Name - Scarsdale Schools
... The day of devotion to my gods my profit and gain. What, however, seems good to one, to a god may be displeasing; What is spurned by oneself may find favor with a god. Who is there who can grasp the will of the gods of heaven? The plan of a god is full of mystery ...
... The day of devotion to my gods my profit and gain. What, however, seems good to one, to a god may be displeasing; What is spurned by oneself may find favor with a god. Who is there who can grasp the will of the gods of heaven? The plan of a god is full of mystery ...
Sumerian Civilization Along the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers
... more water. The Euphrates more silt than the Nile. The Northern part of the valley Mesopotamia, the southern Babylonia. ...
... more water. The Euphrates more silt than the Nile. The Northern part of the valley Mesopotamia, the southern Babylonia. ...
Lesson Plans for the Week of 10/14-10/18 File
... Describe the major achievements of the Akkadian, Babylonian, Assyrian, and Neo-Babylonian Empires. Identify the significance of Hammurabi’s code. Thursday: Unit 3 Test: Ancient Mesopotamia (students will NOT be allowed to use their study guide when taking the test) ...
... Describe the major achievements of the Akkadian, Babylonian, Assyrian, and Neo-Babylonian Empires. Identify the significance of Hammurabi’s code. Thursday: Unit 3 Test: Ancient Mesopotamia (students will NOT be allowed to use their study guide when taking the test) ...
Ancient Mesopotamia Study Guide
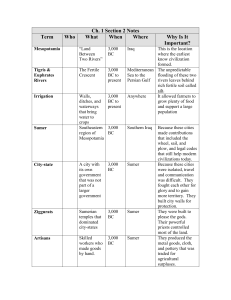
... 1. Mesopotamia - a Greek word meaning between the rivers; Tigris and Euphrates Rivers 2. Fertile Crescent - a large arc of rich, or fertile farmland from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea 3. Silt – a mixture of rich soil and tiny rocks 4. Irrigation – a way of supplying water to an area of l ...
... 1. Mesopotamia - a Greek word meaning between the rivers; Tigris and Euphrates Rivers 2. Fertile Crescent - a large arc of rich, or fertile farmland from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea 3. Silt – a mixture of rich soil and tiny rocks 4. Irrigation – a way of supplying water to an area of l ...
View PDF
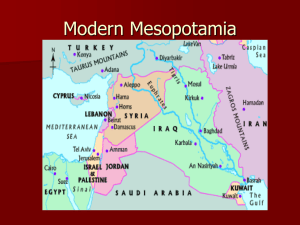
... dry but rich soil lying beyond today's Iraq. It actually includes a portion of modern-day Turkey and Syria, too. Nonetheless, because Iraq represents the bulk of the region, its name and Mesopotamia are nearly synonymous. By all accounts, Mesopotamia (or to a larger extent, a part of the so-called F ...
... dry but rich soil lying beyond today's Iraq. It actually includes a portion of modern-day Turkey and Syria, too. Nonetheless, because Iraq represents the bulk of the region, its name and Mesopotamia are nearly synonymous. By all accounts, Mesopotamia (or to a larger extent, a part of the so-called F ...
notes 1st civilization
... 25 million years ago Hunters and Gathers Nomads Adapted to environment Made fire ...
... 25 million years ago Hunters and Gathers Nomads Adapted to environment Made fire ...
5 th Grade History Test 1
... 21. Ziggurats are the tall temples the Sumerians built for worshiping their gods. 22. The Sumerians were farmers, herdsmen and shepherds. 23. Irrigation is the supplying of land with water. 24. Cuneiform is the Sumerians wedge–shaped form of writing. 25. Sumerians used the arch in their buildings. 2 ...
... 21. Ziggurats are the tall temples the Sumerians built for worshiping their gods. 22. The Sumerians were farmers, herdsmen and shepherds. 23. Irrigation is the supplying of land with water. 24. Cuneiform is the Sumerians wedge–shaped form of writing. 25. Sumerians used the arch in their buildings. 2 ...
Mesopotamia I. Introduction Between the Tigris and Euphrates
... East lies a land once called Mesopotamia. Mesopotamia means “land between the rivers”. In ancient times both rivers were used for transportation, fishing and the irrigation of crops. Today most of this region makes up the nation of Iraq. Mesopotamia was located in an area the Fertile Crescent. This ...
... East lies a land once called Mesopotamia. Mesopotamia means “land between the rivers”. In ancient times both rivers were used for transportation, fishing and the irrigation of crops. Today most of this region makes up the nation of Iraq. Mesopotamia was located in an area the Fertile Crescent. This ...
