All About Astronomy The Planets
... and others. The sun is the center of our solar system; the planets, their moons, a belt of asteroids, comets, and other rocks and gas orbit the sun. The eight planets that orbit the sun are (in order from the sun): Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. Another large body is ...
... and others. The sun is the center of our solar system; the planets, their moons, a belt of asteroids, comets, and other rocks and gas orbit the sun. The eight planets that orbit the sun are (in order from the sun): Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. Another large body is ...
Our Solar System
... Saturn looks like a yellow star in space. When viewed through a telescope, it is seen as a golden sphere, crossed by a series of lightly colored bands parallel to the ...
... Saturn looks like a yellow star in space. When viewed through a telescope, it is seen as a golden sphere, crossed by a series of lightly colored bands parallel to the ...
Standard 1 Information Sheet
... Section C Students know the evidence from geological studies of Earth and other planets suggests that the early Earth was very different from Earth today. The prevailing theory is that Earth formed around 4.6 billion years ago by the contraction under gravity of gases and dust grains found in a part ...
... Section C Students know the evidence from geological studies of Earth and other planets suggests that the early Earth was very different from Earth today. The prevailing theory is that Earth formed around 4.6 billion years ago by the contraction under gravity of gases and dust grains found in a part ...
Quiz # 2 - Oglethorpe University
... B. the changing distance from the Earth to the Sun. C. the tilt of the Earth’s equatorial plane with respect to its orbit. D. changing temperatures of the Sun. E. retrograde motion of the Sun. 2.) At the time of Copernicus, the fact that parallactic shifts of the brighter stars could NOT be detected ...
... B. the changing distance from the Earth to the Sun. C. the tilt of the Earth’s equatorial plane with respect to its orbit. D. changing temperatures of the Sun. E. retrograde motion of the Sun. 2.) At the time of Copernicus, the fact that parallactic shifts of the brighter stars could NOT be detected ...
Quiz 2 Key - Oglethorpe University
... B. the changing distance from the Earth to the Sun. C. the tilt of the Earth’s equatorial plane with respect to its orbit. D. changing temperatures of the Sun. E. retrograde motion of the Sun. 2.) At the time of Copernicus, the fact that parallactic shifts of the brighter stars could NOT be detected ...
... B. the changing distance from the Earth to the Sun. C. the tilt of the Earth’s equatorial plane with respect to its orbit. D. changing temperatures of the Sun. E. retrograde motion of the Sun. 2.) At the time of Copernicus, the fact that parallactic shifts of the brighter stars could NOT be detected ...
Stellar Properties and Stellar Evolution Study Guide Name Why
... Stellar Properties and Stellar Evolution Study Guide ...
... Stellar Properties and Stellar Evolution Study Guide ...
IN THE CENTRE OF THE SUN IT ABOUT 15 MILLION DEGREES
... believe that this dark spot is a raging storm that is the size of Earth. Neptune is one of the windiest planets in the whole solar system no other planet in the solar system has as strong winds as Neptune. The storms that are next to the great dark are believed to have reached up to 1,200 mph which ...
... believe that this dark spot is a raging storm that is the size of Earth. Neptune is one of the windiest planets in the whole solar system no other planet in the solar system has as strong winds as Neptune. The storms that are next to the great dark are believed to have reached up to 1,200 mph which ...
Scale model of solar system
... to scale down the solar system to a ten-billionth the size. In other words, we’re going to make it 10 billion times smaller than it actually is. Size Actual Mass Actual Distance Actual Guess Size Guess Mass guess distance Sun -----------Bowling -------------- 1,000,000 ---------------0 ball pennies ...
... to scale down the solar system to a ten-billionth the size. In other words, we’re going to make it 10 billion times smaller than it actually is. Size Actual Mass Actual Distance Actual Guess Size Guess Mass guess distance Sun -----------Bowling -------------- 1,000,000 ---------------0 ball pennies ...
power_point_slides
... conditions? • Near a moderate-sized, stable, third-generation star neither too close nor too far from the galactic center. • A planet like Earth, in the “habitable zone” of the star for the right temperature range, big enough to have an atmosphere and plate tectonics, not so big as to be a “gas gian ...
