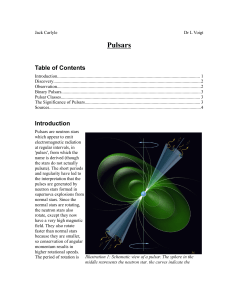
a report on pulsars, written for PHAS1901
... dispersion. All electromagnetic radiation moves at a constant speed through a vacuum, but is slowed proportionally to it's wavelength when it travels through a medium. the interstellar medium is often regarded as a vacuum, but in actual fact is occupied by atoms and free electrons, albeit at extreme ...
... dispersion. All electromagnetic radiation moves at a constant speed through a vacuum, but is slowed proportionally to it's wavelength when it travels through a medium. the interstellar medium is often regarded as a vacuum, but in actual fact is occupied by atoms and free electrons, albeit at extreme ...
Document
... SS433 is a unique massive X-ray binary system with precessing relativistic jets. It is situated at a distance of approximately 5 kpc = 1.5 10^22 cm nearly in the galactic plane. The optical companion V1343 Aquilae was first identified in the survey of stars exhibiting H_alpha (656 nm) emission by S ...
... SS433 is a unique massive X-ray binary system with precessing relativistic jets. It is situated at a distance of approximately 5 kpc = 1.5 10^22 cm nearly in the galactic plane. The optical companion V1343 Aquilae was first identified in the survey of stars exhibiting H_alpha (656 nm) emission by S ...
(BDA) Contribution To Space Weather Investigations
... Normally, in observations of optical coronagraphs the solar disk is occulted and hence only CMEs propagating perpendicular to the line of sight are observed. However, in radio observations, there is no occultation of solar disk and hence CMEs on the disk can also be observed by radio heliographs suc ...
... Normally, in observations of optical coronagraphs the solar disk is occulted and hence only CMEs propagating perpendicular to the line of sight are observed. However, in radio observations, there is no occultation of solar disk and hence CMEs on the disk can also be observed by radio heliographs suc ...
Star Birth - Sierra College Astronomy Home Page
... • As the helium fuses into carbon the temperature increases. Since the core is degenerate, it does not expand which would normally regulate the fusion rate • Since the temperature continues to rise, the rate of the triple alpha process increases rapidly, and the helium in the core ignites in what is ...
... • As the helium fuses into carbon the temperature increases. Since the core is degenerate, it does not expand which would normally regulate the fusion rate • Since the temperature continues to rise, the rate of the triple alpha process increases rapidly, and the helium in the core ignites in what is ...
00 T Tauri Stars Have Extensive Coronae?
... million Kelvin have been proposed in theoretical models by various authors. These models predict strong X-ray radiation from such 106 K coronae. An excellent way to check this prediction are X-ray surveys with the Einstein observatory. Several surveys have been carried out by Gahm (Astrophys. J., 24 ...
... million Kelvin have been proposed in theoretical models by various authors. These models predict strong X-ray radiation from such 106 K coronae. An excellent way to check this prediction are X-ray surveys with the Einstein observatory. Several surveys have been carried out by Gahm (Astrophys. J., 24 ...
PPT - Chandra X-Ray Observatory
... • Wind-accretion calculations (MacDonald 1992) show that ISM accretion is prevented for LB1919 since its L>1L. Instead, massloss rate of 10-18 M/yr will be sustained • Convection not expected in LB1919 • Rotation could lead to meridional mixing, however, WDs are generally slow rotators. In particu ...
... • Wind-accretion calculations (MacDonald 1992) show that ISM accretion is prevented for LB1919 since its L>1L. Instead, massloss rate of 10-18 M/yr will be sustained • Convection not expected in LB1919 • Rotation could lead to meridional mixing, however, WDs are generally slow rotators. In particu ...
Advanced information on the Nobel Prize in Physics 2002, 8 October
... of electrons emitted in nuclear β decay. Fermi’s theory for weak interactions was developed during the 1930’s. At the time, neutrino interaction cross-sections were considered too small for neutrino detection. However, the large neutrino fluxes that later became available with nuclear reactors opene ...
... of electrons emitted in nuclear β decay. Fermi’s theory for weak interactions was developed during the 1930’s. At the time, neutrino interaction cross-sections were considered too small for neutrino detection. However, the large neutrino fluxes that later became available with nuclear reactors opene ...