I - buaron-history
... 3. Farmers raised crops and grazed their livestock on wide, fertile plains a. Early farmers would grow a surplus of crops, which led to more advanced cultures and early civilizations C. Early Civilizations developed in the valleys of four major river systems 1. Tigris and Euphrates Rivers (southwest ...
... 3. Farmers raised crops and grazed their livestock on wide, fertile plains a. Early farmers would grow a surplus of crops, which led to more advanced cultures and early civilizations C. Early Civilizations developed in the valleys of four major river systems 1. Tigris and Euphrates Rivers (southwest ...
Mesopotamia means The Land Between the TWO Rivers
... ➔ Early humans were traveling the world to find the best location to settle permanently. ➔ They found a place in a region called the Fertile Crescent. ➔ Mesopotamia is known as the land between two rivers. ➔ It was the perfect location because it offered rich fertile land that was perfect for farmin ...
... ➔ Early humans were traveling the world to find the best location to settle permanently. ➔ They found a place in a region called the Fertile Crescent. ➔ Mesopotamia is known as the land between two rivers. ➔ It was the perfect location because it offered rich fertile land that was perfect for farmin ...
Mesopotamia
... (The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers) BUT = land between the rivers was inhospitable. Sudden flooding could cause death. It was in this area that humans first gave up their nomadic lifestyle and settled down into permanent settlements. ...
... (The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers) BUT = land between the rivers was inhospitable. Sudden flooding could cause death. It was in this area that humans first gave up their nomadic lifestyle and settled down into permanent settlements. ...
Agricultural Revolution Mesopotamia Review
... •Sargon conquered all the citystates of Mesopotamia and created the first empire ...
... •Sargon conquered all the citystates of Mesopotamia and created the first empire ...
Chapter 2 Section 1 - RedLionWorldHistory
... • 6. What did the Sumerians believe about who it was that ruled their cities? • Te Gods ruled the city, it was a Theocracy ...
... • 6. What did the Sumerians believe about who it was that ruled their cities? • Te Gods ruled the city, it was a Theocracy ...
Mesopotamia intro presentation
... Located in modern day Syria Conquered many parts of old Sumeria Famous leader was Hammurabi--created a law ...
... Located in modern day Syria Conquered many parts of old Sumeria Famous leader was Hammurabi--created a law ...
Mesopotamia - WordPress.com
... and fish. Flooding produces rich soil. Rivers are also a quick way of transportation. The Earliest civilization was Mesopotamia which was located in the land between the Tigris and Euphrates river. Present day this area is know as…. Iraq ...
... and fish. Flooding produces rich soil. Rivers are also a quick way of transportation. The Earliest civilization was Mesopotamia which was located in the land between the Tigris and Euphrates river. Present day this area is know as…. Iraq ...
How did geographic challenges lead to the rise of city
... • Early people who lived in the Fertile Crescent began farming and living in small villages. These villages were located in a land of rolling hills and low plains called Mesopotamia. • Mesopotamia is a Greek word that means the “land between the rivers,” referring to the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. ...
... • Early people who lived in the Fertile Crescent began farming and living in small villages. These villages were located in a land of rolling hills and low plains called Mesopotamia. • Mesopotamia is a Greek word that means the “land between the rivers,” referring to the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. ...
Mesopotamia
... How did geography promote civilization in Mesopotamia? •Flat swampy region was well suited for agriculture •Flooding of Tigris and Euphrates rivers left behind fertile soil, led to more food, which led to more people. •Water from rivers needed to be controlled through canals and dikes. •Large projec ...
... How did geography promote civilization in Mesopotamia? •Flat swampy region was well suited for agriculture •Flooding of Tigris and Euphrates rivers left behind fertile soil, led to more food, which led to more people. •Water from rivers needed to be controlled through canals and dikes. •Large projec ...
Describe city
... • The Israelites believed in Monotheism which is the belief in one god. • As opposed to most religions at the time that worshipped many ...
... • The Israelites believed in Monotheism which is the belief in one god. • As opposed to most religions at the time that worshipped many ...
Euphrates

The Euphrates (/juːˈfreɪtiːz/; Arabic: الفرات: al-Furāt, Syriac: ̇ܦܪܬ: Pǝrāt, Armenian: Եփրատ: Yeprat, Hebrew: פרת: Perat, Turkish: Fırat, Kurdish: Firat) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia. Originating in eastern Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab, which empties into the Persian Gulf.