... conditions? • Near a moderate-sized, stable, third-generation star neither too close nor too far from the galactic center. • A planet like Earth, in the “habitable zone” of the star for the right temperature range, big enough to have an atmosphere and plate tectonics, not so big as to be a “gas gian ...
answer key
... 2. Where did the authors earn their degrees? Harvard & Cambridge 3. What constellation is depicted at the bottom of page 1, and what EM band is it photographed in? Pleiades, optical (visible) 4. What pages are the Star Charts found on? S-1 through S-9 5. What are the three common temperature scales? ...
... 2. Where did the authors earn their degrees? Harvard & Cambridge 3. What constellation is depicted at the bottom of page 1, and what EM band is it photographed in? Pleiades, optical (visible) 4. What pages are the Star Charts found on? S-1 through S-9 5. What are the three common temperature scales? ...
Earth at the Center
... Although the stars seemed to move, they stayed in the same position relative to one another. These patterns of stars, called constellations, kept the same shapes from night to night and from year to year. Greek Observations As the Greeks observed the sky, they noticed something surprising. Several p ...
... Although the stars seemed to move, they stayed in the same position relative to one another. These patterns of stars, called constellations, kept the same shapes from night to night and from year to year. Greek Observations As the Greeks observed the sky, they noticed something surprising. Several p ...
The Solar System
... Our solar system consists of the Sun, eight planets, moons, many dwarf planets (or plutoids), an asteroid belt, comets, meteors, and others. The sun is the center of our solar system; the planets, their moons, a belt of asteroids, comets, and other rocks and gas orbit the sun. The eight planets that ...
... Our solar system consists of the Sun, eight planets, moons, many dwarf planets (or plutoids), an asteroid belt, comets, meteors, and others. The sun is the center of our solar system; the planets, their moons, a belt of asteroids, comets, and other rocks and gas orbit the sun. The eight planets that ...
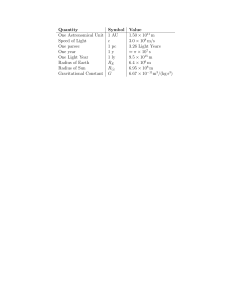
Quantity Symbol Value One Astronomical Unit 1 AU 1.50 × 10
... 1 pc ' 3.1 × 1016 m ' 3.3 ly (a) Explain how such a curious unit of measure came to be defined. Why is it called parsec? (b) What is the distance to the nearest stars and how was this distance measured? 4. Describe qualitatively what is the precession of perihelion. (a) What are the dominant cause o ...
... 1 pc ' 3.1 × 1016 m ' 3.3 ly (a) Explain how such a curious unit of measure came to be defined. Why is it called parsec? (b) What is the distance to the nearest stars and how was this distance measured? 4. Describe qualitatively what is the precession of perihelion. (a) What are the dominant cause o ...
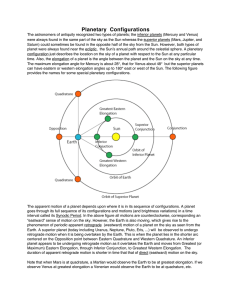
Planetary Configurations
... time it takes to go once around the Sun. i.e., its orbital period. Consider two objects (e.g., planets) orbiting the Sun. For simplicity, we will assume that their orbits are circular and that they move in the same direction and at constant speeds along their respective paths. Each object has an orb ...
... time it takes to go once around the Sun. i.e., its orbital period. Consider two objects (e.g., planets) orbiting the Sun. For simplicity, we will assume that their orbits are circular and that they move in the same direction and at constant speeds along their respective paths. Each object has an orb ...
Solving the Mystery of Massive Star Birth
... collapse of the cloud, which begins to shrink under the pull of its own gravity. As the cloud gets smaller, it gets clumpy. The clumps may eventually become so compact that they begin to heat up, growing hotter and hotter, until eventually they begin “burning” at their core. When the temperature at ...
... collapse of the cloud, which begins to shrink under the pull of its own gravity. As the cloud gets smaller, it gets clumpy. The clumps may eventually become so compact that they begin to heat up, growing hotter and hotter, until eventually they begin “burning” at their core. When the temperature at ...
1. For most of human history it was believed that Earth was at the
... 13. Kepler's 1st Law of planetary motion states that 14. In its elliptical orbit, a planet is closest to the Sun at 15. According to Kepler's 2nd Law of planetary motion, a planet moves fastest in its orbit when it is 16. Kepler's 3rd Law of planetary motion states that 17. The astronomical unit (AU ...
