Here
... • Using a good high resolution spectrum, you can get a much better measurement of the spectral energy distribution. • The disadvantage is that the efficiency is lower (more photons are lost in the complex optics). Also, it is difficult to measure more than one star at a time (in contrast to the dire ...
... • Using a good high resolution spectrum, you can get a much better measurement of the spectral energy distribution. • The disadvantage is that the efficiency is lower (more photons are lost in the complex optics). Also, it is difficult to measure more than one star at a time (in contrast to the dire ...
An interesting nebular object in LDN 288
... cavity. The velocity of the dark cloud is ~2.5 km/s and its distance is estimated as (380-990) pc. The object SNO 85 itself is associated with an IRAS point source IRAS 17547-1832, the infrared colors of this source are typical for a non-evolved source embedded in the dense dark cloud. This region i ...
... cavity. The velocity of the dark cloud is ~2.5 km/s and its distance is estimated as (380-990) pc. The object SNO 85 itself is associated with an IRAS point source IRAS 17547-1832, the infrared colors of this source are typical for a non-evolved source embedded in the dense dark cloud. This region i ...
Black Hole Formation
... electrically neutral black hole. Solutions for rotating and / or charged black holes also exist. Realistic black holes are not expected to have a net charge (because the universe as a whole does not seem to have a net charge), but they are expected to have at least some angular momentum. The relevan ...
... electrically neutral black hole. Solutions for rotating and / or charged black holes also exist. Realistic black holes are not expected to have a net charge (because the universe as a whole does not seem to have a net charge), but they are expected to have at least some angular momentum. The relevan ...
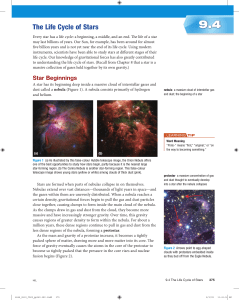
The Life Cycle of Stars
... stars? It was reasoned that these cooler stars have a greater surface area than the hotter, dim stars, resulting in more light being produced. The large, bright, cool stars are called red giants. The small, dim, hot stars are called white dwarfs. The hottest, most luminous stars are very large stars ...
... stars? It was reasoned that these cooler stars have a greater surface area than the hotter, dim stars, resulting in more light being produced. The large, bright, cool stars are called red giants. The small, dim, hot stars are called white dwarfs. The hottest, most luminous stars are very large stars ...
Dark Matter Capture in the first stars
... chemical imprint is not seen) • Helps explain observed black holes: • (I) in centers of galaxies • (ii) billion solar mass BH at z=6 • (iii) excess extragalactic radio signal in ARCADE reported at AAS meeting by Kogut (1K at 1GHz), power law spectrum could come from synchrotron radiation from accret ...
... chemical imprint is not seen) • Helps explain observed black holes: • (I) in centers of galaxies • (ii) billion solar mass BH at z=6 • (iii) excess extragalactic radio signal in ARCADE reported at AAS meeting by Kogut (1K at 1GHz), power law spectrum could come from synchrotron radiation from accret ...
Misalignment & Nucleosynthesis in Microquasars Yousaf M. Butt , Thomas J. Maccarone
... to, the proposed jet-secondary impacts as the source of the observed Li excess. For instance, as proposed by Guessoum & Kazanas (1999), even for well-aligned microquasars (as well as misaligned ones), it is plausible that surface irradiation of the secondary star by neutrons generated in the accreti ...
... to, the proposed jet-secondary impacts as the source of the observed Li excess. For instance, as proposed by Guessoum & Kazanas (1999), even for well-aligned microquasars (as well as misaligned ones), it is plausible that surface irradiation of the secondary star by neutrons generated in the accreti ...
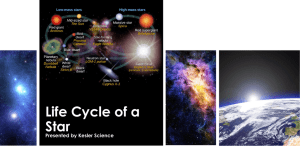
Life Cycle of a Star Vocabulary
... • Inside the nebula are regions of greater and less gravity causing the gas and dust to pull together. • As more atoms gather, their gravitational attraction increases. • Not a very stable phase because many reactions are occurring within the protostar. © KeslerScience.com ...
