The Hidden Lives of Galaxies NSTA 2001
... How does the sun produce energy? How is fusion different from bonding? Do small stars or large stars burn faster? Do small stars or large stars burn hotter? When does fusion stop in a red supergiant? Why? What determines the life cycle of a star? Where do stars begin to form? Why are ty ...
... How does the sun produce energy? How is fusion different from bonding? Do small stars or large stars burn faster? Do small stars or large stars burn hotter? When does fusion stop in a red supergiant? Why? What determines the life cycle of a star? Where do stars begin to form? Why are ty ...
Handout Life of Stars
... variety of atoms we see in the universe around us. The Sun’s own gravity traps and squeezes this ultra-hot gas into a confined space, thus generating enough heat for the fusion reaction to take place. The process remains in equilibrium as long as it retains enough fuel to create this heat- and light ...
... variety of atoms we see in the universe around us. The Sun’s own gravity traps and squeezes this ultra-hot gas into a confined space, thus generating enough heat for the fusion reaction to take place. The process remains in equilibrium as long as it retains enough fuel to create this heat- and light ...
Physics-Y11-LP3 - All Saints` Catholic High School
... • understand the role of observations of Cepheid variable stars in establishing the scale of the Universe and the nature of most spiral nebulas as distant galaxies • describe some of the new information that telescopes revealed about the Milky Way and objects beyond the Milky Way • recall the main i ...
... • understand the role of observations of Cepheid variable stars in establishing the scale of the Universe and the nature of most spiral nebulas as distant galaxies • describe some of the new information that telescopes revealed about the Milky Way and objects beyond the Milky Way • recall the main i ...
The Superhero's Universe: Observing the Cosmos with X-ray Vision and Beyond
... Galaxy: Centaurus A ★ Discovered in 1847 ★ 14 million light-years away ★ 5th brightest visible galaxy ...
... Galaxy: Centaurus A ★ Discovered in 1847 ★ 14 million light-years away ★ 5th brightest visible galaxy ...
Nebula Beginnings - University of Dayton
... This image from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope shows for the first time the inner region of a 200-billion mile diameter dust disk around the star Beta Pictoris. This region has long been hidden from ground-based telescopes because of the glare from the central star. The disk is slightly warped. If th ...
... This image from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope shows for the first time the inner region of a 200-billion mile diameter dust disk around the star Beta Pictoris. This region has long been hidden from ground-based telescopes because of the glare from the central star. The disk is slightly warped. If th ...
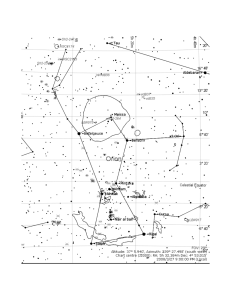
CONSTELLATION CASSIOPEIA named after the
... The constellation is named after Cassiopeia, the queen of Aethiopia. She was the wife of Cepheus, King of Aethiopia and mother of Princess Andromeda who was bound to a rock as prey for the monster Cetus as punishment for Cassiopeia’s boast to be more beautiful than the Nereids. Andromeda was rescued ...
... The constellation is named after Cassiopeia, the queen of Aethiopia. She was the wife of Cepheus, King of Aethiopia and mother of Princess Andromeda who was bound to a rock as prey for the monster Cetus as punishment for Cassiopeia’s boast to be more beautiful than the Nereids. Andromeda was rescued ...
Constellations - Sierra Star Gazers
... Cepheus (CEE-fee-us), the King, is another of the circumpolar constellations, which means that it too may be observed any time of the year. Look for Cepheus between Cassiopeia to the north and the constellations Cygnus and Lyra to the south. Herschel’s Garnet Star , Mu () Cephei, is a 4th magnitude ...
... Cepheus (CEE-fee-us), the King, is another of the circumpolar constellations, which means that it too may be observed any time of the year. Look for Cepheus between Cassiopeia to the north and the constellations Cygnus and Lyra to the south. Herschel’s Garnet Star , Mu () Cephei, is a 4th magnitude ...
