Energy
... only on the initial and final state of the system, but which is independent of the pathway used to go between them. The value for something that is not a state function depends not only on the initial and final state but also on the pathway used to travel between them. ...
... only on the initial and final state of the system, but which is independent of the pathway used to go between them. The value for something that is not a state function depends not only on the initial and final state but also on the pathway used to travel between them. ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
Chem Curr - New Haven Science
... Chemistry is a study of the fundamental structure of matter that serves as a basic understanding of science needed in today’s world. It is a study of matter, energy, atomic and molecular structure, composition, bonding, the periodic law, chemical equations, acid-base reactions, solutions, gas laws, ...
... Chemistry is a study of the fundamental structure of matter that serves as a basic understanding of science needed in today’s world. It is a study of matter, energy, atomic and molecular structure, composition, bonding, the periodic law, chemical equations, acid-base reactions, solutions, gas laws, ...
Multiple Choice Practice. A) P B) S C) Cl D) Li E) 1 F 1. Has the
... When the half reaction above is balanced, how many moles of electrons are needed for every mole of I2 formed by this half-reaction? A) 2 B) 6 C) 8 D) 10 E) 12 30. Which of the following is always true at the triple point of a pure substance? A) The vapor pressure of the solid phase equals the vapor ...
... When the half reaction above is balanced, how many moles of electrons are needed for every mole of I2 formed by this half-reaction? A) 2 B) 6 C) 8 D) 10 E) 12 30. Which of the following is always true at the triple point of a pure substance? A) The vapor pressure of the solid phase equals the vapor ...
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE
... 40. describe the process of osmosis and its effect on pressure and concentration. 41. differentiate between organic and inorganic compounds. 42. name alkenes and alkynes and draw their structures. 43. identify and name isomers. 44. name and describe cyclic compounds.. 45. recognize compounds contain ...
... 40. describe the process of osmosis and its effect on pressure and concentration. 41. differentiate between organic and inorganic compounds. 42. name alkenes and alkynes and draw their structures. 43. identify and name isomers. 44. name and describe cyclic compounds.. 45. recognize compounds contain ...
Chemistry 2008–2012 Written examination – November Examination Specifications
... • make sure chemical equations are balanced and that the formulas for individual substances include an indication of state; for example, H2(g); NaCl(s) ...
... • make sure chemical equations are balanced and that the formulas for individual substances include an indication of state; for example, H2(g); NaCl(s) ...
AP CHEMISTRY SUMMER 2016
... 60. A 2.0g sample of SX6 (g) has a volume of 329.5 cm3 at 1.00 atm and 20oC. Identify the element ‘X’. Name the compound. ...
... 60. A 2.0g sample of SX6 (g) has a volume of 329.5 cm3 at 1.00 atm and 20oC. Identify the element ‘X’. Name the compound. ...
Chapter 6. Therrnochemistry
... energy a wave possesses by virtue of its frequency chemical energy (kinetic and potential energy E associated with bond breakage & formation) thermal energy (kinetic and potential energy E associated with random particle motion) heat (thermal energy transferred between objects at different temperatu ...
... energy a wave possesses by virtue of its frequency chemical energy (kinetic and potential energy E associated with bond breakage & formation) thermal energy (kinetic and potential energy E associated with random particle motion) heat (thermal energy transferred between objects at different temperatu ...
TYPES OF SOLUTION CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... In a certain experiment, 28.0 mL of 0.250 M HNO3 and 53.0 mL of 0.320 M KOH are mixed. Calculate the amount of water formed in the resulting reaction. What is the concentration of H+ or OH- ions in excess after the reaction goes to completion ? ...
... In a certain experiment, 28.0 mL of 0.250 M HNO3 and 53.0 mL of 0.320 M KOH are mixed. Calculate the amount of water formed in the resulting reaction. What is the concentration of H+ or OH- ions in excess after the reaction goes to completion ? ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... 60.A 2.0g sample of SX6 (g) has a volume of 329.5 cm3 at 1.00 atm and 20oC. Identify the element ‘X’. Name the compound. ...
... 60.A 2.0g sample of SX6 (g) has a volume of 329.5 cm3 at 1.00 atm and 20oC. Identify the element ‘X’. Name the compound. ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... 63. A 2.0g sample of SX6 (g) has a volume of 329.5 cm3 at 1.00 atm and 20oC. Identify the element ‘X’. Name the compound. 64. When Hydrogen sulfide gas, H2S, reacts with oxygen, Sulfur dioxide gas and steam are produced. a. Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction. b. How many liters o ...
... 63. A 2.0g sample of SX6 (g) has a volume of 329.5 cm3 at 1.00 atm and 20oC. Identify the element ‘X’. Name the compound. 64. When Hydrogen sulfide gas, H2S, reacts with oxygen, Sulfur dioxide gas and steam are produced. a. Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction. b. How many liters o ...
Course Pack3 Phase Diagrams
... The rule you always hear about miscibility is “like dissolves like” which is an easy way of saying that if the intermolecular forces (IMF) are alike, then compounds are miscible and if the IMFs are not alike, they are not miscible (immiscible). The explanation is that if you are replacing one form o ...
