Astronomy Review Sheet
... 13. How did technology and/or new methods help to change the model of the solar system? Telescopes made the discovery of Jupiter’s moons possible; new methods like using math and the scientific method helped prove the heliocentric model was correct. ...
... 13. How did technology and/or new methods help to change the model of the solar system? Telescopes made the discovery of Jupiter’s moons possible; new methods like using math and the scientific method helped prove the heliocentric model was correct. ...
Review Questions - Dublin City Schools
... 7. The moon’s orbit around the Earth takes approximately how long? (one month) 8. When we can see the half of the moon that is completely reflecting the sun’s light, which phase are we experiencing? (full moon) 9. The moon has three motions: name one of them (it rotates on its axis, it revolves arou ...
... 7. The moon’s orbit around the Earth takes approximately how long? (one month) 8. When we can see the half of the moon that is completely reflecting the sun’s light, which phase are we experiencing? (full moon) 9. The moon has three motions: name one of them (it rotates on its axis, it revolves arou ...
File
... • Is a solid rocky and/or metallic body that independently orbits the sun • Irregular shape with no atmosphere • Large percentage orbit between Mars and Jupiter • Much smaller than planets (100-1000 km in diameter ...
... • Is a solid rocky and/or metallic body that independently orbits the sun • Irregular shape with no atmosphere • Large percentage orbit between Mars and Jupiter • Much smaller than planets (100-1000 km in diameter ...
Science: Solar System Chapter 2 Study Notes
... Two different views of the Solar System: 1. Geocentric System – Earth is at the center and the planets revolve around Earth. Ptolemy (Greek astronomer) thought that the planets revolve around Earth. Ancient Greek model of the universe 2. Heliocentric System – Sun is at the center and planets rev ...
... Two different views of the Solar System: 1. Geocentric System – Earth is at the center and the planets revolve around Earth. Ptolemy (Greek astronomer) thought that the planets revolve around Earth. Ancient Greek model of the universe 2. Heliocentric System – Sun is at the center and planets rev ...
Solar System and Inner Planets
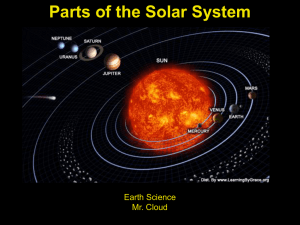
... Solar System and Inner Planets planet-large body of matter that revolves around the sun sun-93 million miles away from Earth the closest star to earth inner planets-planets that are closest to the sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Mercury-closest to the sun NOT the hottest planet does NOT h ...
... Solar System and Inner Planets planet-large body of matter that revolves around the sun sun-93 million miles away from Earth the closest star to earth inner planets-planets that are closest to the sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Mercury-closest to the sun NOT the hottest planet does NOT h ...
exploring plantetary systems 2017 study guide
... 17.This body is no longer consider a planet because it is least like its close neighbor is _PLUTO______. 18.____COPERNICUS___ published the Sun-centered model of the solar system in 1543. 19.When small pieces of rock moving through space enter Earth’s atmosphere and completely burn up, they are call ...
... 17.This body is no longer consider a planet because it is least like its close neighbor is _PLUTO______. 18.____COPERNICUS___ published the Sun-centered model of the solar system in 1543. 19.When small pieces of rock moving through space enter Earth’s atmosphere and completely burn up, they are call ...
The planets
... The asteroid belt is roughly located between the orbits of the planets Mars and Jupiter, and this region is where the vast majority of asteroids. ...
... The asteroid belt is roughly located between the orbits of the planets Mars and Jupiter, and this region is where the vast majority of asteroids. ...
Review Handout - Sturgeon Moodle
... Below are a few sample questions from the unit that will help you review and remember the material we discussed in class for the unit exam. Take the time to try to answer these questions yourself before you use your notes or other sources to find the answers. Before beginning your review, how do you ...
... Below are a few sample questions from the unit that will help you review and remember the material we discussed in class for the unit exam. Take the time to try to answer these questions yourself before you use your notes or other sources to find the answers. Before beginning your review, how do you ...
Extra-Solar Planets continued
... planet also sits 3 million miles from its star and whips around in a tight circular orbit once every 2.64 days. Besides the exoplanet's size, what makes the discovery remarkable is that Gliese 436 is a red dwarf star that produces only 2 or 3 percent as much light as the Sun. Stars in this category ...
... planet also sits 3 million miles from its star and whips around in a tight circular orbit once every 2.64 days. Besides the exoplanet's size, what makes the discovery remarkable is that Gliese 436 is a red dwarf star that produces only 2 or 3 percent as much light as the Sun. Stars in this category ...
Solar System Notes - Science with Mrs. Wilson
... A. Ptolemy (A.D. 140) said that the earth was the center of the universe. 1. Everything orbited around us while the earth was still. 2. Called the geocentric universe (geo – earth; centric – centered) B. Copernicus (1500s) believed that the sun was the center of the universe. 1. Everything orbited a ...
... A. Ptolemy (A.D. 140) said that the earth was the center of the universe. 1. Everything orbited around us while the earth was still. 2. Called the geocentric universe (geo – earth; centric – centered) B. Copernicus (1500s) believed that the sun was the center of the universe. 1. Everything orbited a ...
Study Guide for Quiz on Astronomy: The Moon, Sun
... 17. How is distance measured in the universe? __________________________________________ 18. In which galaxy do we live? __________________________________What kind of galaxy is it? ___________ At what location in our galaxy is our solar system?________________________ 19. Which planet is considered ...
