The Solar System
... Jupiter – The Red Spot • The famous Red Spot is a high pressure system of gas/clouds, like a hurricane (which are around areas of low pressure). • The storm never stops because the gases never move over land. The storm is feed by Jupiter’s internal heat. • The spot is ever-changing and at times abs ...
... Jupiter – The Red Spot • The famous Red Spot is a high pressure system of gas/clouds, like a hurricane (which are around areas of low pressure). • The storm never stops because the gases never move over land. The storm is feed by Jupiter’s internal heat. • The spot is ever-changing and at times abs ...
Explain why the jovian planets are so much different
... asteroids with eccentric orbits and often large tilts relative to the equatorial plane. Why are jovian moons generally more geologically active than terrestrial planets? In some cases (Io and Europa), the moons have a continual source of internal heat due to tidal heating (from Jupiter) whereb ...
... asteroids with eccentric orbits and often large tilts relative to the equatorial plane. Why are jovian moons generally more geologically active than terrestrial planets? In some cases (Io and Europa), the moons have a continual source of internal heat due to tidal heating (from Jupiter) whereb ...
meteoroid
... atmosphere), “Earth’s twin” (size), retrograde rotation (East to West) • Earth- life, H2O • Mars- red, dust storms ...
... atmosphere), “Earth’s twin” (size), retrograde rotation (East to West) • Earth- life, H2O • Mars- red, dust storms ...
Astro Ch 19 planets
... • Movies show asteroids as being very close to one another and dangerous to pass through, but they are VERY far apart… so far that it’s unlikely you’ll even pass by one! ...
... • Movies show asteroids as being very close to one another and dangerous to pass through, but they are VERY far apart… so far that it’s unlikely you’ll even pass by one! ...
Overview Presentation on Pluto and Occultations
... (1) A "planet"1 is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and (c) has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit. (2) A "dwarf planet" is a cel ...
... (1) A "planet"1 is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and (c) has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit. (2) A "dwarf planet" is a cel ...
the workSHeet
... The planets in our Solar System are very different in size. Did you realise just how small Mercury and Pluto are compared to the Sun? The next activity will now demonstrate just how big our Solar System is and how far apart the planets actually are. ...
... The planets in our Solar System are very different in size. Did you realise just how small Mercury and Pluto are compared to the Sun? The next activity will now demonstrate just how big our Solar System is and how far apart the planets actually are. ...
Giant Planets (also called jovian planets)
... Jupiter & Saturn radiate more heat than they receive from the sun. Energy from formation (accretion). Saturn being smaller than Jupiter should have cooled off more by now. ...
... Jupiter & Saturn radiate more heat than they receive from the sun. Energy from formation (accretion). Saturn being smaller than Jupiter should have cooled off more by now. ...
The Solar System
... The Second way to Lose Atmosphere… • …maybe easier to understand - Impact Cratering! Big comets and asteroids hitting the planet will deposit a lot of kinetic energy which becomes heat, blowing off a significant amount of atmosphere all at once. • This is a Big issue especially in dense areas (inne ...
... The Second way to Lose Atmosphere… • …maybe easier to understand - Impact Cratering! Big comets and asteroids hitting the planet will deposit a lot of kinetic energy which becomes heat, blowing off a significant amount of atmosphere all at once. • This is a Big issue especially in dense areas (inne ...
The Solar System - Net Start Class
... Uranus is the seventh planet to the Sun. Uranus has 5 large moons and at least 10 small ones. It rotates on its sides and has rings. ...
... Uranus is the seventh planet to the Sun. Uranus has 5 large moons and at least 10 small ones. It rotates on its sides and has rings. ...
Uranus and Neptune are Comparable in Size
... No. The rings are composed of thin, closely spaced ringlets consisting of particles of ice and ice-coated rocks. ...
... No. The rings are composed of thin, closely spaced ringlets consisting of particles of ice and ice-coated rocks. ...