Assessment Schedule
... appearance of a supernova. OR Explains gas clouds are the birth places for new stars. Supernova gives out clouds of gases and plasma exploding off its surface. AND These gas clouds are the birth places for new stars. AND After this process ceases, a black hole or a dense neutron star remains (detail ...
... appearance of a supernova. OR Explains gas clouds are the birth places for new stars. Supernova gives out clouds of gases and plasma exploding off its surface. AND These gas clouds are the birth places for new stars. AND After this process ceases, a black hole or a dense neutron star remains (detail ...
Level 2 Science (90764) 2011 Assessment Schedule
... appearance of a supernova. OR Explains gas clouds are the birth places for new stars. Supernova gives out clouds of gases and plasma exploding off its surface. AND These gas clouds are the birth places for new stars. AND After this process ceases, a black hole or a dense neutron star remains (detail ...
... appearance of a supernova. OR Explains gas clouds are the birth places for new stars. Supernova gives out clouds of gases and plasma exploding off its surface. AND These gas clouds are the birth places for new stars. AND After this process ceases, a black hole or a dense neutron star remains (detail ...
Written in the stars THE NOBEL PRIZE IN PHYSICS 2011
... This year’s Nobel Laureates expected to measure the cosmic deceleration, or how the expansion of the Universe is slowing. Their method was in principle the same as the one used by astronomers more than six decades earlier: to locate distant stars and to measure how they move. However, that is easier ...
... This year’s Nobel Laureates expected to measure the cosmic deceleration, or how the expansion of the Universe is slowing. Their method was in principle the same as the one used by astronomers more than six decades earlier: to locate distant stars and to measure how they move. However, that is easier ...
Astronomy
... Some neutron stars spin, these are pulsars – Links: Cosmic Pearls supernova, Elusive Jellyfish nebula (neutron star), Tycho’s Supernova Remnant, A Dark Pulsar in CTA 1, Crab Pulsar Wind Nebula ...
... Some neutron stars spin, these are pulsars – Links: Cosmic Pearls supernova, Elusive Jellyfish nebula (neutron star), Tycho’s Supernova Remnant, A Dark Pulsar in CTA 1, Crab Pulsar Wind Nebula ...
Stellar Structure - McMurry University
... A. The temperature at their centers never gets high enough. B. The density at their centers is too low. C. Iron fusion consumes energy. D. Not enough iron is present. ...
... A. The temperature at their centers never gets high enough. B. The density at their centers is too low. C. Iron fusion consumes energy. D. Not enough iron is present. ...
Black Hole
... After all the Hydrogen in the star was converted to Helium, for about a Million years other elements such as Carbon And others are cooked within the Star. The Supernova then throws them out in the Faraway Sky. Thus all the elements of which our Human Bodies are made were Cooked in faraway stars once ...
... After all the Hydrogen in the star was converted to Helium, for about a Million years other elements such as Carbon And others are cooked within the Star. The Supernova then throws them out in the Faraway Sky. Thus all the elements of which our Human Bodies are made were Cooked in faraway stars once ...
starevolution - Global Change Program
... supernova remnant is 6,500 light years away. Another beautiful example of a supernova remnant is the Cygnus Loop, lying about 2,500 light years away (on right). The evolution of even more massive stars produce other objects in our universe. Perhaps the most intriguing object that can form from a mas ...
... supernova remnant is 6,500 light years away. Another beautiful example of a supernova remnant is the Cygnus Loop, lying about 2,500 light years away (on right). The evolution of even more massive stars produce other objects in our universe. Perhaps the most intriguing object that can form from a mas ...
Measuring Distances - Stockton University
... nature of galaxies which many had thought until that point to be part of our own Galaxy. • Cepheids continue to be one of the cornerstones of astronomy today. ...
... nature of galaxies which many had thought until that point to be part of our own Galaxy. • Cepheids continue to be one of the cornerstones of astronomy today. ...
