Formation of the Solar System Section 28.1
... Center of mass Newton determined that each planet orbits a point between it and the Sun called the center of mass. Just as the balance point on a seesaw is closer to the heavier box, the center of mass between two orbiting bodies is closer to the more massive body. ...
... Center of mass Newton determined that each planet orbits a point between it and the Sun called the center of mass. Just as the balance point on a seesaw is closer to the heavier box, the center of mass between two orbiting bodies is closer to the more massive body. ...
Longevity of moons around habitable planets
... hypothesis, Earth’s initial angular spin velocity would have been from 5 to 8 h rev− 1 and the initial Earth–Moon distance is * 20 000 km corresponding to the orbital angular velocity of 7.8 h rev− 1. The Earth–Moon system may have thus started near a planet–moon synchronized state, but an unstable ...
... hypothesis, Earth’s initial angular spin velocity would have been from 5 to 8 h rev− 1 and the initial Earth–Moon distance is * 20 000 km corresponding to the orbital angular velocity of 7.8 h rev− 1. The Earth–Moon system may have thus started near a planet–moon synchronized state, but an unstable ...
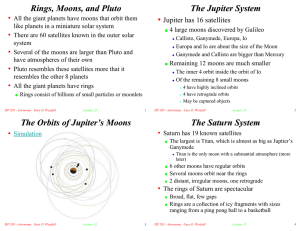
Rings, Moons, and Pluto The Jupiter System The Orbits of Jupiter`s
... Titans were a family of giants, the children of Uranus and Gaia, who sought to rule the heavens but were overthrown and supplanted by the family of Zeus. ...
... Titans were a family of giants, the children of Uranus and Gaia, who sought to rule the heavens but were overthrown and supplanted by the family of Zeus. ...
Lecture13
... 1655 by the Dutch Astronomer Christian Huygens, the first moon to be found after Galileo saw the four large moons of Jupiter Titan is roughly the same size as Callisto and Ganymede but its composition is unknown Titan has a substantial atmosphere ...
... 1655 by the Dutch Astronomer Christian Huygens, the first moon to be found after Galileo saw the four large moons of Jupiter Titan is roughly the same size as Callisto and Ganymede but its composition is unknown Titan has a substantial atmosphere ...
ASTR 1010 Homework Solutions
... and the north celestial pole at the top of the diagram. (b) For an observer at the equator, Figure 2-10 would have the Earth’s poles and the celestial poles at the sides of the diagram, 90° away from the top. (c) Since the north pole is at 90° N latitude and the north celestial pole is 90° above the ...
... and the north celestial pole at the top of the diagram. (b) For an observer at the equator, Figure 2-10 would have the Earth’s poles and the celestial poles at the sides of the diagram, 90° away from the top. (c) Since the north pole is at 90° N latitude and the north celestial pole is 90° above the ...
Analysis of Two Pulsating X-ray Sources
... itself is the stellar core of a Sun-sized star at the end of its evolutionary history – a rotating carbon core. The light curve above is produced by the dynamics of the system and not the white dwarf itself, which emits most of its radiation in X-rays. More massive stars, which catastrophically coll ...
... itself is the stellar core of a Sun-sized star at the end of its evolutionary history – a rotating carbon core. The light curve above is produced by the dynamics of the system and not the white dwarf itself, which emits most of its radiation in X-rays. More massive stars, which catastrophically coll ...
Atmospheric circulations of terrestrial planets orbiting low
... Within the past few years, planets not much larger than Earth, so-called ‘‘superEarths’’, have been discovered in orbit around nearby M stars (Udry et al., 2007; Von Bloh et al., 2008). Earth-size M-star planets may be found within the near future (Basri et al., 2005). These planets are expected to ...
... Within the past few years, planets not much larger than Earth, so-called ‘‘superEarths’’, have been discovered in orbit around nearby M stars (Udry et al., 2007; Von Bloh et al., 2008). Earth-size M-star planets may be found within the near future (Basri et al., 2005). These planets are expected to ...
PDF - Amazing Space, STScI
... Pluto’s only other known moon. The moons’ common color further reinforces the idea that all three moons were born from a single titanic collision between Pluto and another similarly sized Kuiper Belt object billions of years ago. With Hubble’s help, astronomers discovered that another Kuiper Belt ob ...
... Pluto’s only other known moon. The moons’ common color further reinforces the idea that all three moons were born from a single titanic collision between Pluto and another similarly sized Kuiper Belt object billions of years ago. With Hubble’s help, astronomers discovered that another Kuiper Belt ob ...
September 2013 - astronomy for beginners
... After the summer recess we are back and into the 2013 – 2014 astronomical observing session that runs from September 2013 through to June 2014. The Newbury Astronomical Society had its most successful year in the last session. The membership of the society is now at an all-time high with 100 paid up ...