Phys 214. Planets and Life
... Several of jovian moons still have a source of internal heat, despite their smaller size. Io (one of Jupiter’s moons) is the most volcanically active body in our solar system! Its internal source of heat is very different from that of planets = tidal heat due to tidal forces. Even though Jupiter’s m ...
... Several of jovian moons still have a source of internal heat, despite their smaller size. Io (one of Jupiter’s moons) is the most volcanically active body in our solar system! Its internal source of heat is very different from that of planets = tidal heat due to tidal forces. Even though Jupiter’s m ...
Astro 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 5
... a) is highest for the moon closest to the planet and lowest for the most distant. b) the same for all the moons, about 5500 kg/m3. c) is lowest for the closest moon and highest for the most distant moon. d) is completely unrelated to the moons distance from the planet. 7. The volcanoes of Io are a) ...
... a) is highest for the moon closest to the planet and lowest for the most distant. b) the same for all the moons, about 5500 kg/m3. c) is lowest for the closest moon and highest for the most distant moon. d) is completely unrelated to the moons distance from the planet. 7. The volcanoes of Io are a) ...
$doc.title
... planetesimals that incorporated the hydrogen and helium gas that makes up most of Jupiter and Saturn • At the position of the Earth, only silicates and other more “refractory” substances would have precipitated from the ...
... planetesimals that incorporated the hydrogen and helium gas that makes up most of Jupiter and Saturn • At the position of the Earth, only silicates and other more “refractory” substances would have precipitated from the ...
The Outer Planets - Duplin County Schools
... In 1980 and 1981, flyby missions of the nuclear-powered Voyagers 1 and 2 spacecraft came within 100,000 kilometers of Saturn More information was gained in a few days that had been acquired since Galileo first viewed this elegant planet 1. Saturn’s atmosphere is very active, with winds roaring at up ...
... In 1980 and 1981, flyby missions of the nuclear-powered Voyagers 1 and 2 spacecraft came within 100,000 kilometers of Saturn More information was gained in a few days that had been acquired since Galileo first viewed this elegant planet 1. Saturn’s atmosphere is very active, with winds roaring at up ...
planets - Personal.psu.edu
... • Radius: 71,500 km (112 times Earth’s) • Density: 1300 kg/m3—cannot be rocky or metallic as inner planets are • Rotation rate: Problematic, as Jupiter has no solid surface; different parts of atmosphere rotate at different rates • From magnetic field, rotation period is 9 hr, 55 min ...
... • Radius: 71,500 km (112 times Earth’s) • Density: 1300 kg/m3—cannot be rocky or metallic as inner planets are • Rotation rate: Problematic, as Jupiter has no solid surface; different parts of atmosphere rotate at different rates • From magnetic field, rotation period is 9 hr, 55 min ...
Chapter 3: the Sun
... rises; we see deeper where the high ammonia clouds have been depleted by precipitation, much as on Earth rain will often mean clearer skies. ...
... rises; we see deeper where the high ammonia clouds have been depleted by precipitation, much as on Earth rain will often mean clearer skies. ...
mayreview3
... • Describe current ideas describing this surface. • What is believed to be the overall composition and structure of this planet? • What object in the solar system does it most resemble? ...
... • Describe current ideas describing this surface. • What is believed to be the overall composition and structure of this planet? • What object in the solar system does it most resemble? ...
Week 20 Satellites and Probes
... spacecraft, was launched 16 days before its sister craft with a lower initial velocity and similar mission. Voyager 2’s primary mission—the exploration of the four gas giants—was completed in full with a number of interesting discoveries. Studies in the Jovian system included analysis of the Great R ...
... spacecraft, was launched 16 days before its sister craft with a lower initial velocity and similar mission. Voyager 2’s primary mission—the exploration of the four gas giants—was completed in full with a number of interesting discoveries. Studies in the Jovian system included analysis of the Great R ...
Unit Assesment
... 6) True or False: There are 9 planets in the Solar System. a) True b) False 7) True or False: Mercury is the smallest planet in our Solar System. a) True b) False ...
