Science 9 Unit 5: Space Name
... remote-controlled ‘landers’ that put equipment on or close to planets where no human has gone before. Probes have done remote sensing on Mercury and Jupiter, taken soil samples on Mars, landed on Venus, and studied Saturn’s rings up close. The most recent probes to explore Mars are still there. The ...
... remote-controlled ‘landers’ that put equipment on or close to planets where no human has gone before. Probes have done remote sensing on Mercury and Jupiter, taken soil samples on Mars, landed on Venus, and studied Saturn’s rings up close. The most recent probes to explore Mars are still there. The ...
INV 12B MOTION WITH CHANGING SPEED DRY LAB DATA
... k. a large cloud of gas and dust in space where stars are born l. the time in the life of a star when it generates energy by fusion of hydrogen into helium in its core m. a shrinking, spinning region in space with a central concentration of matter n. a large explosion of a star that makes it brighte ...
... k. a large cloud of gas and dust in space where stars are born l. the time in the life of a star when it generates energy by fusion of hydrogen into helium in its core m. a shrinking, spinning region in space with a central concentration of matter n. a large explosion of a star that makes it brighte ...
Astronomy 1001/1005 Midterm (200 points) Name:
... In the Oort cloud. In the Kuiper belt. Between Saturn and Uranus. Between Mars and Jupiter. None of the above. ...
... In the Oort cloud. In the Kuiper belt. Between Saturn and Uranus. Between Mars and Jupiter. None of the above. ...
Ancient Astronomy
... Since Mercury and Venus are always observed near the sun they must be closer to the sun. The other planets, which could be seen at midnight, must be further away from the sun then the Earth. ...
... Since Mercury and Venus are always observed near the sun they must be closer to the sun. The other planets, which could be seen at midnight, must be further away from the sun then the Earth. ...
ASTR 150
... Either icy planetesimals or rocky planetesimals with some water from near the frost line (beyond Mars’ orbit) ...
... Either icy planetesimals or rocky planetesimals with some water from near the frost line (beyond Mars’ orbit) ...
Astro 10: Introductory Astronomy
... • These observations indicated that Al-26 was injected rapidly, within 20,000 years, into the young solar nebula while it was hot enough (>1600K) for CAI material to not yet have solidified. • Gritschneder et.al. 2011 hydro simulations show a massive star supernova (type II SN) within a Giant Molecu ...
... • These observations indicated that Al-26 was injected rapidly, within 20,000 years, into the young solar nebula while it was hot enough (>1600K) for CAI material to not yet have solidified. • Gritschneder et.al. 2011 hydro simulations show a massive star supernova (type II SN) within a Giant Molecu ...
What is the Nice model? - Lunar and Planetary Institute
... 2 model (Nesvorný and Morbidelli 2013). If we combine this with the factor of 3 to 6 given above, the impact rate on giant planet satellites during the Late Heavy Bombardment appears to be about an order of magnitude smaller than assumed by, e.g., Barr and Canup (2010). In fact, Nimmo and Korycansky ...
... 2 model (Nesvorný and Morbidelli 2013). If we combine this with the factor of 3 to 6 given above, the impact rate on giant planet satellites during the Late Heavy Bombardment appears to be about an order of magnitude smaller than assumed by, e.g., Barr and Canup (2010). In fact, Nimmo and Korycansky ...
Planet Characteristics - Beacon Learning Center
... Mercury and Pluto are sometimes referred to as lesser planets (not to be confused with minor planets which is the official term for asteroids). ...
... Mercury and Pluto are sometimes referred to as lesser planets (not to be confused with minor planets which is the official term for asteroids). ...
Is anything out there revised
... 2. Cross out the names of planets that don’t have what’s just right for life. Which planet(s) are you left with that could support life? 3. Use the information on the planet cards to plot planet distance from the Sun against temperature on the graph ‘Planet temperatures and distances from the sun’. ...
... 2. Cross out the names of planets that don’t have what’s just right for life. Which planet(s) are you left with that could support life? 3. Use the information on the planet cards to plot planet distance from the Sun against temperature on the graph ‘Planet temperatures and distances from the sun’. ...