Milky Way
... •High mass stars tend to burn hotter (bluer) and don’t last long •Low mass stars tend to burn cooler (redder) and last a long time •The color of a collection of stars (clusters) tells you about them: •Young clusters look bluish •Old clusters look reddish ...
... •High mass stars tend to burn hotter (bluer) and don’t last long •Low mass stars tend to burn cooler (redder) and last a long time •The color of a collection of stars (clusters) tells you about them: •Young clusters look bluish •Old clusters look reddish ...
What is a white dwarf?
... over from a low-mass star, supported against the crush of gravity by electron degeneracy pressure. • What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? • It can acquire hydrogen from its companion through an accretion disk. As hydrogen builds up on the white dwarf’s surface, it may ignite wi ...
... over from a low-mass star, supported against the crush of gravity by electron degeneracy pressure. • What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? • It can acquire hydrogen from its companion through an accretion disk. As hydrogen builds up on the white dwarf’s surface, it may ignite wi ...
gravitational collapse to black holes
... These result from applying conformal transformations (i.e. those which keep angles intact) to the spacetime, and from compactification, i.e. mapping an infinite coordinate range to a finite ...
... These result from applying conformal transformations (i.e. those which keep angles intact) to the spacetime, and from compactification, i.e. mapping an infinite coordinate range to a finite ...
What is a black hole?
... You may not even make it that far. Some black holes greedily gobble down matter, stealing it from an orbiting companion star or, in the case of supermassive black holes, from surrounding gas clouds. As the matter falls in, it piles up into a disk just outside the hole. Orbiting at huge speeds, the m ...
... You may not even make it that far. Some black holes greedily gobble down matter, stealing it from an orbiting companion star or, in the case of supermassive black holes, from surrounding gas clouds. As the matter falls in, it piles up into a disk just outside the hole. Orbiting at huge speeds, the m ...
Model Solutions
... which any number of alternatives may be correct. You get 5 marks for each correct answer. No marks are deducted for any wrong answers. You will get credit for the question if and only if you mark all correct choices and no wrong choices. There is no partial credit. • For both these sections, you hav ...
... which any number of alternatives may be correct. You get 5 marks for each correct answer. No marks are deducted for any wrong answers. You will get credit for the question if and only if you mark all correct choices and no wrong choices. There is no partial credit. • For both these sections, you hav ...
Black Holes
... brightest star in the sky below and to left of Orion's belt, and Betelgeuse is the reddish star just above Orion's belt. As the movie progresses the observer moves toward the black hole. An odd diffuse glow of light appears in the center of the screen. Soon a black spot appears - the black hole itse ...
... brightest star in the sky below and to left of Orion's belt, and Betelgeuse is the reddish star just above Orion's belt. As the movie progresses the observer moves toward the black hole. An odd diffuse glow of light appears in the center of the screen. Soon a black spot appears - the black hole itse ...
poster
... The YSOVAR project (Morales-Calderon et al. 2011) monitored about a dozen star forming regions in 3.6 m and 4.5m using the warm mission capabilities of Spitzer. The sampling varies with the region, but most star forming regions were observed 50-100 times, on scales of hours to months. Here, we pre ...
... The YSOVAR project (Morales-Calderon et al. 2011) monitored about a dozen star forming regions in 3.6 m and 4.5m using the warm mission capabilities of Spitzer. The sampling varies with the region, but most star forming regions were observed 50-100 times, on scales of hours to months. Here, we pre ...
Paper 3 (pdf)
... strength of their magnetic fields, but also can provide an estimate of their radius and distance and provide the first demonstration of vacuum birefringence (also known as vacuum polarization), a predicted but hitherto unobserved QED effect.27, 28 This effect arises from interactions with virtual ph ...
... strength of their magnetic fields, but also can provide an estimate of their radius and distance and provide the first demonstration of vacuum birefringence (also known as vacuum polarization), a predicted but hitherto unobserved QED effect.27, 28 This effect arises from interactions with virtual ph ...
Projet d`observation
... energy due to Thomson scattering by a factor exp(- Neστ)” (στ: Thomson cross-section) ...
... energy due to Thomson scattering by a factor exp(- Neστ)” (στ: Thomson cross-section) ...
Age patterns in a sample of spiral galaxies
... pointed to other factors that could influence Hα/FUV flux ratio, such as variations in the IMF, SFH, and metallicity (e.g. [13, 21, 17]). Different levels of dust attenuation between individual HII regions also has a major influence, especially in the highly extincted FUV region. Clearly, any effort ...