... 6) True or False: There are 9 planets in the Solar System. a) True b) False 7) True or False: Mercury is the smallest planet in our Solar System. a) True b) False ...
Chapter 10 The Outer Worlds… Jupiter Jupiter Jupiter`s Interior
... objects • These objects are very dark, implying they are rich in carbon particles or organic-like materials • The extremely narrow rings may be held in place by shepherding satellites ...
... objects • These objects are very dark, implying they are rich in carbon particles or organic-like materials • The extremely narrow rings may be held in place by shepherding satellites ...
Ch10_Lecture
... • This, together with the vast amount of material in the outer Solar System, lead to the creation of the four large Jovian planets – Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune • Composed mainly of gaseous and liquid hydrogen and its compounds, these planets lack solid surfaces and may have cores of molten ...
... • This, together with the vast amount of material in the outer Solar System, lead to the creation of the four large Jovian planets – Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune • Composed mainly of gaseous and liquid hydrogen and its compounds, these planets lack solid surfaces and may have cores of molten ...
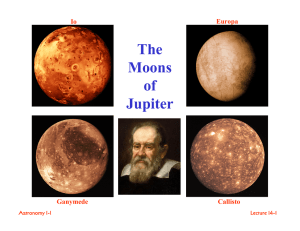
The Moons of Jupiter
... iron/iron sulfide core surrounded by a rocky interior Outer layer of water/ice ~100 km thick Questions as to how this outer layer is actually ...
... iron/iron sulfide core surrounded by a rocky interior Outer layer of water/ice ~100 km thick Questions as to how this outer layer is actually ...
Exploration of Jupiter

The exploration of Jupiter has been conducted via close observations by automated spacecraft. It began with the arrival of Pioneer 10 into the Jovian system in 1973, and, as of 2014, has continued with seven further spacecraft missions. All of these missions were undertaken by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), and all but one have been flybys that take detailed observations without the probe landing or entering orbit. These probes make Jupiter the most visited of the Solar System's outer planets as all missions to the outer Solar System have used Jupiter flybys to reduce fuel requirements and travel time. Plans for more missions to the Jovian system are under development, none of which are scheduled to arrive at the planet before 2016. Sending a craft to Jupiter entails many technical difficulties, especially due to the probes' large fuel requirements and the effects of the planet's harsh radiation environment.The first spacecraft to visit Jupiter was Pioneer 10 in 1973, followed a year later by Pioneer 11. Aside from taking the first close-up pictures of the planet, the probes discovered its magnetosphere and its largely fluid interior. The Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes visited the planet in 1979, and studied its moons and the ring system, discovering the volcanic activity of Io and the presence of water ice on the surface of Europa. Ulysses further studied Jupiter's magnetosphere in 1992 and then again in 2000. The Cassini probe approached the planet in 2000 and took very detailed images of its atmosphere. The New Horizons spacecraft passed by Jupiter in 2007 and made improved measurements of its and its satellites' parameters.The Galileo spacecraft is the only one to have entered orbit around Jupiter, arriving in 1995 and studying the planet until 2003. During this period Galileo gathered a large amount of information about the Jovian system, making close approaches to all of the four large Galilean moons and finding evidence for thin atmospheres on three of them, as well as the possibility of liquid water beneath their surfaces. It also discovered a magnetic field around Ganymede. As it approached Jupiter, it also witnessed the impact of Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9. In December 1995, it sent an atmospheric probe into the Jovian atmosphere, so far the only craft to do so.Future probes planned by NASA include the Juno spacecraft, launched in 2011, which will enter a polar orbit around Jupiter to determine whether it has a rocky core. The European Space Agency selected the L1-class JUICE mission in 2012 as part of its Cosmic Vision programme to explore three of Jupiter's Galilean moons, with a possible Ganymede lander provided by Roscosmos. JUICE is proposed to be launched in 2022. Some NASA administrators have even speculated as to the possibility of human exploration of Jupiter, but such missions are not considered feasible with current technology; such as radiation protection.