Kepler*s laws of planetary motion
... average distance of a planet from the sun and the planet’s orbital period • Orbital period- time required for planet to complete one orbit • Helps astronomers find out how far away planets are from the sun ...
... average distance of a planet from the sun and the planet’s orbital period • Orbital period- time required for planet to complete one orbit • Helps astronomers find out how far away planets are from the sun ...
Introduction Worksheet 1
... Astronomical observations indicate that the sun is tracing a circular orbit around the center of our galaxy. The radius of orbit is 2.7 x 1020 m with period T = 200 million years. a) Calculate the total mass of the central stars. b) Assume all of these stars have the same mass as our sun. How many d ...
... Astronomical observations indicate that the sun is tracing a circular orbit around the center of our galaxy. The radius of orbit is 2.7 x 1020 m with period T = 200 million years. a) Calculate the total mass of the central stars. b) Assume all of these stars have the same mass as our sun. How many d ...
07 solar system
... gravitational encounters with other planets. Only (some of) those within the asteroid belt and within the Kuiper belt are on stable orbits. The rest have been flung far out into the Oort cloud, some of which remain on highly elliptical orbits and plunge back into the solar system. ...
... gravitational encounters with other planets. Only (some of) those within the asteroid belt and within the Kuiper belt are on stable orbits. The rest have been flung far out into the Oort cloud, some of which remain on highly elliptical orbits and plunge back into the solar system. ...
Planetary Systems Unit Part 3: The Solar System
... 100 pounds (your Earth weight) multiplied by 0.17 (the gravity factor for the moon) = 17 pounds. Remember, your mass does not change at different locations. Your mass remains the same; it is your weight that changes due to the force of gravity on the different planets. ...
... 100 pounds (your Earth weight) multiplied by 0.17 (the gravity factor for the moon) = 17 pounds. Remember, your mass does not change at different locations. Your mass remains the same; it is your weight that changes due to the force of gravity on the different planets. ...
Nebula Theory - GSHS Mrs. Francomb
... the disk of the nebula was whirling around the core, as described above. The protoplanets continued this motion by revolving around the newly evolved Sun. In addition, the protoplanets, and the planets, as they formed, began to rotate, or spin on an internal axis. This took place as some of the forc ...
... the disk of the nebula was whirling around the core, as described above. The protoplanets continued this motion by revolving around the newly evolved Sun. In addition, the protoplanets, and the planets, as they formed, began to rotate, or spin on an internal axis. This took place as some of the forc ...
Are there Earth-like planets around other stars?
... which is still a subject of intense debate between scientists), but it is next to nothing compared with the huge gas masses of Jupiter and the other gas planets. It was therefore a big surprise when the first planet discovered around another star, in 1995, was a gigantic gas planet in a tiny orbit. ...
... which is still a subject of intense debate between scientists), but it is next to nothing compared with the huge gas masses of Jupiter and the other gas planets. It was therefore a big surprise when the first planet discovered around another star, in 1995, was a gigantic gas planet in a tiny orbit. ...
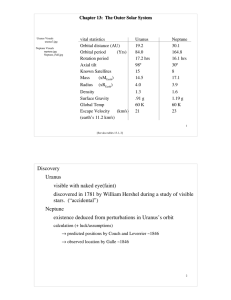
Discovery Uranus visible with naked eye(faint) discovered in 1781
... Pluto (and Charon) [figure 13.23, Plutoids.jpg] Pluto's discovery: additional perturbations of Uranus’s orbit → prediction by Lowell ~ 1905 Pluto found much smaller than predicted, via photographs ~ 1930 [discovering_pluto.jpg] ...
... Pluto (and Charon) [figure 13.23, Plutoids.jpg] Pluto's discovery: additional perturbations of Uranus’s orbit → prediction by Lowell ~ 1905 Pluto found much smaller than predicted, via photographs ~ 1930 [discovering_pluto.jpg] ...
Galloping Through the Gas Giants Interactive Posters
... giants - in our solar system! Jupiter and Saturn are mostly made of Hydrogen with Helium. Neptune and Uranus are made of rock and ice and some Hydrogen and Helium. Their atmospheres contain a little methane gas – which gives these planets their blue color! It would be very hard to land on the Gas Gi ...
