Ch 17 Lesson Questions
... 2. What features of the Moon are caused by rocks or comets that crash into its surface? 3. Why do craters on the Moon last for millions of years? 4. Do you think that you would see different parts of the Moon if you lived on the other side of the Earth? 5. Are the Moon phases predictable? Why or why ...
... 2. What features of the Moon are caused by rocks or comets that crash into its surface? 3. Why do craters on the Moon last for millions of years? 4. Do you think that you would see different parts of the Moon if you lived on the other side of the Earth? 5. Are the Moon phases predictable? Why or why ...
The Earth - TeacherWeb
... The Earth rotates on its axis. When the side is facing the sun it is day and when it is facing away from the sun it is night. ...
... The Earth rotates on its axis. When the side is facing the sun it is day and when it is facing away from the sun it is night. ...
Overview of our Solar System 1112 notes
... • At the center of our solar system • Contains 98.5% of all of the mass of the solar system • The first thing formed in our solar system • The largest and only star in our solar system • Provides almost all of the energy used in the solar system • Earth only gets 0.000000001% of the sun’s total ener ...
... • At the center of our solar system • Contains 98.5% of all of the mass of the solar system • The first thing formed in our solar system • The largest and only star in our solar system • Provides almost all of the energy used in the solar system • Earth only gets 0.000000001% of the sun’s total ener ...
HOW DID OUR MOON FORM?
... The Earth-Moon system has a large amount of mass, spin, and orbital motion — angular momentum — compared to other planets and moons. Scientists developed different theories to explain these observations, but none could explain all of them. One theory was that Earth “captured” the Moon as it passed b ...
... The Earth-Moon system has a large amount of mass, spin, and orbital motion — angular momentum — compared to other planets and moons. Scientists developed different theories to explain these observations, but none could explain all of them. One theory was that Earth “captured” the Moon as it passed b ...
The Universe
... background star - second known planet with rings 5 planetary rings discovered Second set discovered by HST in 2005 Composed of very small dust particles Moon System ~27 moons 13 small and in very close orbit Some orbital periods 12-24 hours Collisions may have supplied material for rings Some collis ...
... background star - second known planet with rings 5 planetary rings discovered Second set discovered by HST in 2005 Composed of very small dust particles Moon System ~27 moons 13 small and in very close orbit Some orbital periods 12-24 hours Collisions may have supplied material for rings Some collis ...
Chapter 30 Section 3
... and ammonia that travels through space and develops a bright, distinctive tail as it approaches the Sun ...
... and ammonia that travels through space and develops a bright, distinctive tail as it approaches the Sun ...
File
... Revolution – 687 days (1.88 years); Rotation 24.6 hours Diameter is 0.53 times Earth’s ...
... Revolution – 687 days (1.88 years); Rotation 24.6 hours Diameter is 0.53 times Earth’s ...
Quiz on Solar System study guide with key
... 11. This planet has surface temperatures of 460 ˚C due to an extreme greenhouse effect and has a surface pressure 90 times greater than Earth’s. 12. This planet’s axis is tilted about 90˚ so it looks like it is on its side and was the first new planet to be discovered since ancient times. 13. This p ...
... 11. This planet has surface temperatures of 460 ˚C due to an extreme greenhouse effect and has a surface pressure 90 times greater than Earth’s. 12. This planet’s axis is tilted about 90˚ so it looks like it is on its side and was the first new planet to be discovered since ancient times. 13. This p ...
Day-39
... tails. Ion tail created by the solar wind interacting with ions of the nucleus. Dust tail created from solar wind and sunlight. Comet tails point away from the Sun. ...
... tails. Ion tail created by the solar wind interacting with ions of the nucleus. Dust tail created from solar wind and sunlight. Comet tails point away from the Sun. ...
Beautiful Venus - The Evening Star
... found in the southwestern sky after sunset, often referred to as the evening star, is the planet Venus. This so-called “twin” of Earth is only so in relative size, being about 82% the mass of the Earth. Because it is one of just two planets closer to the sun than Earth, when observed through a teles ...