... pointed to other factors that could influence Hα/FUV flux ratio, such as variations in the IMF, SFH, and metallicity (e.g. [13, 21, 17]). Different levels of dust attenuation between individual HII regions also has a major influence, especially in the highly extincted FUV region. Clearly, any effort ...
Unit 11: Stellar Evolution
... the neutrinos being radiated away from the core. In a fraction of a second, the earthsized iron core is transformed into a neutron core about 10 miles across. The unsupported outer regions are now free-falling toward the neutron core. The implosion is converted into an explosion by a combination of ...
... the neutrinos being radiated away from the core. In a fraction of a second, the earthsized iron core is transformed into a neutron core about 10 miles across. The unsupported outer regions are now free-falling toward the neutron core. The implosion is converted into an explosion by a combination of ...
The physics of high-mass star formation
... and allows photons to escape lowering radiation pressure (jet) iii. “Merging’’ of many stars with M*< 8 M⊙: insensitive to radiation pressure … but needs >106 stars/pc3 >> observed 104 stars/pc3 !!! ...
... and allows photons to escape lowering radiation pressure (jet) iii. “Merging’’ of many stars with M*< 8 M⊙: insensitive to radiation pressure … but needs >106 stars/pc3 >> observed 104 stars/pc3 !!! ...
Neutron Stars - Lick Observatory
... half a million Kelvin is found, and from its flux a radius of order 10 km is inferred. Circumstantial evidence indicates that it was born in a supernova explosion a million years ago. Such an age and surface temperature is compatible with standard cooling predictions. Binary pulsars were discovered ...
... half a million Kelvin is found, and from its flux a radius of order 10 km is inferred. Circumstantial evidence indicates that it was born in a supernova explosion a million years ago. Such an age and surface temperature is compatible with standard cooling predictions. Binary pulsars were discovered ...
Problem 1. Marking scheme Lagrange Point
... In 3rd July the Earth is at the aphelion. The speed of the Earth is smaller than the speed of Earth on a circular orbit with radius r0,max a0 1 e0 . . b) In 3rd January the Earth is at perihelion. The speed of the Earth is bigger than the speed of Earth on a circular orbit with radius r0,max ...
... In 3rd July the Earth is at the aphelion. The speed of the Earth is smaller than the speed of Earth on a circular orbit with radius r0,max a0 1 e0 . . b) In 3rd January the Earth is at perihelion. The speed of the Earth is bigger than the speed of Earth on a circular orbit with radius r0,max ...
Cygnus X-1
Cygnus X-1 (abbreviated Cyg X-1) is a well-known galactic X-ray source, thought to be a black hole, in the constellation Cygnus. It was discovered in 1964 during a rocket flight and is one of the strongest X-ray sources seen from Earth, producing a peak X-ray flux density of 6977229999999999999♠2.3×10−23 Wm−2 Hz−1 (7003230000000000000♠2.3×103 Jansky). Cygnus X-1 was the first X-ray source widely accepted to be a black hole and it remains among the most studied astronomical objects in its class. The compact object is now estimated to have a mass about 14.8 times the mass of the Sun and has been shown to be too small to be any known kind of normal star, or other likely object besides a black hole. If so, the radius of its event horizon is about 7004440000000000000♠44 km.Cygnus X-1 belongs to a high-mass X-ray binary system about 7019574266339685654♠6070 ly from the Sun that includes a blue supergiant variable star designated HDE 226868 which it orbits at about 0.2 AU, or 20% of the distance from the Earth to the Sun. A stellar wind from the star provides material for an accretion disk around the X-ray source. Matter in the inner disk is heated to millions of degrees, generating the observed X-rays. A pair of jets, arranged perpendicular to the disk, are carrying part of the energy of the infalling material away into interstellar space.This system may belong to a stellar association called Cygnus OB3, which would mean that Cygnus X-1 is about five million years old and formed from a progenitor star that had more than 7001400000000000000♠40 solar masses. The majority of the star's mass was shed, most likely as a stellar wind. If this star had then exploded as a supernova, the resulting force would most likely have ejected the remnant from the system. Hence the star may have instead collapsed directly into a black hole.Cygnus X-1 was the subject of a friendly scientific wager between physicists Stephen Hawking and Kip Thorne in 1975, with Hawking betting that it was not a black hole. He conceded the bet in 1990 after observational data had strengthened the case that there was indeed a black hole in the system. This hypothesis has not been confirmed due to a lack of direct observation but has generally been accepted from indirect evidence.