alkalinity of groundwater samples
... The endpoint is signalled by a colour change of a pH indicator, such as phenolphthalein or methyl orange or by using a pH meter. Alkalinity is a general water chemistry parameter and can be used to predict photosynthetic productivity and the buffering capacity of a lake against acid deposition. Note ...
... The endpoint is signalled by a colour change of a pH indicator, such as phenolphthalein or methyl orange or by using a pH meter. Alkalinity is a general water chemistry parameter and can be used to predict photosynthetic productivity and the buffering capacity of a lake against acid deposition. Note ...
Chemical equilibrium and the kinetic theory of gases
... large extent by an equation known as the ideal gas law. You will see below how this law is derived from very simple principles. ...
... large extent by an equation known as the ideal gas law. You will see below how this law is derived from very simple principles. ...
Regents Chemistry Topic Review Packet
... 4. A physical change results in the rearrangement of existing particles in a substance; no new types of particles result from this type of change. A chemical change results in the formation of different particles with changed properties. Distinguish between chemical and physical changes based on w ...
... 4. A physical change results in the rearrangement of existing particles in a substance; no new types of particles result from this type of change. A chemical change results in the formation of different particles with changed properties. Distinguish between chemical and physical changes based on w ...
CHAPTER 1 Differentiate b/w Mendeleev`s periodic law and modern
... The electronegativities of group IV-A decrease down the group along with their increasing sizes. These two parameters are responsible for creating van der Waal's forces of attraction among the hydrides. In this way, their melting and boiling points increase. Water is liquid at room temperature while ...
... The electronegativities of group IV-A decrease down the group along with their increasing sizes. These two parameters are responsible for creating van der Waal's forces of attraction among the hydrides. In this way, their melting and boiling points increase. Water is liquid at room temperature while ...
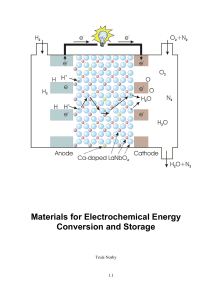
Materials for Electrochemical Energy Conversion and Storage
... current – it converts chemical energy to electrical. We call them galvanic cells. A cell in which the chemically energetic reactants are installed during manufacture and that are designed for only one discharge cycle are called primary batteries, most often simply batteries. If they can be recharged ...
... current – it converts chemical energy to electrical. We call them galvanic cells. A cell in which the chemically energetic reactants are installed during manufacture and that are designed for only one discharge cycle are called primary batteries, most often simply batteries. If they can be recharged ...
Review of: “On the composition of ammonia
... end state rather than any dynamic process along specific growth pathways (e.g. for positively charged or negatively charged clusters only). If the cluster distribution is impacted by conversion from charged to uncharged clusters, this might impact the interpretation, since growth pathways for positi ...
... end state rather than any dynamic process along specific growth pathways (e.g. for positively charged or negatively charged clusters only). If the cluster distribution is impacted by conversion from charged to uncharged clusters, this might impact the interpretation, since growth pathways for positi ...
File - Fidaa`s Level 2 Portfolio
... An ester was produced in each reaction because after all of the carboxylic acids were added to the alcohols; some bonds are broken and create two new bonds. One bond of water and one bond of a new chemical including an ester. The evidence we have is that an ester is a double bond oxygen that is bond ...
... An ester was produced in each reaction because after all of the carboxylic acids were added to the alcohols; some bonds are broken and create two new bonds. One bond of water and one bond of a new chemical including an ester. The evidence we have is that an ester is a double bond oxygen that is bond ...
Chemical Bonding
... powder. Molecular compounds in solid form tend to have a softer or waxy texture, and many have melting and boiling points so low that they are gases or liquids at room temperature. If we can classify a substance as either ionic or molecular, we should be able to predict some of its properties. Conve ...
... powder. Molecular compounds in solid form tend to have a softer or waxy texture, and many have melting and boiling points so low that they are gases or liquids at room temperature. If we can classify a substance as either ionic or molecular, we should be able to predict some of its properties. Conve ...
File
... Chemical bonds are forces that cause a group of atoms to behave as a unit. Energy is stored in chemical bonds. To break bonds, energy must be added. When bonds form, energy is released. All chemical reactions involve changes in energy. Energy is either produced or absorbed during a chemical reaction ...
... Chemical bonds are forces that cause a group of atoms to behave as a unit. Energy is stored in chemical bonds. To break bonds, energy must be added. When bonds form, energy is released. All chemical reactions involve changes in energy. Energy is either produced or absorbed during a chemical reaction ...
Electrolyte Solutions: Thermodynamics, Crystallization
... influence of salts on the vapor pressure of aqueous solutions of organic material may be important for the proper choice of a separation process. Salts may even introduce a liquidliquid phase splitting in aqueous solutions of organic substances. Electrolytes dissociate into ions when they are dissol ...
... influence of salts on the vapor pressure of aqueous solutions of organic material may be important for the proper choice of a separation process. Salts may even introduce a liquidliquid phase splitting in aqueous solutions of organic substances. Electrolytes dissociate into ions when they are dissol ...
Kinetics and Equilibrium of the Reversible Formic Acid
... through the reactor walls. However, H2 leaked through the quartz walls very slowly as pointed out in the original paper [5f]. Because the reaction is carried out in heterogeneous (sub-critical) conditions, the gaseous reaction products are present in both phases. For this reason, we need to take int ...
... through the reactor walls. However, H2 leaked through the quartz walls very slowly as pointed out in the original paper [5f]. Because the reaction is carried out in heterogeneous (sub-critical) conditions, the gaseous reaction products are present in both phases. For this reason, we need to take int ...
Unit 1 Atoms, Molecules and Stoichiometry
... In 1897, J. J. Thomson investigated the conductivity of electricity by gases at very low pressure. At ordinary pressures gases are electrical insulators, but when they are subjected to very high voltages at very low pressures (below 0.01 atm) they break down and conduct electricity. When Thomson app ...
... In 1897, J. J. Thomson investigated the conductivity of electricity by gases at very low pressure. At ordinary pressures gases are electrical insulators, but when they are subjected to very high voltages at very low pressures (below 0.01 atm) they break down and conduct electricity. When Thomson app ...
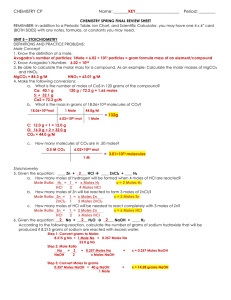
practice problems
... Analyze: We are given two thermochemical equations, and our goal is to combine them in such a way as to obtain the third equation and its enthalpy. Plan: We will use Hess’s law. In doing so, we first note the numbers of moles of substances among the reactants and products in the target equation, (3) ...
... Analyze: We are given two thermochemical equations, and our goal is to combine them in such a way as to obtain the third equation and its enthalpy. Plan: We will use Hess’s law. In doing so, we first note the numbers of moles of substances among the reactants and products in the target equation, (3) ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.