Discovery of Cells
... • All organisms are composed of one or more cells. • The cell is the basic unit of life in all living things. • All cells come from existing cells. ...
... • All organisms are composed of one or more cells. • The cell is the basic unit of life in all living things. • All cells come from existing cells. ...
Nanolive AG from Ecublens (VD) – 3D research on living cells
... Nanolive AG from Ecublens (VD) – 3D research on living cells Nanolive SA is a start-up operating from the EPFL Innovation Park at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (ETHL). The biotech company was founded in 2013 and developed a tomographic microscope which, for the first time ever, allows ...
... Nanolive AG from Ecublens (VD) – 3D research on living cells Nanolive SA is a start-up operating from the EPFL Innovation Park at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (ETHL). The biotech company was founded in 2013 and developed a tomographic microscope which, for the first time ever, allows ...
Cell Theory - OnMyCalendar
... write a report to the Governor about Cells. Make sure you include information on the following points: *explain how the cell theory developed. *describe differences between plant and animal cells *describe three structures that plant and animal cells share and include their functions ...
... write a report to the Governor about Cells. Make sure you include information on the following points: *explain how the cell theory developed. *describe differences between plant and animal cells *describe three structures that plant and animal cells share and include their functions ...
Chapter 3/Lesson 1 Part 2 Notes
... •A diploid cell contains pairs of chromosomes that equal the chromosome number of that organism’s species. •For example, a diploid human cell has 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes or 46 total. •Homologous chromosomes are similar but not identical. Creating Haploid Cells •A haploid cell is a cell th ...
... •A diploid cell contains pairs of chromosomes that equal the chromosome number of that organism’s species. •For example, a diploid human cell has 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes or 46 total. •Homologous chromosomes are similar but not identical. Creating Haploid Cells •A haploid cell is a cell th ...
Introduction: Apoptosis – programmed cell death significantly
... maintaining of tissue homeostasis. Its alteration is leading to cancer disease. Inositolhexaphosphate (IP6) is naturally occurring substance that is present in most legumes, cereals and seems. IP6 and its lower phosphorylated forms are also found in most mammalian cells, where they assist in regulat ...
... maintaining of tissue homeostasis. Its alteration is leading to cancer disease. Inositolhexaphosphate (IP6) is naturally occurring substance that is present in most legumes, cereals and seems. IP6 and its lower phosphorylated forms are also found in most mammalian cells, where they assist in regulat ...
Subcellular Organelles and Structures
... Liver Cell (TEM x9,400). This image is copyright Dennis Kunkel ...
... Liver Cell (TEM x9,400). This image is copyright Dennis Kunkel ...
Criterion
... Make scientific drawings for 2 different cells. Choose one red blood cell and one respiration cell. The drawing must be done to scale. Draw only a few cells. Use solid lines, no shading but stippling is encouraged. Be sure to carefully record the magnification. Label the parts of your cell. Guidelin ...
... Make scientific drawings for 2 different cells. Choose one red blood cell and one respiration cell. The drawing must be done to scale. Draw only a few cells. Use solid lines, no shading but stippling is encouraged. Be sure to carefully record the magnification. Label the parts of your cell. Guidelin ...
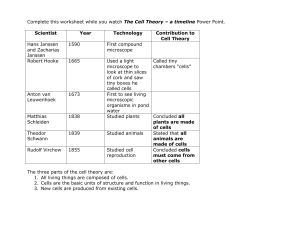
Cell Theory Timeline
... Get your notebook. Grab a notecard from the front. Put your name on it. Answer the following questions: ...
... Get your notebook. Grab a notecard from the front. Put your name on it. Answer the following questions: ...
The human kinome and all its associated signaling proteins
... kinases involved largely in cell cycle control in fungi, mammals and other eukaryotes. hNek5 is a new member of the human Nek family of yet unknown function. Analysis of RT-PCR products showed that hNek5 mRNA was expressed in asynchronous HeLa cells, but, the expression was strongly regulated during ...
... kinases involved largely in cell cycle control in fungi, mammals and other eukaryotes. hNek5 is a new member of the human Nek family of yet unknown function. Analysis of RT-PCR products showed that hNek5 mRNA was expressed in asynchronous HeLa cells, but, the expression was strongly regulated during ...
The wacky history of cell theory
... d. All cells come from pre-existing cells. 4. Can you describe a time when collaboration worked well for you? Where there ever any disagreements that led to a false assumption (like cells spontaneously crystalizing into ...
... d. All cells come from pre-existing cells. 4. Can you describe a time when collaboration worked well for you? Where there ever any disagreements that led to a false assumption (like cells spontaneously crystalizing into ...
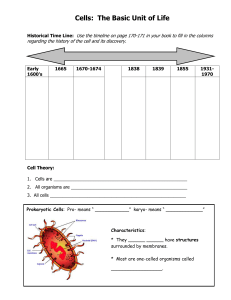
Label the organelles in the animal cell (see page 175
... 1. Cells are ______________________________________________________ 2. All organisms are _______________________________________________ 3. All cells _______________________________________________________ Prokaryotic Cells: Pro- means “ ____________” karyo- means “ _____________” ...