... giants - in our solar system! Jupiter and Saturn are mostly made of Hydrogen with Helium. Neptune and Uranus are made of rock and ice and some Hydrogen and Helium. Their atmospheres contain a little methane gas – which gives these planets their blue color! It would be very hard to land on the Gas Gi ...
Motion in the Sky & Getting to know the Sky
... therefore it appears very small in the sky. Venus is in the “new” phase when it is at its closest distance to the earth, so the “narrow crescent” Venus looks very large (and very bright)! ...
... therefore it appears very small in the sky. Venus is in the “new” phase when it is at its closest distance to the earth, so the “narrow crescent” Venus looks very large (and very bright)! ...
ASTR2050 Intro A&A NAMES: ____________________ ____________________ Work sheet
... Build a scale model of the solar system, including the sizes and orbital radii of the sun and planets. Most of the data you need can be found in Kutner, Appendices B and D, and Figure 17.3. Show the units in the following lists. 1. What celestial object did you use to set the scale, and what did you ...
... Build a scale model of the solar system, including the sizes and orbital radii of the sun and planets. Most of the data you need can be found in Kutner, Appendices B and D, and Figure 17.3. Show the units in the following lists. 1. What celestial object did you use to set the scale, and what did you ...
chapter 1 section 2
... Every planet travels on a path known as their ORBIT. An orbit is a elliptical shape (stretched out circle) Every planet takes a different amount of time to complete their orbit Earth takes 365 ¼ days to go around the sun once. ...
... Every planet travels on a path known as their ORBIT. An orbit is a elliptical shape (stretched out circle) Every planet takes a different amount of time to complete their orbit Earth takes 365 ¼ days to go around the sun once. ...
Astronomy Quiz Units 1 to 3
... The answer as to why this object is not a planet is that it is not spherical. “A planet (from Greek πλανήτης, alternative form of πλάνης "wanderer") is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonu ...
... The answer as to why this object is not a planet is that it is not spherical. “A planet (from Greek πλανήτης, alternative form of πλάνης "wanderer") is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonu ...
signatures of life on other worlds
... Kasting notes that this interpretation of the surface morphology on Mars is not universally accepted, but it is appealing. The possibility of a liquid-water phase in the planet’s history raises the question of whether life might have had an early start there with a thicker atmosphere that trapped he ...
... Kasting notes that this interpretation of the surface morphology on Mars is not universally accepted, but it is appealing. The possibility of a liquid-water phase in the planet’s history raises the question of whether life might have had an early start there with a thicker atmosphere that trapped he ...
Definition of planet

The definition of planet, since the word was coined by the ancient Greeks, has included within its scope a wide range of celestial bodies. Greek astronomers employed the term asteres planetai (ἀστέρες πλανῆται), ""wandering stars"", for star-like objects which apparently moved over the sky. Over the millennia, the term has included a variety of different objects, from the Sun and the Moon to satellites and asteroids.By the end of the 19th century the word planet, though it had yet to be defined, had become a working term applied only to a small set of objects in the Solar System. After 1992, however, astronomers began to discover many additional objects beyond the orbit of Neptune, as well as hundreds of objects orbiting other stars. These discoveries not only increased the number of potential planets, but also expanded their variety and peculiarity. Some were nearly large enough to be stars, while others were smaller than Earth's moon. These discoveries challenged long-perceived notions of what a planet could be.The issue of a clear definition for planet came to a head in 2005 with the discovery of the trans-Neptunian object Eris, a body more massive than the smallest then-accepted planet, Pluto. In its 2006 response, the International Astronomical Union (IAU), recognised by astronomers as the world body responsible for resolving issues of nomenclature, released its decision on the matter. This definition, which applies only to the Solar System, states that a planet is a body that orbits the Sun, is massive enough for its own gravity to make it round, and has ""cleared its neighbourhood"" of smaller objects around its orbit. Under this new definition, Pluto and the other trans-Neptunian objects do not qualify as planets. The IAU's decision has not resolved all controversies, and while many scientists have accepted the definition, some in the astronomical community have rejected it outright.