Lecture 13 Local group chapter 4 of S+G
... Mtotal=Mgas+Mstar=constant (Mbaryons) ; Mhmass of heavy elements in gas =ZMgas dM'stars =total mass made into stars, dM''stars =amount of mass instantaneously returned to ISM enriched with metals dMstars =dM'stars -dM''stars net matter turned into stars define y as the yield of heavy elements- yMsta ...
... Mtotal=Mgas+Mstar=constant (Mbaryons) ; Mhmass of heavy elements in gas =ZMgas dM'stars =total mass made into stars, dM''stars =amount of mass instantaneously returned to ISM enriched with metals dMstars =dM'stars -dM''stars net matter turned into stars define y as the yield of heavy elements- yMsta ...
A Search for New Solar-Type Post-T Tauri Stars in
... by the AIS, due to avoidance of the galactic plane, is young stars. According to Fischer (1998; PhD Thesis, UCSC) only 1% (2/189) of a volume-limited (d < 25 pc) sample of K stars have lithium abundances and chromospheric activity suggesting ages possibly <100 Myr, with an additional 6% (11/189) pla ...
... by the AIS, due to avoidance of the galactic plane, is young stars. According to Fischer (1998; PhD Thesis, UCSC) only 1% (2/189) of a volume-limited (d < 25 pc) sample of K stars have lithium abundances and chromospheric activity suggesting ages possibly <100 Myr, with an additional 6% (11/189) pla ...
The Quantum Mechanics of Black Holes
... that many of the new phenomena that were being discovered, such as quasars, pulsars and compact X-ray sources, indicated the existence of very strong gravitational fields, fields that could be described only by general relativity. Quasars are star-like objects that must be many times brighter than e ...
... that many of the new phenomena that were being discovered, such as quasars, pulsars and compact X-ray sources, indicated the existence of very strong gravitational fields, fields that could be described only by general relativity. Quasars are star-like objects that must be many times brighter than e ...
Thermonuclear supernovae and cosmology
... binary systems, influx of matter from the companion is crucial for all explosion mechanisms. Favored mechanism for spectrally-normal SNIa: single-degenerate scenario. WD mass steadily increases by accretion from the companion, accreted matter steadily burns into C and O on WD surface. When WD mass r ...
... binary systems, influx of matter from the companion is crucial for all explosion mechanisms. Favored mechanism for spectrally-normal SNIa: single-degenerate scenario. WD mass steadily increases by accretion from the companion, accreted matter steadily burns into C and O on WD surface. When WD mass r ...
No Slide Title
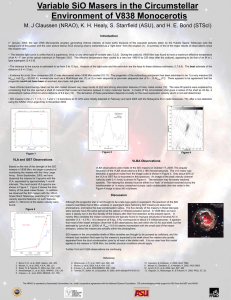
... (Aa+Ab) = 262 days, (Ba+Bb) = 315 days (Torres et al., 1995) and separations of ~ 1AU. • Distance = 46.7±6pc, and current AB separation = 0.8", so is easily resolved at all HST 's. • Member of the TW Hydrae Association (Kastner et al. 1997; Webb et al. 1999). • Soderbloom et al. (1998) estimates ag ...
... (Aa+Ab) = 262 days, (Ba+Bb) = 315 days (Torres et al., 1995) and separations of ~ 1AU. • Distance = 46.7±6pc, and current AB separation = 0.8", so is easily resolved at all HST 's. • Member of the TW Hydrae Association (Kastner et al. 1997; Webb et al. 1999). • Soderbloom et al. (1998) estimates ag ...
Post Main Sequence Evolution Since a star`s luminosity on the main
... demand for energy flow from the center is decreased. (In stars with M > 10M¯ , the core temperature will never actually decrease, while in stars with radiative cores, core contraction won’t actually occur, since it has been adjusting to the decrease in hydrogen all along.) • While this is happening, ...
... demand for energy flow from the center is decreased. (In stars with M > 10M¯ , the core temperature will never actually decrease, while in stars with radiative cores, core contraction won’t actually occur, since it has been adjusting to the decrease in hydrogen all along.) • While this is happening, ...
PHYS3380_111115_bw - The University of Texas at Dallas
... - required some revisions to models of high mass stellar evolution, which had suggested that supernovae would result from red supergiants. Now believe star was chemically poor in elements heavier than He - contracted and heated up after phase as cool, red supergiant during which it lost much of its ...