... • Inside the nebula are regions of greater and less gravity causing the gas and dust to pull together. • As more atoms gather, their gravitational attraction increases. • Not a very stable phase because many reactions are occurring within the protostar. © KeslerScience.com ...
MS Word version
... The following sequence of directions are steps an instructor might choose to follow in demonstrating the Eclipsing Binary Simulator in a classroom situation. We provide these suggestions with appropriate questions (shown in bold italics) to pose to the class as an aid in promoting interactivity. We ...
... The following sequence of directions are steps an instructor might choose to follow in demonstrating the Eclipsing Binary Simulator in a classroom situation. We provide these suggestions with appropriate questions (shown in bold italics) to pose to the class as an aid in promoting interactivity. We ...
The Stars education kit - Student activities 11-20
... disk. Material closer to the black hole is spinning faster than the material at the edge of the accretion disk. This generates friction, heating the disk to temperatures over 100 million degrees C. Matter this hot emits X-ray radiation. Black holes can also be found if a star is discovered to be orb ...
... disk. Material closer to the black hole is spinning faster than the material at the edge of the accretion disk. This generates friction, heating the disk to temperatures over 100 million degrees C. Matter this hot emits X-ray radiation. Black holes can also be found if a star is discovered to be orb ...
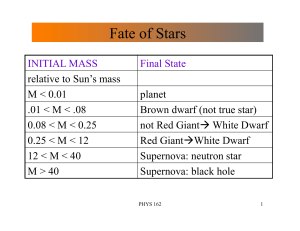
Fate of Stars
... White Dwarves Mass vs Radius • In WD, gravity is balanced by pressure due to degenerate electrons • A heavier WD will have smaller radius • if Mass(WD) > 1.4 M(Sun) electrons can not resist gravity ! called Chandrasekhar limit and no WD has a mass greater than this • If WD can acquire mass from ...
... White Dwarves Mass vs Radius • In WD, gravity is balanced by pressure due to degenerate electrons • A heavier WD will have smaller radius • if Mass(WD) > 1.4 M(Sun) electrons can not resist gravity ! called Chandrasekhar limit and no WD has a mass greater than this • If WD can acquire mass from ...
ppt - Institute for Astronomy
... We used Subaru to do photometry and spectroscopy and indeed found the new companion to be a pre-main sequence star, most likely a K-type star with IR excess ...
... We used Subaru to do photometry and spectroscopy and indeed found the new companion to be a pre-main sequence star, most likely a K-type star with IR excess ...
Coding Einstein`s Legacy - the Neukom Institute
... found two stars orbiting each other that were getting closer to one another at the exact same rate predicted by Einstein’s theory. They were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for this discovery in 1993. But why are the stars found by Taylor and Hulse approaching one another? The reason is that in E ...
... found two stars orbiting each other that were getting closer to one another at the exact same rate predicted by Einstein’s theory. They were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for this discovery in 1993. But why are the stars found by Taylor and Hulse approaching one another? The reason is that in E ...
M BH
... 1. Astrophysical black holes 2. Formation of black holes 3. Evolution of black holes Ref: Proc. Carnegie sympo. on coevolution of black holes and galaxies (2003) ...
... 1. Astrophysical black holes 2. Formation of black holes 3. Evolution of black holes Ref: Proc. Carnegie sympo. on coevolution of black holes and galaxies (2003) ...
Electromagnetic pulse from final gravitational stellar collapse
... occurred before escape. Our collapse code in the present paper shows beyond a doubt, that if no hydrodynamic bounce occurs, these diffusing neutrinos are trapped in the infalling nuclear material and are carried into the resulting black hole. Thus observation of neutrinos associated with particular ...
... occurred before escape. Our collapse code in the present paper shows beyond a doubt, that if no hydrodynamic bounce occurs, these diffusing neutrinos are trapped in the infalling nuclear material and are carried into the resulting black hole. Thus observation of neutrinos associated with particular ...
Slide 1
... comfortable with general relativity (ok, it’s pretty tricky even if you are… )! Multiple models can help us to understand by giving different angles on the issues, so let’s briefly review two other models we looked at for event horizons. There are more! ...