... After the summer recess we are back and into the 2013 – 2014 astronomical observing session that runs from September 2013 through to June 2014. The Newbury Astronomical Society had its most successful year in the last session. The membership of the society is now at an all-time high with 100 paid up ...
Moons, Pluto, and Rings - Wayne State University
... direction, or else have orbits with high eccentricity or high inclination These satellites are usually smaller, located relatively far from their planet, probably formed far away and subsequently captured by the planet they now orbit 22 February 2005 ...
... direction, or else have orbits with high eccentricity or high inclination These satellites are usually smaller, located relatively far from their planet, probably formed far away and subsequently captured by the planet they now orbit 22 February 2005 ...
Extrasolar Planets: An Amateur`s Search
... are limited, if one could better know what stars to observe with these methods, the likelihood of finding such planets might increase. Thus, the importance of this study in understanding the planet forming factors of stars. 1.2 Planetary Formation and Planet Forming Factors There has been significan ...
... are limited, if one could better know what stars to observe with these methods, the likelihood of finding such planets might increase. Thus, the importance of this study in understanding the planet forming factors of stars. 1.2 Planetary Formation and Planet Forming Factors There has been significan ...
Comet-like tail-formation of exospheres of hot rocky exoplanets
... study the thermal evaporation of hydrogen-rich exoplanets by applying a mass loss formula which includes Roche Lobe effects, heating efficiencies, etc. and are in agreement with hydrodynamic model results during evolutionary epochs (Penz et al., 2008). Leitzinger et al. (2009) placed virtual exoplane ...
... study the thermal evaporation of hydrogen-rich exoplanets by applying a mass loss formula which includes Roche Lobe effects, heating efficiencies, etc. and are in agreement with hydrodynamic model results during evolutionary epochs (Penz et al., 2008). Leitzinger et al. (2009) placed virtual exoplane ...
August Newsletter
... What's Up in the Night Sky? There are five August constellations right above us (in the southern hemisphere) and include some of the most spectacular and well-known objects in the sky. The centre of our Milky Way galaxy is located in the direction of Sagittarius and because of this Sagittarius cont ...
... What's Up in the Night Sky? There are five August constellations right above us (in the southern hemisphere) and include some of the most spectacular and well-known objects in the sky. The centre of our Milky Way galaxy is located in the direction of Sagittarius and because of this Sagittarius cont ...
Teachers` Manual - Amundsen High School
... Structure of Atoms (nucleus and orbiting electrons) The Elements (number of protons in nucleus determines kind of element) Atoms store energy by lifting electrons to higher orbits Return of electron to lower orbit releases energy which appears as light (or more generally, electromagnetic radiation) ...
... Structure of Atoms (nucleus and orbiting electrons) The Elements (number of protons in nucleus determines kind of element) Atoms store energy by lifting electrons to higher orbits Return of electron to lower orbit releases energy which appears as light (or more generally, electromagnetic radiation) ...
The Moon - DTFizzix
... The Moon rotates once each time it orbits the Earth, as can be seen from the changing position of the exaggerated lunar mountain. Notice that at (A) the lunar peak is to the right, while at (B) it is to the left. Thus, from the Earth, we always see the same side of the Moon even though it turns on ...
... The Moon rotates once each time it orbits the Earth, as can be seen from the changing position of the exaggerated lunar mountain. Notice that at (A) the lunar peak is to the right, while at (B) it is to the left. Thus, from the Earth, we always see the same side of the Moon even though it turns on ...
EVENT HORIZON November 2014 T M
... of the wonders of our night sky. If you are a solar observer, then you’ll know that the Sun has put on quite a show over the last 10 days with a massive sunspot group named AR2192. This object was so active and so large that it grew to nearly the size of the planet Jupiter and was the largest sunspo ...
... of the wonders of our night sky. If you are a solar observer, then you’ll know that the Sun has put on quite a show over the last 10 days with a massive sunspot group named AR2192. This object was so active and so large that it grew to nearly the size of the planet Jupiter and was the largest sunspo ...
A Human-Powered Orrery: Connecting Learners with the Night Sky*
... motions each of the planets around the Sun. For Venus, Earth, and Mars, each circle represents 16 days of orbital motion. Because Mercury moves much faster in its orbit, the circles are separated by 8 day intervals. Use Table 1 below to find where a planet is located on any given date. We use six al ...
