The Cradle of Civilization
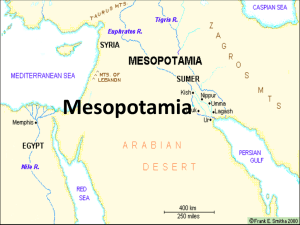
... 1. What two rivers run through the Fertile Crescent? Tigris & Euphrates Rivers 2. Which two river valley civilizations are shown on this map? ...
... 1. What two rivers run through the Fertile Crescent? Tigris & Euphrates Rivers 2. Which two river valley civilizations are shown on this map? ...
Locate and label various places on a map.
... Fertile Crescent Large area of fertile land that stretched from the Mediterranean Sea to the Persian Gulf. ...
... Fertile Crescent Large area of fertile land that stretched from the Mediterranean Sea to the Persian Gulf. ...
Study Guide
... When studying, be sure to review your lecture notes, Chapter 1, the in-class Hammurabi’s Code assignment, and the questions and answers from the video, “Egypt: Quest for Immortality.” The exam will contain multiple choice, short answer, and listing questions. You must bring a Grademaster 23130 form ...
... When studying, be sure to review your lecture notes, Chapter 1, the in-class Hammurabi’s Code assignment, and the questions and answers from the video, “Egypt: Quest for Immortality.” The exam will contain multiple choice, short answer, and listing questions. You must bring a Grademaster 23130 form ...
Study Guide
... - What are the five characteristics of civilization? Briefly (1-2 sentences) describe each one. Why does Mr. Duffy argue that civilization is “all about the food surplus”? ...
... - What are the five characteristics of civilization? Briefly (1-2 sentences) describe each one. Why does Mr. Duffy argue that civilization is “all about the food surplus”? ...
Mesopotamia (Geography) www.sascurriculumpathways.com/portal
... Select the Ancient Cities map. Identify four cities located at the mouth of the Tigris and Euphrates, where the rivers meet along the ancient coastline (noted by the purple boundary). ...
... Select the Ancient Cities map. Identify four cities located at the mouth of the Tigris and Euphrates, where the rivers meet along the ancient coastline (noted by the purple boundary). ...
File
... Over time, Mesopotamian settlements grew in size and complexity. They gradually developed into cities between 4000 and 3000 BC.Despite the growth of cities, society in Mesopotamia was still based on agriculture. Most people still worked in farming jobs. However, cities were becoming important places ...
... Over time, Mesopotamian settlements grew in size and complexity. They gradually developed into cities between 4000 and 3000 BC.Despite the growth of cities, society in Mesopotamia was still based on agriculture. Most people still worked in farming jobs. However, cities were becoming important places ...
Ancient Civilizations: Mesopotamia
... On which continent was Mesopotamia located? ___________________; in what is modern day _____________, Syria & Turkey On which rivers did the ancient Mesopotamians settle? Between the ________________________ & __________________________ Rivers; in an area known as the _______________________________ ...
... On which continent was Mesopotamia located? ___________________; in what is modern day _____________, Syria & Turkey On which rivers did the ancient Mesopotamians settle? Between the ________________________ & __________________________ Rivers; in an area known as the _______________________________ ...
Social Studies, chapter 2 studyguide
... Part 3 Short answers 18. Where was Sumer located? southwest Asia between Tigris and Euphrates rivers 19. Name the 2 rivers of this region. Tigris / Euphrates 20. What 2 inventions helped control the waters? Dikes and dams were one, canals were the other 21. What kind of government did the early city ...
... Part 3 Short answers 18. Where was Sumer located? southwest Asia between Tigris and Euphrates rivers 19. Name the 2 rivers of this region. Tigris / Euphrates 20. What 2 inventions helped control the waters? Dikes and dams were one, canals were the other 21. What kind of government did the early city ...
Mesopotamia Test Study Guide
... 2. Identify the following places on a map of Mesopotamia: the Fertile Crescent, Sumer, Babylon, Ur, Euphrates River, Tigris River, Persian Gulf, and the Mediterranean Sea. 3. Explain why civilizations formed by rivers. 4. Draw an irrigation system for the wet and dry season. Religion 5. Describe the ...
... 2. Identify the following places on a map of Mesopotamia: the Fertile Crescent, Sumer, Babylon, Ur, Euphrates River, Tigris River, Persian Gulf, and the Mediterranean Sea. 3. Explain why civilizations formed by rivers. 4. Draw an irrigation system for the wet and dry season. Religion 5. Describe the ...