... 13. Kepler's 1st Law of planetary motion states that 14. In its elliptical orbit, a planet is closest to the Sun at 15. According to Kepler's 2nd Law of planetary motion, a planet moves fastest in its orbit when it is 16. Kepler's 3rd Law of planetary motion states that 17. The astronomical unit (AU ...
UV Radiation in Different Stellar Systems
... Therefore, the main target for these kind of studies are the solar-type stars, which are similar to the Sun in mass and evolutionary state. In practical terms, Soderblom & King (1998) defined “solar-like” as main sequence stars of spectral class F8V to K2V (or B-V within 0.50 to 1.00). Several extra ...
... Therefore, the main target for these kind of studies are the solar-type stars, which are similar to the Sun in mass and evolutionary state. In practical terms, Soderblom & King (1998) defined “solar-like” as main sequence stars of spectral class F8V to K2V (or B-V within 0.50 to 1.00). Several extra ...
Eris en Dysnomia
... slightly dimmer than Pluto. Makemake, however, has an orbit much more tilted to the ecliptic plane of the planets than Pluto. Designated 2005 FY9 soon after its discovery by a team led by Mike Brown (Caltech) in 2005, the outer Solar System orb was recently renamed Makemake for the creator of humani ...
... slightly dimmer than Pluto. Makemake, however, has an orbit much more tilted to the ecliptic plane of the planets than Pluto. Designated 2005 FY9 soon after its discovery by a team led by Mike Brown (Caltech) in 2005, the outer Solar System orb was recently renamed Makemake for the creator of humani ...
Universal Gravitation
... of the work of early scientists (Galileo, Kepler, Newton, etc..) we know that planets, stars, comets and other bodies follow the same laws as objects do on Earth. ...
... of the work of early scientists (Galileo, Kepler, Newton, etc..) we know that planets, stars, comets and other bodies follow the same laws as objects do on Earth. ...
Week of: October 8, 2011
... and pictures on. They will find information including: Size, mass, volume, weather, surface features, length of rotation and revolution, and average temperatures. While finding information, the students will fill out their research page. Once all of the information is found, they will put it all tog ...
... and pictures on. They will find information including: Size, mass, volume, weather, surface features, length of rotation and revolution, and average temperatures. While finding information, the students will fill out their research page. Once all of the information is found, they will put it all tog ...
Other Solar Systems Around Other Stars
... the star’s spectrum due to the planetary atmosphere’s varying opacity at different wavelengths, during the transit. This tells us directly what the planet’s atmosphere is made of, via this “transmission spectrum” • Over 2000 possible (most are unconfirmed) planets have now been found in Kepler data. ...
... the star’s spectrum due to the planetary atmosphere’s varying opacity at different wavelengths, during the transit. This tells us directly what the planet’s atmosphere is made of, via this “transmission spectrum” • Over 2000 possible (most are unconfirmed) planets have now been found in Kepler data. ...
Definition of planet

The definition of planet, since the word was coined by the ancient Greeks, has included within its scope a wide range of celestial bodies. Greek astronomers employed the term asteres planetai (ἀστέρες πλανῆται), ""wandering stars"", for star-like objects which apparently moved over the sky. Over the millennia, the term has included a variety of different objects, from the Sun and the Moon to satellites and asteroids.By the end of the 19th century the word planet, though it had yet to be defined, had become a working term applied only to a small set of objects in the Solar System. After 1992, however, astronomers began to discover many additional objects beyond the orbit of Neptune, as well as hundreds of objects orbiting other stars. These discoveries not only increased the number of potential planets, but also expanded their variety and peculiarity. Some were nearly large enough to be stars, while others were smaller than Earth's moon. These discoveries challenged long-perceived notions of what a planet could be.The issue of a clear definition for planet came to a head in 2005 with the discovery of the trans-Neptunian object Eris, a body more massive than the smallest then-accepted planet, Pluto. In its 2006 response, the International Astronomical Union (IAU), recognised by astronomers as the world body responsible for resolving issues of nomenclature, released its decision on the matter. This definition, which applies only to the Solar System, states that a planet is a body that orbits the Sun, is massive enough for its own gravity to make it round, and has ""cleared its neighbourhood"" of smaller objects around its orbit. Under this new definition, Pluto and the other trans-Neptunian objects do not qualify as planets. The IAU's decision has not resolved all controversies, and while many scientists have accepted the definition, some in the astronomical community have rejected it outright.