Microsoft Word Document
... Video – How the Universe Works: Supernovas (Discovery Channel 2010) 1. If a supernova occurred within a few dozen lightyears of earth, how would it affect life on our ...
... Video – How the Universe Works: Supernovas (Discovery Channel 2010) 1. If a supernova occurred within a few dozen lightyears of earth, how would it affect life on our ...
Bez tytułu slajdu
... The neutron ball is similar to a giant atomic nucleus with Z=1057. With such a big compression, neutrons start to "crowd-up", following the Pauli's rule, which does not allow them to be in the same quantum state. It is energetically useful to replace some neutrons with protons, or even by isolated q ...
... The neutron ball is similar to a giant atomic nucleus with Z=1057. With such a big compression, neutrons start to "crowd-up", following the Pauli's rule, which does not allow them to be in the same quantum state. It is energetically useful to replace some neutrons with protons, or even by isolated q ...
The Hubble Space Telescope
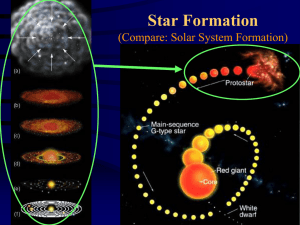
... and debris from the disk eventually nuclear fusion occurs and a STAR is BORN Heat and radiation create a stellar wind sweeping away lose matter, but some debris remains eventually clumping together to become ...
... and debris from the disk eventually nuclear fusion occurs and a STAR is BORN Heat and radiation create a stellar wind sweeping away lose matter, but some debris remains eventually clumping together to become ...
Chapter-3-Section-1-p.-64-67-Cornell
... where stars are born or where stars explode at the end of their lives o Gravity and pressure interact in a nebula to form stars ...
... where stars are born or where stars explode at the end of their lives o Gravity and pressure interact in a nebula to form stars ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... Where Stars come from: the Interstellar Medium • Gas – Single atoms and molecules – Mostly hydrogen (90%), 9% helium; deficient in heavier elements ...
... Where Stars come from: the Interstellar Medium • Gas – Single atoms and molecules – Mostly hydrogen (90%), 9% helium; deficient in heavier elements ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... • Also faintly visible at other wavelengths • A few hundred are now known • What are they? Rapidly spinning neutron stars, whose strong magnetic fields accelerate plasma to produce the beam of radio waves ...
... • Also faintly visible at other wavelengths • A few hundred are now known • What are they? Rapidly spinning neutron stars, whose strong magnetic fields accelerate plasma to produce the beam of radio waves ...
Starry Night¨ Times - October 2008
... magnification, you should start out low (40x) to find the object, and then try 100x and 200x. The name "planetary" is misleading, as these objects are not planets at all but stars at the end of their life cycle. However, they do look something like cloudy planets, and this fact confused earlier obse ...
... magnification, you should start out low (40x) to find the object, and then try 100x and 200x. The name "planetary" is misleading, as these objects are not planets at all but stars at the end of their life cycle. However, they do look something like cloudy planets, and this fact confused earlier obse ...
A1993KK54100001
... preferred to attribute these sources to distant galaxies, not to stellar objects. The pulsars now seemed to represent just the stellar objects I had discussed then. Calculations existed for the collapsed "neutron stars" that indicated approximately their size, as small as a few kilometers, and their ...
... preferred to attribute these sources to distant galaxies, not to stellar objects. The pulsars now seemed to represent just the stellar objects I had discussed then. Calculations existed for the collapsed "neutron stars" that indicated approximately their size, as small as a few kilometers, and their ...
Slide 1
... supernova is an exploding star that can become three times as bright as the sun. When a supernova occurs. All the dust particles, gas, and Dupree collect up. Creating a Nebula. These Nebulas can create many stars like our sun. Some stars can be brighter then others. This is an example of a Supernova ...
... supernova is an exploding star that can become three times as bright as the sun. When a supernova occurs. All the dust particles, gas, and Dupree collect up. Creating a Nebula. These Nebulas can create many stars like our sun. Some stars can be brighter then others. This is an example of a Supernova ...
Hubble Offers a Dazzling View of Necklace Nebula
... gasps have caught the eye of astronomers. They used the Hubble Space Telescope to view the Necklace Nebula, socalled because of its resemblance to a piece of glittering jewelry. ...
... gasps have caught the eye of astronomers. They used the Hubble Space Telescope to view the Necklace Nebula, socalled because of its resemblance to a piece of glittering jewelry. ...
Lecture19
... Crab nebula: believed to be the remnant of the supernova that went off in 1054 A.D. Nebula is still expanding, at ~1450 km/s The source of the ...
... Crab nebula: believed to be the remnant of the supernova that went off in 1054 A.D. Nebula is still expanding, at ~1450 km/s The source of the ...
Slide 1
... it will become a red giant fairly quickly. • When its fusion stops, a central iron core remains. • The temperature heats up dramatically and causes a supernova. • A neutron star is the mass that remains. ...
... it will become a red giant fairly quickly. • When its fusion stops, a central iron core remains. • The temperature heats up dramatically and causes a supernova. • A neutron star is the mass that remains. ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... sun will enter the ______________ _____________ phase, which means it loses its outer layers. The star’s mass is lost until it collapses into a _____________ dwarf, which will lose energy and become a ______________ dwarf. ...
