Neptune - pridescience
... "Welcome to the PDS." Welcome to the Planetary Data System. N.p., n.d. Web. 18 Dec. 2013. ...
... "Welcome to the PDS." Welcome to the Planetary Data System. N.p., n.d. Web. 18 Dec. 2013. ...
ScaleSolarSystemUnit
... A. An explanation of why we see phases of the Moon B. An explanation of why we have seasons on Earth C. A model of the solar system, based on an everyday object, to help the 4th grader understand its size and distances. (You have a choice in how you want to present this model- it could be a video, a ...
... A. An explanation of why we see phases of the Moon B. An explanation of why we have seasons on Earth C. A model of the solar system, based on an everyday object, to help the 4th grader understand its size and distances. (You have a choice in how you want to present this model- it could be a video, a ...
Grade 6 Space Program
... Prior to any mission, the astronauts and other members of the team (ground control) need to understand the nature of the mission – what are they going to do? Why? What are the obstacles they may face and the possible solutions? What are the risks? Seat the students in the seating area of the Space D ...
... Prior to any mission, the astronauts and other members of the team (ground control) need to understand the nature of the mission – what are they going to do? Why? What are the obstacles they may face and the possible solutions? What are the risks? Seat the students in the seating area of the Space D ...
The Physical Forces of Everyday Life, 3, 10
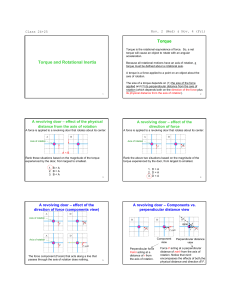
... first, to introduce the concept of torque or the moment of force. This concept provides a measure of the turning tendency or twisting strength of a force. That turning tendency depends not only on the strength and direction of the force itself but also on where the force is applied relative to the a ...
... first, to introduce the concept of torque or the moment of force. This concept provides a measure of the turning tendency or twisting strength of a force. That turning tendency depends not only on the strength and direction of the force itself but also on where the force is applied relative to the a ...
File
... 7. As a result of the Sun's gravity, planets orbit the Sun in nearly circular orbits. The shape of each planet's orbit is a special kind of oval called an ellipse. The shape of an ellipse can vary from long and narrow to circular. The planets' elliptical orbits are nearly circular in shape. 8. Here ...
... 7. As a result of the Sun's gravity, planets orbit the Sun in nearly circular orbits. The shape of each planet's orbit is a special kind of oval called an ellipse. The shape of an ellipse can vary from long and narrow to circular. The planets' elliptical orbits are nearly circular in shape. 8. Here ...
integrals of motion
... From the example of Sun-Earth-Moon system we find that: integrals of motion guarantee no-escape from the allowed regions of motion for an infinite period of time, which is better than either the general or the special perturbation theory can do but only if the assumptions of the theory are satisfied ...
... From the example of Sun-Earth-Moon system we find that: integrals of motion guarantee no-escape from the allowed regions of motion for an infinite period of time, which is better than either the general or the special perturbation theory can do but only if the assumptions of the theory are satisfied ...
Teaching How Scientists Use Models with What Makes Up Most of
... objects or processes that happen too slowly, too quickly, or on too small of a scale to observe directly. They also use models to explore phenomena that are too vast, too complex, or too dangerous to study firsthand. Scientists use different types of models depending on the question they are investi ...
... objects or processes that happen too slowly, too quickly, or on too small of a scale to observe directly. They also use models to explore phenomena that are too vast, too complex, or too dangerous to study firsthand. Scientists use different types of models depending on the question they are investi ...
Midterm #1 Info
... 1 unordinary star 8 classical planets 5 dwarf planets 240+ known satellites (moons) Millions of comets and asteroids Countless particles; and interplanetary space Earth, the Sun, and other objects in the Solar System originated at the same time from the same source and have evolved in varying ways s ...
... 1 unordinary star 8 classical planets 5 dwarf planets 240+ known satellites (moons) Millions of comets and asteroids Countless particles; and interplanetary space Earth, the Sun, and other objects in the Solar System originated at the same time from the same source and have evolved in varying ways s ...
Chapter 4
... much of the re-emitted photons from the chromosphere atoms corresponds to light we cannot see – typically infrared light. We can tell this because some solar satellites are equipped with infrared cameras that show the light coming from the chromosphere quite well. The chromosphere is also beautifull ...
... much of the re-emitted photons from the chromosphere atoms corresponds to light we cannot see – typically infrared light. We can tell this because some solar satellites are equipped with infrared cameras that show the light coming from the chromosphere quite well. The chromosphere is also beautifull ...
PlanetaryScience
... moon’s orbital period over evolutionary time – Mean recession rate of 2.16 cm/yr over the last 650 Myr – Between 2.5Gyr and 650Myr, mean rate was 1.27 cm/yr ...
... moon’s orbital period over evolutionary time – Mean recession rate of 2.16 cm/yr over the last 650 Myr – Between 2.5Gyr and 650Myr, mean rate was 1.27 cm/yr ...
The Sun Times
... wind, and solar prominences. Sunspots are magnetic storms on the photosphere which appear as dark areas. Sunspots regularly appear and disappear in eleven year cycles. Sunspots appear darker because they are cooler than the rest of the sun’s surface. Solar flares are spectacular discharges of magnet ...
... wind, and solar prominences. Sunspots are magnetic storms on the photosphere which appear as dark areas. Sunspots regularly appear and disappear in eleven year cycles. Sunspots appear darker because they are cooler than the rest of the sun’s surface. Solar flares are spectacular discharges of magnet ...
Rigid Body - Kinematics
... Commutative (unlike finite rotation) Behaves as an axial vector (like angular momentum) ...