... The rule you always hear about miscibility is “like dissolves like” which is an easy way of saying that if the intermolecular forces (IMF) are alike, then compounds are miscible and if the IMFs are not alike, they are not miscible (immiscible). The explanation is that if you are replacing one form o ...
Direct production of hydrogen peroxide from CO, O2, and H2O over
... Table 1 shows the catalytic results for H2O2 production from CO/O2/H2O over several types of metal nanoparticles dispersed on alumina prepared by the wet reduction (WR) method, which has recently been shown to be an effective method for the preparation of various amorphous alloy catalysts for versati ...
... Table 1 shows the catalytic results for H2O2 production from CO/O2/H2O over several types of metal nanoparticles dispersed on alumina prepared by the wet reduction (WR) method, which has recently been shown to be an effective method for the preparation of various amorphous alloy catalysts for versati ...
Gupta 2014 Credit: Google Images for the pictures Chapter 1
... Hydrolysis = compound reacting with water. • Watch for soluble salts that contain anions of weak acid the anion is a conjugate base and cations of weak bases that are conjugate acids. Reactions of coordinate compounds and complex ...
... Hydrolysis = compound reacting with water. • Watch for soluble salts that contain anions of weak acid the anion is a conjugate base and cations of weak bases that are conjugate acids. Reactions of coordinate compounds and complex ...
Chemistry 3202 Grading Standards June 2006
... (ii) When the equilibrium is placed in an ice bath it turns pale pink. Is )H for the forward reaction positive or negative? Justify your answer. Answer: A shift towards pale pink indicates that the reverse reaction is favored. The energy term must be on the reactant side if there is a decrease in en ...
... (ii) When the equilibrium is placed in an ice bath it turns pale pink. Is )H for the forward reaction positive or negative? Justify your answer. Answer: A shift towards pale pink indicates that the reverse reaction is favored. The energy term must be on the reactant side if there is a decrease in en ...
Chapter 3 Powerpoint
... reactions that produce a flame. They require air (O2) as a reactant. • When hydrocarbons are combusted completely, the products are CO2 and H2O. • Generic Reaction: CxHy + O2 CO2 + H2O • Real Reaction: C3H8 + 5O2 3CO2 + ...
... reactions that produce a flame. They require air (O2) as a reactant. • When hydrocarbons are combusted completely, the products are CO2 and H2O. • Generic Reaction: CxHy + O2 CO2 + H2O • Real Reaction: C3H8 + 5O2 3CO2 + ...
CHEM 30 REDOX
... of unreacted mixture in the photocell system, which produces an electric current that causes the needle in the meter to move from its resting place. The operator then rotates a knob to bring the needle back to the resting place and reads the level of alcohol from the knob -- the more the operator mu ...
... of unreacted mixture in the photocell system, which produces an electric current that causes the needle in the meter to move from its resting place. The operator then rotates a knob to bring the needle back to the resting place and reads the level of alcohol from the knob -- the more the operator mu ...
Coordination Chemistry of Life Processes: Bioinorganic Chemistry
... plays a crucial role in controlling the reactivity of the metal site. In some cases the protein can force metal ions into unusual geometries; the protein environment may be the determining factor controlling the activity of the increasing number of functionally distinct metalloproteins that have ess ...
... plays a crucial role in controlling the reactivity of the metal site. In some cases the protein can force metal ions into unusual geometries; the protein environment may be the determining factor controlling the activity of the increasing number of functionally distinct metalloproteins that have ess ...
File
... Reactions without an enzyme: require more energy to start Reactions with an enzyme: require less energy to start ...
... Reactions without an enzyme: require more energy to start Reactions with an enzyme: require less energy to start ...
Lecture 4
... The charge the atom would have in a molecule (or an ionic compound) if electrons were completely transferred. 1. Free elements (uncombined state) have an oxidation number of zero. ...
... The charge the atom would have in a molecule (or an ionic compound) if electrons were completely transferred. 1. Free elements (uncombined state) have an oxidation number of zero. ...
Sign of enthalpy changes Exothermic vs endothermic Acid
... Problem: 0.3 mL of 1mM solution of a drug is added to a tube with a protein solution. Some of the drug reacts with the protein to form 1:1 protein-drug complex. The reaction produces a heat of –2.4 x 10–3 cal. Estimate the molar enthalpy of binding binding. ...
... Problem: 0.3 mL of 1mM solution of a drug is added to a tube with a protein solution. Some of the drug reacts with the protein to form 1:1 protein-drug complex. The reaction produces a heat of –2.4 x 10–3 cal. Estimate the molar enthalpy of binding binding. ...
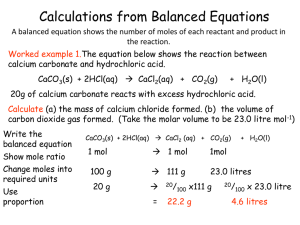
Calculations from Balanced Equations
... Excess reactants You can use the relative numbers of moles of substances, as shown in balanced equations, to calculate the amounts of reactants needed or the amounts of products produced. A limiting reactant is the substance that is fully used up and thereby limits the possible extent of the reacti ...
... Excess reactants You can use the relative numbers of moles of substances, as shown in balanced equations, to calculate the amounts of reactants needed or the amounts of products produced. A limiting reactant is the substance that is fully used up and thereby limits the possible extent of the reacti ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.