... - required some revisions to models of high mass stellar evolution, which had suggested that supernovae would result from red supergiants. Now believe star was chemically poor in elements heavier than He - contracted and heated up after phase as cool, red supergiant during which it lost much of its ...
Formation of spiral and elliptical galaxies in a CDM cosmogony
... Figure 2: Snapshot of gas particle distribution in a forming spiral galaxy at a redshift of z = 6. Left frame: Projected distribution of all gas particles in the x{y{plane. Middle frame: Position of gas particles which will form old and metal rich (bulge) stars. Right frame: Position of gas particl ...
... Figure 2: Snapshot of gas particle distribution in a forming spiral galaxy at a redshift of z = 6. Left frame: Projected distribution of all gas particles in the x{y{plane. Middle frame: Position of gas particles which will form old and metal rich (bulge) stars. Right frame: Position of gas particl ...
aaswinter06
... of an A – F star at the optical maximum in February 2002. The effective temperature then cooled to a very low ~800 K by 230 days after the outburst, appearing to be that of an M or L type supergiant (2.4.5.6). • The distance to the source is estimated to be from 5 to 12 kpc. Analysis of the light ec ...
... of an A – F star at the optical maximum in February 2002. The effective temperature then cooled to a very low ~800 K by 230 days after the outburst, appearing to be that of an M or L type supergiant (2.4.5.6). • The distance to the source is estimated to be from 5 to 12 kpc. Analysis of the light ec ...
Astrophysics - Cathkin High School
... surprising to find that the rate of loss of hydrogen from the Earth’s atmosphere to outer space is considerable. In fact there is very little hydrogen remaining in the atmosphere. Oxygen molecules on the other hand simply have too small a velocity to escape the pull of the Earth. The Moon has no atm ...
... surprising to find that the rate of loss of hydrogen from the Earth’s atmosphere to outer space is considerable. In fact there is very little hydrogen remaining in the atmosphere. Oxygen molecules on the other hand simply have too small a velocity to escape the pull of the Earth. The Moon has no atm ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint
... Diameter ~ 50'', vel. dispersion ~100 km s-1, (assuming a Hubble flow) rate dispersion~2 km s-1 arcsec-1 ...
... Diameter ~ 50'', vel. dispersion ~100 km s-1, (assuming a Hubble flow) rate dispersion~2 km s-1 arcsec-1 ...
– 1 – 1. Historical Notes for Ay 123 1.1.
... All other stellar masses are from binaries except for a few gravitational redshifts for white dwarfs. The problems of binaries are: we only see the orbit projected onto the sky, not the full 3D orbit, and we do not know the inclination angle, the angle that the orbital plane makes with the plane of ...
... All other stellar masses are from binaries except for a few gravitational redshifts for white dwarfs. The problems of binaries are: we only see the orbit projected onto the sky, not the full 3D orbit, and we do not know the inclination angle, the angle that the orbital plane makes with the plane of ...
UMich w/s
... CDM predicts many more satellite galaxies than observed, at all masses `Solutions’: warm DM; self-interacting DM; star formation suppression by reionization; self-regulated star formation; very high M/L plus some other variant; predictions `wrong’, count different things; ...
... CDM predicts many more satellite galaxies than observed, at all masses `Solutions’: warm DM; self-interacting DM; star formation suppression by reionization; self-regulated star formation; very high M/L plus some other variant; predictions `wrong’, count different things; ...
Constraining the Bulk Properties of Dense Matter by Measuring
... dense matter. (Considerable effort is also being put into observations of X-ray pulsars to determine neutron star radii and masses. This is the subject of a separate white paper. Xray instrumentation can also study neutron star cooling, which is important to understand nuclear processes and the comp ...
... dense matter. (Considerable effort is also being put into observations of X-ray pulsars to determine neutron star radii and masses. This is the subject of a separate white paper. Xray instrumentation can also study neutron star cooling, which is important to understand nuclear processes and the comp ...
A Reservoir of Ionized Gas in the Galactic Halo to Sustain Star
... the foreground of stars at known distances from the sun. Recently, based on observations of high-velocity interstellar absorption in the ultraviolet spectra of two Galactic stars, two of these iHVCs were found within 8–15 kpc from the sun (17, 18). One of them was found toward the inner Galaxy and h ...