... 17. How is distance measured in the universe? __________________________________________ 18. In which galaxy do we live? __________________________________What kind of galaxy is it? ___________ At what location in our galaxy is our solar system?________________________ 19. Which planet is considered ...
OurSolarSystem_part1
... Jupiter, the fifth planet from the Sun, is the largest planet in our solar system. Jupiter is so big that over 1,000 planets the size of Earth could fit into it. It has over 60 moons and 2 rings. Can life exist on Jupiter's moon, Europa? ...
... Jupiter, the fifth planet from the Sun, is the largest planet in our solar system. Jupiter is so big that over 1,000 planets the size of Earth could fit into it. It has over 60 moons and 2 rings. Can life exist on Jupiter's moon, Europa? ...
Unit 8: Astronomy
... Strongest winds in the solar system estimated at 2,500 km/hr Neptune has 8 moons ...
... Strongest winds in the solar system estimated at 2,500 km/hr Neptune has 8 moons ...
Saint Mary`s College ASTRONOMY EXAM -
... 13. According to Kepler's Second Law, when is an object in an elliptical orbit around the Sun is travelling fastest or slowest? 14. What kind of model of the solar system was devised by Claudius Ptolemy? Copernicus? ...
... 13. According to Kepler's Second Law, when is an object in an elliptical orbit around the Sun is travelling fastest or slowest? 14. What kind of model of the solar system was devised by Claudius Ptolemy? Copernicus? ...
Formation of the Solar System
... Some of it accretes, or comes together, in clouds of gas and dust About 5 billion years ago, one of these clouds began to be drawn together by gravity after it increased due to a nearby supernova or other ...
... Some of it accretes, or comes together, in clouds of gas and dust About 5 billion years ago, one of these clouds began to be drawn together by gravity after it increased due to a nearby supernova or other ...
Universal Law of Gravity Notes
... We can use gravity to figure out the mass of a planet ◦ We look at the size of the orbit of its moons, and the speed the moons are moving around the planet ◦ Next, we can figure out how strong the gravitational pull is between the moon and the planet Heavier planets=faster moons If a planet does ...
... We can use gravity to figure out the mass of a planet ◦ We look at the size of the orbit of its moons, and the speed the moons are moving around the planet ◦ Next, we can figure out how strong the gravitational pull is between the moon and the planet Heavier planets=faster moons If a planet does ...
Science Homework Week 1 Term 4
... Pluto is no longer a planet due to it’s very small mass in comparison to other planets. 4c Two other dwarf planets: Eris and Makemake 5 What does ‘terrestrial planet’ mean? It means a planet that has a surface and geological features similar to the earth’s. 6 Why is there less information about the ...
... Pluto is no longer a planet due to it’s very small mass in comparison to other planets. 4c Two other dwarf planets: Eris and Makemake 5 What does ‘terrestrial planet’ mean? It means a planet that has a surface and geological features similar to the earth’s. 6 Why is there less information about the ...
- Glasgow Science Centre
... This short activity is intended to help gauge existing knowledge about the eight planets in the solar system. Learning Objectives ...
... This short activity is intended to help gauge existing knowledge about the eight planets in the solar system. Learning Objectives ...
Our Solar System
... Earth? Here! Number three, Earth is home to you and me. Mars? Here! Number four, Red and ready to explore! Jupiter? Here! Number five, Largest planet, that's no jive! Saturn? Here! Number six, With rings of dust and ice that mix. Uranus? Here! Number seven, A planet tilted high in heaven. Neptune? H ...
... Earth? Here! Number three, Earth is home to you and me. Mars? Here! Number four, Red and ready to explore! Jupiter? Here! Number five, Largest planet, that's no jive! Saturn? Here! Number six, With rings of dust and ice that mix. Uranus? Here! Number seven, A planet tilted high in heaven. Neptune? H ...
Definition of planet

The definition of planet, since the word was coined by the ancient Greeks, has included within its scope a wide range of celestial bodies. Greek astronomers employed the term asteres planetai (ἀστέρες πλανῆται), ""wandering stars"", for star-like objects which apparently moved over the sky. Over the millennia, the term has included a variety of different objects, from the Sun and the Moon to satellites and asteroids.By the end of the 19th century the word planet, though it had yet to be defined, had become a working term applied only to a small set of objects in the Solar System. After 1992, however, astronomers began to discover many additional objects beyond the orbit of Neptune, as well as hundreds of objects orbiting other stars. These discoveries not only increased the number of potential planets, but also expanded their variety and peculiarity. Some were nearly large enough to be stars, while others were smaller than Earth's moon. These discoveries challenged long-perceived notions of what a planet could be.The issue of a clear definition for planet came to a head in 2005 with the discovery of the trans-Neptunian object Eris, a body more massive than the smallest then-accepted planet, Pluto. In its 2006 response, the International Astronomical Union (IAU), recognised by astronomers as the world body responsible for resolving issues of nomenclature, released its decision on the matter. This definition, which applies only to the Solar System, states that a planet is a body that orbits the Sun, is massive enough for its own gravity to make it round, and has ""cleared its neighbourhood"" of smaller objects around its orbit. Under this new definition, Pluto and the other trans-Neptunian objects do not qualify as planets. The IAU's decision has not resolved all controversies, and while many scientists have accepted the definition, some in the astronomical community have rejected it outright.