... motions each of the planets around the Sun. For Venus, Earth, and Mars, each circle represents 16 days of orbital motion. Because Mercury moves much faster in its orbit, the circles are separated by 8 day intervals. Use Table 1 below to find where a planet is located on any given date. We use six al ...
the ringed giants – jupiter and saturn
... In the year 2003 alone, 21 new moons were discovered orbiting Jupiter. New telescope technology has made it possible to detect fainter objects than ever before. Jupiter is now known to have 61 natural satellites (Saturn has 31). The majority of these are smaller than 200 km diameter, in fact, the ne ...
... In the year 2003 alone, 21 new moons were discovered orbiting Jupiter. New telescope technology has made it possible to detect fainter objects than ever before. Jupiter is now known to have 61 natural satellites (Saturn has 31). The majority of these are smaller than 200 km diameter, in fact, the ne ...
society journal - Auckland Astronomical Society
... Next month’s film night will be on Monday 22th December at 8pm at Stardome. It features A film from the Sci Fi Science series that looks at how future space travel might work and whether it could be possible to travel faster than the speed of light. This is a very futuristic view of space travel tak ...
... Next month’s film night will be on Monday 22th December at 8pm at Stardome. It features A film from the Sci Fi Science series that looks at how future space travel might work and whether it could be possible to travel faster than the speed of light. This is a very futuristic view of space travel tak ...
powerpoint - High Energy Physics at Wayne State
... The dust tail forms when solar photons collide with the dust in the coma. Ejected dust particles form a long, curved tail that lies slightly farther our from the Sun than the nucleus' orbit. The dust tail has a yellow-white color from reflected sunlight. Both of the tails will stretch for millions ...
... The dust tail forms when solar photons collide with the dust in the coma. Ejected dust particles form a long, curved tail that lies slightly farther our from the Sun than the nucleus' orbit. The dust tail has a yellow-white color from reflected sunlight. Both of the tails will stretch for millions ...
the curious incident of the dog in the night-time
... more quickly the burning transitions to heavier elements in the core. When the original mass of a star is too great, the end result is an explosion that sprays all those heavy elements into space. A star that explodes in this way is called a supernova, of which there are a few types. When the hydrog ...
... more quickly the burning transitions to heavier elements in the core. When the original mass of a star is too great, the end result is an explosion that sprays all those heavy elements into space. A star that explodes in this way is called a supernova, of which there are a few types. When the hydrog ...
5th Grade “I Can Statements”
... I can describe and demonstrate with models or drawings that a lunar eclipse occurs when the sun, Earth, and full moon are aligned with the earth in the middle, and the moon passes through the earth's shadow. I can describe and demonstrate with models or drawings that a solar eclipse occurs when the ...
... I can describe and demonstrate with models or drawings that a lunar eclipse occurs when the sun, Earth, and full moon are aligned with the earth in the middle, and the moon passes through the earth's shadow. I can describe and demonstrate with models or drawings that a solar eclipse occurs when the ...
Poster 49 | PDF (852 kB)
... T dwarfs are the coolest and least massive compact astrophysical objects that we can directly observe outside our Solar System. They share many properties with the expanding population of known exoplanets (almost all of which are inaccessible to direct observation themselves). An understanding of T ...
... T dwarfs are the coolest and least massive compact astrophysical objects that we can directly observe outside our Solar System. They share many properties with the expanding population of known exoplanets (almost all of which are inaccessible to direct observation themselves). An understanding of T ...
Definition of planet

The definition of planet, since the word was coined by the ancient Greeks, has included within its scope a wide range of celestial bodies. Greek astronomers employed the term asteres planetai (ἀστέρες πλανῆται), ""wandering stars"", for star-like objects which apparently moved over the sky. Over the millennia, the term has included a variety of different objects, from the Sun and the Moon to satellites and asteroids.By the end of the 19th century the word planet, though it had yet to be defined, had become a working term applied only to a small set of objects in the Solar System. After 1992, however, astronomers began to discover many additional objects beyond the orbit of Neptune, as well as hundreds of objects orbiting other stars. These discoveries not only increased the number of potential planets, but also expanded their variety and peculiarity. Some were nearly large enough to be stars, while others were smaller than Earth's moon. These discoveries challenged long-perceived notions of what a planet could be.The issue of a clear definition for planet came to a head in 2005 with the discovery of the trans-Neptunian object Eris, a body more massive than the smallest then-accepted planet, Pluto. In its 2006 response, the International Astronomical Union (IAU), recognised by astronomers as the world body responsible for resolving issues of nomenclature, released its decision on the matter. This definition, which applies only to the Solar System, states that a planet is a body that orbits the Sun, is massive enough for its own gravity to make it round, and has ""cleared its neighbourhood"" of smaller objects around its orbit. Under this new definition, Pluto and the other trans-Neptunian objects do not qualify as planets. The IAU's decision has not resolved all controversies, and while many scientists have accepted the definition, some in the astronomical community have rejected it outright.