... the foreground of stars at known distances from the sun. Recently, based on observations of high-velocity interstellar absorption in the ultraviolet spectra of two Galactic stars, two of these iHVCs were found within 8–15 kpc from the sun (17, 18). One of them was found toward the inner Galaxy and h ...
SouthamptonTalkPitkin - LIGO dcc
... For two 1.4 M⊙ neutron stars near coalescence at a distance of 10 Mpc ℎ~1.4 × 10−22 ...
... For two 1.4 M⊙ neutron stars near coalescence at a distance of 10 Mpc ℎ~1.4 × 10−22 ...
Variable Blue Stragglers in M67
... and S1284; physical parameters for the 3 variable BSs are determined, evolutionary status and probable formation mechanism are discussed; S1036 and S1082; waiting for more observations. ...
... and S1284; physical parameters for the 3 variable BSs are determined, evolutionary status and probable formation mechanism are discussed; S1036 and S1082; waiting for more observations. ...
Today in Astronomy 102: “real” black holes, as formed in the
... stars are electrically neutral, with equal numbers of positively- and negatively-charged elementary particles. Spin makes the black hole horizon depart from spherical ...
... stars are electrically neutral, with equal numbers of positively- and negatively-charged elementary particles. Spin makes the black hole horizon depart from spherical ...
Astronomy 114 – Summary of Important Concepts #2 1 Stars: key
... λo is the original wavelength at which the light was emitted, also known as the rest wavelength. λs is the measured wavelength, which will be shifted from the original wavelength due to the motion of the source. v is the velocity with which the source is moving with respect to the observer and c is ...
... λo is the original wavelength at which the light was emitted, also known as the rest wavelength. λs is the measured wavelength, which will be shifted from the original wavelength due to the motion of the source. v is the velocity with which the source is moving with respect to the observer and c is ...
test - Scioly.org
... a) Which type of stellar system is this object? b) Why does this object experience dynamic instability in luminosity and size? c) In what wavelength does this object emit most of its radiation? d) Which wavelength(s) is Image D shown in? Specify if you are describing left or right. 26) Which DSO is ...
... a) Which type of stellar system is this object? b) Why does this object experience dynamic instability in luminosity and size? c) In what wavelength does this object emit most of its radiation? d) Which wavelength(s) is Image D shown in? Specify if you are describing left or right. 26) Which DSO is ...
Cygnus X-1
Cygnus X-1 (abbreviated Cyg X-1) is a well-known galactic X-ray source, thought to be a black hole, in the constellation Cygnus. It was discovered in 1964 during a rocket flight and is one of the strongest X-ray sources seen from Earth, producing a peak X-ray flux density of 6977229999999999999♠2.3×10−23 Wm−2 Hz−1 (7003230000000000000♠2.3×103 Jansky). Cygnus X-1 was the first X-ray source widely accepted to be a black hole and it remains among the most studied astronomical objects in its class. The compact object is now estimated to have a mass about 14.8 times the mass of the Sun and has been shown to be too small to be any known kind of normal star, or other likely object besides a black hole. If so, the radius of its event horizon is about 7004440000000000000♠44 km.Cygnus X-1 belongs to a high-mass X-ray binary system about 7019574266339685654♠6070 ly from the Sun that includes a blue supergiant variable star designated HDE 226868 which it orbits at about 0.2 AU, or 20% of the distance from the Earth to the Sun. A stellar wind from the star provides material for an accretion disk around the X-ray source. Matter in the inner disk is heated to millions of degrees, generating the observed X-rays. A pair of jets, arranged perpendicular to the disk, are carrying part of the energy of the infalling material away into interstellar space.This system may belong to a stellar association called Cygnus OB3, which would mean that Cygnus X-1 is about five million years old and formed from a progenitor star that had more than 7001400000000000000♠40 solar masses. The majority of the star's mass was shed, most likely as a stellar wind. If this star had then exploded as a supernova, the resulting force would most likely have ejected the remnant from the system. Hence the star may have instead collapsed directly into a black hole.Cygnus X-1 was the subject of a friendly scientific wager between physicists Stephen Hawking and Kip Thorne in 1975, with Hawking betting that it was not a black hole. He conceded the bet in 1990 after observational data had strengthened the case that there was indeed a black hole in the system. This hypothesis has not been confirmed due to a lack of direct observation but has generally been accepted from indirect evidence.