... Commutative (unlike finite rotation) Behaves as an axial vector (like angular momentum) ...
ARibbon at the Solar Systems Edge
... The combined scattering and neutralization processes now observed at the Moon have implications for interactions with objects across the solar system, such as asteroids, Kuiper Belt objects and other moons. The plasma-surface interactions occurring within protostellar nebula, the region of space tha ...
... The combined scattering and neutralization processes now observed at the Moon have implications for interactions with objects across the solar system, such as asteroids, Kuiper Belt objects and other moons. The plasma-surface interactions occurring within protostellar nebula, the region of space tha ...
Saturn, the R - Teacher|Greycaps
... Earth takes 24 hours to complete a day, while Saturn takes around 10 hours to complete a day. Saturn makes a complete orbit around the sun in 29 Earth years. ...
... Earth takes 24 hours to complete a day, while Saturn takes around 10 hours to complete a day. Saturn makes a complete orbit around the sun in 29 Earth years. ...
Chapter 3: the Sun
... • As with terrestrials, composition can be guessed from mean density. But the high compressibility of volatiles must be accounted for Initially, as they accrete mass they grow in radius But at a mass of ~300 earth masses, further accretion causes the radius to decrease. ...
... • As with terrestrials, composition can be guessed from mean density. But the high compressibility of volatiles must be accounted for Initially, as they accrete mass they grow in radius But at a mass of ~300 earth masses, further accretion causes the radius to decrease. ...
Monday Mar. 9 - University of Manitoba Physics Department
... • For each planet: – Does it revolve in the same direction as the other planets? – Is it primarily composed of rock or of gas? – Is it small or large? (i.e. closer to Earth size or Jupiter size?) – Is it in the outer region or inner region of the solar system? – Is it hot or cold? – Lots of moons or ...
... • For each planet: – Does it revolve in the same direction as the other planets? – Is it primarily composed of rock or of gas? – Is it small or large? (i.e. closer to Earth size or Jupiter size?) – Is it in the outer region or inner region of the solar system? – Is it hot or cold? – Lots of moons or ...
Where Is That Satellite?
... Students may be surprised by three things after doing this activity: (1) that some satellites orbit very close to the earth’s surface while others orbit very far, (2) that satellite orbits are not always circular; some are noticeably elliptical, and (3) some satellites orbit once every 24 hours alon ...
... Students may be surprised by three things after doing this activity: (1) that some satellites orbit very close to the earth’s surface while others orbit very far, (2) that satellite orbits are not always circular; some are noticeably elliptical, and (3) some satellites orbit once every 24 hours alon ...
Outer Space Vocabulary Solar System – The Sun and
... a planet or moon, usually caused by a meteorite. 15) impactor - something (ex. a meteorite) that comes forcibly in contact with a surface (like the moon). 16) eclipse - The total or partial blocking of light from one object in space by another. EX: solar eclipse ...
... a planet or moon, usually caused by a meteorite. 15) impactor - something (ex. a meteorite) that comes forcibly in contact with a surface (like the moon). 16) eclipse - The total or partial blocking of light from one object in space by another. EX: solar eclipse ...
Avoiding a Collision with an Asteroid
... using Newton’s laws and the programming language Scilab, and track the trajectory of the asteroid Apophis in the month prior to April 2029. We were successful in achieving these objectives. We also discovered that it takes an enormous amount of force to change the orbit of Apophis. Statement of prob ...
... using Newton’s laws and the programming language Scilab, and track the trajectory of the asteroid Apophis in the month prior to April 2029. We were successful in achieving these objectives. We also discovered that it takes an enormous amount of force to change the orbit of Apophis. Statement of prob ...
Section 2 Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky
... north or south an object is from the celestial equator. Declination is similar to latitude. It is measured in degrees. The celestial equator has a declination of zero degrees. Objects north of the celestial equator have a positive value. Those south of the celestial equator have a negative value. On ...
... north or south an object is from the celestial equator. Declination is similar to latitude. It is measured in degrees. The celestial equator has a declination of zero degrees. Objects north of the celestial equator have a positive value. Those south of the celestial equator have a negative value. On ...
Chronometry of Meteorites and the Formation of the Earth and Moon
... requires an understanding of what had happened to the cores of accreted bodies during their descent through Earth’s mantle. Efficient equilibration would have occurred if the impactor core completely emulsified as small metal droplets in the terrestrial magma ocean (FIG. 4A). This is likely to have ...
... requires an understanding of what had happened to the cores of accreted bodies during their descent through Earth’s mantle. Efficient equilibration would have occurred if the impactor core completely emulsified as small metal droplets in the terrestrial magma ocean (FIG. 4A). This is likely to have ...
Coriolis Force
... the absolute frame of reference. FM is some arbitrary “mystery” force (per unit mass) acting on the parcel to maintain its position over the same spot on the earth’s surface. ...
... the absolute frame of reference. FM is some arbitrary “mystery” force (per unit mass) acting on the parcel to maintain its position over the same spot on the earth’s surface. ...
Earth's rotation

Earth's rotation is the rotation of the planet Earth around its own axis. The Earth rotates from the west towards east. As viewed from North Star or polestar Polaris, the Earth turns counter-clockwise.The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. This point is distinct from the Earth's North Magnetic Pole. The South Pole is the other point where the Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface, in Antarctica.The Earth rotates once in about 24 hours with respect to the sun and once every 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds with respect to the stars (see below). Earth's rotation is slowing slightly with time; thus, a day was shorter in the past. This is due to the tidal effects the Moon has on Earth's rotation. Atomic clocks show that a modern-day is longer by about 1.7 milliseconds than a century ago, slowly increasing the rate at which UTC is adjusted by leap seconds.