Mesopotamia Unit Test Study Guide
... 1) How did the Mesopotamians use AND control the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers? ...
... 1) How did the Mesopotamians use AND control the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers? ...
1.4.Ancient Near East
... 1. What does the word “Mesopotamia” mean? 2. What two rivers was it located between? 3. How did Mesopotamian’s control the river water? 4. How did people become slaves in Mesopotamia? 5. What group has the highest/most important job in Mesopotamian society? ...
... 1. What does the word “Mesopotamia” mean? 2. What two rivers was it located between? 3. How did Mesopotamian’s control the river water? 4. How did people become slaves in Mesopotamia? 5. What group has the highest/most important job in Mesopotamian society? ...
Mesopotamia and Hammurabi*s Code
... • The two rivers The Tigris and the Euphrates flow southeastward towards the Persian Gulf • When they flooded it would fertilize the ground making optimal ground for farming ...
... • The two rivers The Tigris and the Euphrates flow southeastward towards the Persian Gulf • When they flooded it would fertilize the ground making optimal ground for farming ...
Mesopotamia - cloudfront.net
... seasonal rain. In Southern Mesopotamia, the land is mostly flat and barren. There is very little rainfall. The area does have slight seasons. It can get quite cool at certain times of the year. Many ...
... seasonal rain. In Southern Mesopotamia, the land is mostly flat and barren. There is very little rainfall. The area does have slight seasons. It can get quite cool at certain times of the year. Many ...
Ch. 1 Sec. 2 Outline Notes Civilization – complex societies. They
... class division, and a writing system. 1. Rivers – All early civilizations developed next to rivers, in order to have fresh water, travel, and trade with other areas. 2. Government - civilizations need laws in order to maintain a safety for people. Also government provided basic needs and infrastruct ...
... class division, and a writing system. 1. Rivers – All early civilizations developed next to rivers, in order to have fresh water, travel, and trade with other areas. 2. Government - civilizations need laws in order to maintain a safety for people. Also government provided basic needs and infrastruct ...
Mesopotamia Notes
... Asia Mesopotamia=Fertile Crescent=land between the rivers Rivers: Tigris and Euphrates ...
... Asia Mesopotamia=Fertile Crescent=land between the rivers Rivers: Tigris and Euphrates ...
ANCIENT MIDDLE EAST REVIEW SHEET
... ANCIENT MIDDLE EAST REVIEW SHEET pp. 19-23, 29-32, 32-34, 62-63, 73-76, 77-82 ,95-98, 99-103 MAP- ...
... ANCIENT MIDDLE EAST REVIEW SHEET pp. 19-23, 29-32, 32-34, 62-63, 73-76, 77-82 ,95-98, 99-103 MAP- ...
Mesopotamia - Cherry Creek Academy
... conquered Mesopotamia in about 2000 B.C. Its capital, Babylon, was on the Euphrates River. • About 1790 B.C.E., the king of Babylon, Hammurabi, brought the empire (much of Mesopotamia) under his control. ...
... conquered Mesopotamia in about 2000 B.C. Its capital, Babylon, was on the Euphrates River. • About 1790 B.C.E., the king of Babylon, Hammurabi, brought the empire (much of Mesopotamia) under his control. ...
NAME______________________________
... 3) Why is the land in northern Mesopotamia quite fertile? 4) What did early settlers in southern Mesopotamia have to do in order to grow their crops? ...
... 3) Why is the land in northern Mesopotamia quite fertile? 4) What did early settlers in southern Mesopotamia have to do in order to grow their crops? ...
For each Empire, mark the features that describe it
... Was a crossroads for trade Ruler built a gigantic palace Great warriors Invented writing Ruled by Chaldeans A city of great learning Located in Mesopotamia Earliest city-states Had a famous library Scientists charted the path of the stars The largest of the empires Believed gods descended to earth u ...
... Was a crossroads for trade Ruler built a gigantic palace Great warriors Invented writing Ruled by Chaldeans A city of great learning Located in Mesopotamia Earliest city-states Had a famous library Scientists charted the path of the stars The largest of the empires Believed gods descended to earth u ...
Euphrates

The Euphrates (/juːˈfreɪtiːz/; Arabic: الفرات: al-Furāt, Syriac: ̇ܦܪܬ: Pǝrāt, Armenian: Եփրատ: Yeprat, Hebrew: פרת: Perat, Turkish: Fırat, Kurdish: Firat) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia. Originating in eastern Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab, which empties into the Persian Gulf.