necessarily the same substance. For example, there are many compounds other than isooctane that also have a carbon-to-hydrogen mass ratio of 5.33:1.00. Dalton also used data from Proust, as well as results from his own experimen ...
Supplemental Methods 1. Amino acid conformation clustering Amino
... reference system P-R-Q as described in the previous section, the amino acid type of the parent residue containing atom P, and the conformational type of the parent amino acid. Interacting atoms outside the sphere with the radius equal to the sum of the van der Waals radii of the interacting atom and ...
... reference system P-R-Q as described in the previous section, the amino acid type of the parent residue containing atom P, and the conformational type of the parent amino acid. Interacting atoms outside the sphere with the radius equal to the sum of the van der Waals radii of the interacting atom and ...
Chem 465 Biochemistry II
... dehydrogenase complex and á-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex. Pyruvate dehydrogenase catalyzes the reaction Pyruvate + CoASH 6AcetylCoA + NADH + H+ á-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase catalyzes the reaction á-ketoglutarate + CoASH 6SuccinylCoA + NADH + H+. Pyruvate dehydrogenase and á-ketoglutarate deh ...
... dehydrogenase complex and á-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex. Pyruvate dehydrogenase catalyzes the reaction Pyruvate + CoASH 6AcetylCoA + NADH + H+ á-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase catalyzes the reaction á-ketoglutarate + CoASH 6SuccinylCoA + NADH + H+. Pyruvate dehydrogenase and á-ketoglutarate deh ...
Core_Class_Science_Chemistry_for_the_web 838.3 KB
... Electrons are negatively charged particles (E-) located on the outside of the nucleus. Electrons constantly move around the nucleus in energy levels. Today’s Objectives: Diagram the particles that make up an atom. Compare covalent and ionic One: bonds. Answer: ...
... Electrons are negatively charged particles (E-) located on the outside of the nucleus. Electrons constantly move around the nucleus in energy levels. Today’s Objectives: Diagram the particles that make up an atom. Compare covalent and ionic One: bonds. Answer: ...
CHAPTER
... In Chapter 11, you learned that volumes of gases always combine in definite ratios. This observation, called the law of combining volumes, is based on measurements of the gas volumes. When Avogadro suggested that gases combine in fixed ratios because equal volumes of gases at the same temperature an ...
... In Chapter 11, you learned that volumes of gases always combine in definite ratios. This observation, called the law of combining volumes, is based on measurements of the gas volumes. When Avogadro suggested that gases combine in fixed ratios because equal volumes of gases at the same temperature an ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.