... comfortable with general relativity (ok, it’s pretty tricky even if you are… )! Multiple models can help us to understand by giving different angles on the issues, so let’s briefly review two other models we looked at for event horizons. There are more! ...
Stellar Physics - Craigie High School
... The two tides per day that we observe are caused by the unequal attractions of the Moon (and Sun) for masses at different sides of the Earth. In addition the rotation of the Earth and Moon also has an effect on tidal patterns. The Sun causes two tides per day and the Moon causes two tides every 25 h ...
... The two tides per day that we observe are caused by the unequal attractions of the Moon (and Sun) for masses at different sides of the Earth. In addition the rotation of the Earth and Moon also has an effect on tidal patterns. The Sun causes two tides per day and the Moon causes two tides every 25 h ...
Fill in the blanks of each frame using the list of missing words given
... over from the supernova can either form a neutron star, or if it’s massive enough, can form a black hole. ...
... over from the supernova can either form a neutron star, or if it’s massive enough, can form a black hole. ...
File
... radiation, was found to have a very large mass all confined to a very small volume. This discovery was made by mapping the velocity to within half a light year of the galaxies center, and therefore concluding that the object was less than half a light year in radius. The combination of findings that ...
... radiation, was found to have a very large mass all confined to a very small volume. This discovery was made by mapping the velocity to within half a light year of the galaxies center, and therefore concluding that the object was less than half a light year in radius. The combination of findings that ...
Galactic components Structure and kinematics
... Thin disk The galactic disk is a complex system including stars, dust and gas clouds, active star forming regions, spiral arm structures, spurs, ring, ... However, most of disk stars belong to an “axisymmetric” structure, the Thin disk, which is usually represented by an exponential density law: ...
... Thin disk The galactic disk is a complex system including stars, dust and gas clouds, active star forming regions, spiral arm structures, spurs, ring, ... However, most of disk stars belong to an “axisymmetric” structure, the Thin disk, which is usually represented by an exponential density law: ...
Stars Part 1
... 108K, other elements can be formed by other fusion reactions. This only works for elements up to the iron-56. At this point, more energy would be consumed ...
... 108K, other elements can be formed by other fusion reactions. This only works for elements up to the iron-56. At this point, more energy would be consumed ...
Cygnus X-1
Cygnus X-1 (abbreviated Cyg X-1) is a well-known galactic X-ray source, thought to be a black hole, in the constellation Cygnus. It was discovered in 1964 during a rocket flight and is one of the strongest X-ray sources seen from Earth, producing a peak X-ray flux density of 6977229999999999999♠2.3×10−23 Wm−2 Hz−1 (7003230000000000000♠2.3×103 Jansky). Cygnus X-1 was the first X-ray source widely accepted to be a black hole and it remains among the most studied astronomical objects in its class. The compact object is now estimated to have a mass about 14.8 times the mass of the Sun and has been shown to be too small to be any known kind of normal star, or other likely object besides a black hole. If so, the radius of its event horizon is about 7004440000000000000♠44 km.Cygnus X-1 belongs to a high-mass X-ray binary system about 7019574266339685654♠6070 ly from the Sun that includes a blue supergiant variable star designated HDE 226868 which it orbits at about 0.2 AU, or 20% of the distance from the Earth to the Sun. A stellar wind from the star provides material for an accretion disk around the X-ray source. Matter in the inner disk is heated to millions of degrees, generating the observed X-rays. A pair of jets, arranged perpendicular to the disk, are carrying part of the energy of the infalling material away into interstellar space.This system may belong to a stellar association called Cygnus OB3, which would mean that Cygnus X-1 is about five million years old and formed from a progenitor star that had more than 7001400000000000000♠40 solar masses. The majority of the star's mass was shed, most likely as a stellar wind. If this star had then exploded as a supernova, the resulting force would most likely have ejected the remnant from the system. Hence the star may have instead collapsed directly into a black hole.Cygnus X-1 was the subject of a friendly scientific wager between physicists Stephen Hawking and Kip Thorne in 1975, with Hawking betting that it was not a black hole. He conceded the bet in 1990 after observational data had strengthened the case that there was indeed a black hole in the system. This hypothesis has not been confirmed due to a lack of direct observation but has generally been accepted from indirect evidence.