... 1. Cells are ______________________________________________________ 2. All organisms are _______________________________________________ 3. All cells _______________________________________________________ Prokaryotic Cells: Pro- means “ ____________” karyo- means “ _____________” ...
Meiosis & Mitosis Process
... The process by which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half to form sex cells. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. Then line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Move to upset ends of the cell. Two new cells are formed. Line up in the center of the cell. Then the chromoso ...
... The process by which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half to form sex cells. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. Then line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Move to upset ends of the cell. Two new cells are formed. Line up in the center of the cell. Then the chromoso ...
Cancer Guided Notes
... ______________________: stops tumor growth _____________________: corrects mistakes in DNA made during replication ...
... ______________________: stops tumor growth _____________________: corrects mistakes in DNA made during replication ...
Mitosis and Cancer - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... Under normal conditions instructions in a cell’s DNA control its rate of cell division. ...
... Under normal conditions instructions in a cell’s DNA control its rate of cell division. ...
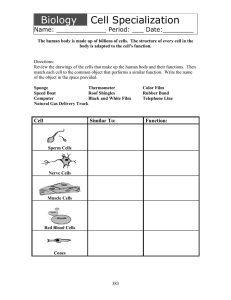
cell specialization
... Name: _____________ Period: ___ Date:________ The human body is made up of billions of cells. The structure of every cell in the body is adapted to the cell’s function. ...
... Name: _____________ Period: ___ Date:________ The human body is made up of billions of cells. The structure of every cell in the body is adapted to the cell’s function. ...
Microscope and Cell Theory
... Cell Theory • The ideas of these scientists lead to the cell theory 1 All living things are composed of cells. 2 Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. 3 All cells come from preexisting cells. ...
... Cell Theory • The ideas of these scientists lead to the cell theory 1 All living things are composed of cells. 2 Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. 3 All cells come from preexisting cells. ...
Cancer Cells - Answers - Iowa State University
... Who was Henrietta Lacks and why was she important? Henrietta Lacks was a women who developed Cervical Cancer in the late 1940s, early 50s (died in 1951). These were the first cancer cells to be culture (from a pap smear, in vitro). These cells were deemed ‘immortal’ because they never died - they ju ...
... Who was Henrietta Lacks and why was she important? Henrietta Lacks was a women who developed Cervical Cancer in the late 1940s, early 50s (died in 1951). These were the first cancer cells to be culture (from a pap smear, in vitro). These cells were deemed ‘immortal’ because they never died - they ju ...
Bio07_TR_U03_CH10.QXD
... 5. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about external regulators. a. They direct cells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle. b. They prevent the cell from entering anaphase until all its chromosomes are attached to the mitotic spindle. c. They include growth factors. d. They prevent e ...
... 5. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about external regulators. a. They direct cells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle. b. They prevent the cell from entering anaphase until all its chromosomes are attached to the mitotic spindle. c. They include growth factors. d. They prevent e ...
HeLa

A HeLa cell /ˈhiːlɑː/, also Hela or hela cell, is a cell type in an immortal cell line used in scientific research. It is the oldest and most commonly used human cell line. The line was derived from cervical cancer cells taken on February 8, 1951, from Henrietta Lacks, a patient who eventually died of her cancer on October 4, 1951. The cell line was found to be remarkably durable and prolific — which has led to its contamination of many other cell lines used in research.The cells from Lacks's tumor were taken without her knowledge or consent by researcher George Gey, who found that they could be kept alive. Before this, cells cultured from other cells would only survive for a few days. Scientists spent more time trying to keep the cells alive than performing actual research on the cells, but some cells from Lacks's tumor sample behaved differently from others. George Gey was able to isolate one specific cell, multiply it, and start a cell line. Gey named the sample HeLa, after the initial letters of Henrietta Lacks' name. As the first human cells grown in a lab that were ""immortal"" (they do not die after a few cell divisions), they could be used for conducting many experiments. This represented an enormous boon to medical and biological research.The stable growth of HeLa enabled a researcher at the University of Minnesota hospital to successfully grow polio virus, enabling the development of a vaccine. By 1954 Jonas Salk developed a vaccine for polio using these cells. To test Salk's new vaccine, the cells were quickly put into mass production in the first-ever cell production factory.In 1955 HeLa cells were the first human cells successfully cloned.Demand for the HeLa cells quickly grew. Since they were put into mass production, Lacks's cells have been used by scientists around the globe for ""research into cancer, AIDS, the effects of radiation and toxic substances, gene mapping, and countless other scientific pursuits"". HeLa cells have been used to test human sensitivity to tape, glue, cosmetics, and many other products. Scientists have grown some 20 tons of her cells, and there are almost 11,000 patents involving HeLa cells.