Cosmology Handouts
... Rainbows reveal that white light is a combination of all the colours. In 1666, Isaac Newton showed that white light could be separated into its component colours using glass prisms. Soon scientists were using this new tool to analyze the light coming from several different light sources. Some scient ...
... Rainbows reveal that white light is a combination of all the colours. In 1666, Isaac Newton showed that white light could be separated into its component colours using glass prisms. Soon scientists were using this new tool to analyze the light coming from several different light sources. Some scient ...
Hubble`s Expansion of the Universe
... As we go further out into the Universe, eventually we are no longer able to use Cepheid variables as a distance indicator as they become too faint. At this point, we use another object known as type Ia supernovae. A supernova marks the end of a star’s life in an extremely energetic explosion. When a ...
... As we go further out into the Universe, eventually we are no longer able to use Cepheid variables as a distance indicator as they become too faint. At this point, we use another object known as type Ia supernovae. A supernova marks the end of a star’s life in an extremely energetic explosion. When a ...
Astronomy 103 Exam 2 Review
... surface and one at rest high above the Earth’s surface. Which statement is correct? A. Each observer will see the other's clock to be running slow with respect to the observer's own clock. B. Each observer will see the other's clock to be running fast with respect to the observer's own clock ...
... surface and one at rest high above the Earth’s surface. Which statement is correct? A. Each observer will see the other's clock to be running slow with respect to the observer's own clock. B. Each observer will see the other's clock to be running fast with respect to the observer's own clock ...
The Mass Assembly of Galaxies
... but may be in conflict with the photometric temperature scale. Determination of Teff to 50K is required. Interesting challenge for the VLTI? ...
... but may be in conflict with the photometric temperature scale. Determination of Teff to 50K is required. Interesting challenge for the VLTI? ...
Astronomy Fall 2013 Final Exam History of Astronomy Know: speed
... light on earth you see a flash of light like a light house. 7. What produces a Type II supernova? Supermassive (greater than 12 solar masses) cloud starts fusing elements until it makes an iron core- then it recoils and explodes 8.Almost half of all known millisecond pulsars are found in what type o ...
... light on earth you see a flash of light like a light house. 7. What produces a Type II supernova? Supermassive (greater than 12 solar masses) cloud starts fusing elements until it makes an iron core- then it recoils and explodes 8.Almost half of all known millisecond pulsars are found in what type o ...
Supernovae
... monuclear reactions and prevent the runaway process. Eventually, the temperature increases to the level where the thermal and degenerate-electron pressure components become comparable and the material begins to expand, but at that time, the expansion is unable to quench the fast thermonuclear burni ...
... monuclear reactions and prevent the runaway process. Eventually, the temperature increases to the level where the thermal and degenerate-electron pressure components become comparable and the material begins to expand, but at that time, the expansion is unable to quench the fast thermonuclear burni ...
Unit 60 to 79
... b. Exceed its Chandrasekhar limit c. Have begun life as a high-mass star d. Continue the fusion cycle until its core is completely composed of iron 7) Which of the following events will not leave any remnant? a. Type I supernova b. Type II supernova c. Nova 8) The Sun will likely never become a nova ...
... b. Exceed its Chandrasekhar limit c. Have begun life as a high-mass star d. Continue the fusion cycle until its core is completely composed of iron 7) Which of the following events will not leave any remnant? a. Type I supernova b. Type II supernova c. Nova 8) The Sun will likely never become a nova ...
History of supernova observation

The known history of supernova observation goes back to 185 CE, when, supernova SN 185 appeared, the oldest appearance of a supernova recorded by humankind. Several additional supernovae within the Milky Way galaxy have been recorded since that time, with SN 1604 being the most recent supernova to be observed in this galaxy.Since the development of the telescope, the field of supernova discovery has expanded to other galaxies. These occurrences provide important information on the distances of galaxies. Successful models of supernova behavior have also been developed, and the role of supernovae in the star formation process is now increasingly understood.