... sun will enter the ______________ _____________ phase, which means it loses its outer layers. The star’s mass is lost until it collapses into a _____________ dwarf, which will lose energy and become a ______________ dwarf. ...
Stellar Evolution
... Nova explosion In many cases: Cycle of repeating explosions every few years – decades. ...
... Nova explosion In many cases: Cycle of repeating explosions every few years – decades. ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... form a protostar • Depending on the size of the star that forms, a different fate is met • Low and medium mass stars burn out to become white dwarfs • High mass stars burn out in an amazing explosion called a supernova, which gives birth to a new nebula ...
... form a protostar • Depending on the size of the star that forms, a different fate is met • Low and medium mass stars burn out to become white dwarfs • High mass stars burn out in an amazing explosion called a supernova, which gives birth to a new nebula ...
Objects Beyond our Solar System
... black dwarf…this has yet to happen as it is estimated to take longer than the known age of the universe, 13.8 billion years. ...
... black dwarf…this has yet to happen as it is estimated to take longer than the known age of the universe, 13.8 billion years. ...
observingnebulaeclusters-1
... Space Telescope Science Institute. It begins with a "backyard" view of the sky around the constellation Orion (by Skip Westphal, STScI) and a more detailed view of the Orion Nebula, M42 . Images taken with the 4-meter telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory. A spectacular cloud of gas surrounds ...
... Space Telescope Science Institute. It begins with a "backyard" view of the sky around the constellation Orion (by Skip Westphal, STScI) and a more detailed view of the Orion Nebula, M42 . Images taken with the 4-meter telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory. A spectacular cloud of gas surrounds ...
The Life of Stars
... Stars smaller than our sun never become red giants – they just fizzle out into white dwarfs ...
... Stars smaller than our sun never become red giants – they just fizzle out into white dwarfs ...
Nebulas & Stars
... is PKS-2349 which is only about 1500 million light years away from Earth Quasars can live for a very long time scientists say that quasars that were discovered around 35 ...
... is PKS-2349 which is only about 1500 million light years away from Earth Quasars can live for a very long time scientists say that quasars that were discovered around 35 ...
Physical Science 1 Quiz 10 1 ID # or name:
... 3. (1 pt.) Gas and dust distributed among the stars is known as the _______________. a. interstellar vacuum b. interstellar void c. ...
... 3. (1 pt.) Gas and dust distributed among the stars is known as the _______________. a. interstellar vacuum b. interstellar void c. ...
Eagle Nebula - Amazing Space
... Fast Facts Age The Eagle Nebula is two million years old, the EGGs will live for another 1020,000 years. Location In the constellation Serpens, the Serpent, alongside the southern Milky Way Distance from Earth 7,000 light years ...
... Fast Facts Age The Eagle Nebula is two million years old, the EGGs will live for another 1020,000 years. Location In the constellation Serpens, the Serpent, alongside the southern Milky Way Distance from Earth 7,000 light years ...
Chapter 13
... Nearby supernovae (< 50 light years) could kill many life forms on Earth through gamma radiation and high-energy particles. ...
... Nearby supernovae (< 50 light years) could kill many life forms on Earth through gamma radiation and high-energy particles. ...
Life Cycle of Stars: Chapter 21
... • Becomes a red giant as hydrogen is depleted • Expands and collapses to facilitate helium burning – Becomes helium burning star ...
... • Becomes a red giant as hydrogen is depleted • Expands and collapses to facilitate helium burning – Becomes helium burning star ...
Crab Nebula

The Crab Nebula (catalogue designations M1, NGC 1952, Taurus A) is a supernova remnant and pulsar wind nebula in the constellation of Taurus. It is not, as its name might suggest, in Cancer. The now-current name is due to William Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse, who observed the object in 1840 using a 36-inch telescope and produced a drawing that looked somewhat like a crab. Corresponding to a bright supernova recorded by Chinese astronomers in 1054, the nebula was observed later by English astronomer John Bevis in 1731. The nebula was the first astronomical object identified with a historical supernova explosion.At an apparent magnitude of 8.4, comparable to that of Saturn's moon Titan, it is not visible to the naked eye but can be made out using binoculars under favourable conditions. The nebula lies in the Perseus Arm of the Milky Way galaxy, at a distance of about 2.0 kiloparsecs (6,500 ly) from Earth. It has a diameter of 3.4 parsecs (11 ly), corresponding to an apparent diameter of some 7 arcminutes, and is expanding at a rate of about 1,500 kilometres per second (930 mi/s), or 0.5% c.At the center of the nebula lies the Crab Pulsar, a neutron star 28–30 kilometres (17–19 mi) across with a spin rate of 30.2 times per second, which emits pulses of radiation from gamma rays to radio waves. At X-ray and gamma ray energies above 30 keV, the Crab is generally the strongest persistent source in the sky, with measured flux extending to above 10 TeV. The nebula's radiation allows for the detailed studying of celestial bodies that occult it. In the 1950s and 1960s, the Sun's corona was mapped from observations of the Crab's radio waves passing through it, and in 2003, the thickness of the atmosphere of Saturn's moon Titan was measured as it blocked out X-rays from the nebula.