... found in the southwestern sky after sunset, often referred to as the evening star, is the planet Venus. This so-called “twin” of Earth is only so in relative size, being about 82% the mass of the Earth. Because it is one of just two planets closer to the sun than Earth, when observed through a teles ...
Third Grade Standards of Study First Quarter
... that includes the sun (a star), planets and many moons and the earth is the third planet from the sun in our solar system. I can identify that Earth is the third planet from the Sun and that Earth and other objects revolve Recognize that changes in the length and direction of an object’s shadow indi ...
... that includes the sun (a star), planets and many moons and the earth is the third planet from the sun in our solar system. I can identify that Earth is the third planet from the Sun and that Earth and other objects revolve Recognize that changes in the length and direction of an object’s shadow indi ...
Mars as a Solar System Body Physical Properties and Composition
... more than 40,000 km away From the Earth, Mars looks like a big, reddish star. ...
... more than 40,000 km away From the Earth, Mars looks like a big, reddish star. ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... 1. Assistant to Tycho Brahe, who had the best observations yet of the sky 2. Devised 3 laws from the data: Testable Rules or Empirical Laws a) Planetary orbits are ellipses, not circles b) Orbital radius sweeps out equal areas in equal times ...
... 1. Assistant to Tycho Brahe, who had the best observations yet of the sky 2. Devised 3 laws from the data: Testable Rules or Empirical Laws a) Planetary orbits are ellipses, not circles b) Orbital radius sweeps out equal areas in equal times ...
8th Planets of the solar system Planets Rocky Gas Giants
... rotation of the planet on its axis. Its day is 10 hours, 39 minutes long, and it takes 29.5 Earth years to revolve about the Sun. The atmosphere is primarily composed of hydrogen with small amounts of helium and methane. Saturn is the only planet less dense than water (about 30 percent less). In the ...
... rotation of the planet on its axis. Its day is 10 hours, 39 minutes long, and it takes 29.5 Earth years to revolve about the Sun. The atmosphere is primarily composed of hydrogen with small amounts of helium and methane. Saturn is the only planet less dense than water (about 30 percent less). In the ...
VENUS • Second planet from sun. • named after the
... massive than its near-twin Uranus, which is 15 times the mass of Earth but not as dense. ...
... massive than its near-twin Uranus, which is 15 times the mass of Earth but not as dense. ...
Evangelical Christian Academy
... Compare and contrast terrestrial or Jovian planets. Investigate the significant characteristics of planetary objects other than Earth in the solar system. Discuss how Neptune, Uranus, and Pluto were discovered. Summarize several of the missions and importance of the planetary space probes. ...
... Compare and contrast terrestrial or Jovian planets. Investigate the significant characteristics of planetary objects other than Earth in the solar system. Discuss how Neptune, Uranus, and Pluto were discovered. Summarize several of the missions and importance of the planetary space probes. ...
Understanding the Biosphere
... From the beginning… Earth was formed by aggregation of dust – Pressure produced heat that melted materials • lighter materials went to the surface (atmosphere) • heavier materials remained in the core ...
... From the beginning… Earth was formed by aggregation of dust – Pressure produced heat that melted materials • lighter materials went to the surface (atmosphere) • heavier materials remained in the core ...
Chapter 9 Notes
... have many 77._______________. Each of these four planets also has a system of 78.________________. 79._________________ is small and is made of rocks and frozen gases. It has no 80.__________________ and only one 81._________________. The Asteroid Belt is an area between the 82._____________________ ...
... have many 77._______________. Each of these four planets also has a system of 78.________________. 79._________________ is small and is made of rocks and frozen gases. It has no 80.__________________ and only one 81._________________. The Asteroid Belt is an area between the 82._____________________ ...
Our Solar System
... What’s in Our Solar System? • Our Solar System consists of a central star (the Sun), the nine planets orbiting the sun, moons, asteroids, comets, meteors, interplanetary gas, dust, and all the “space” in between them. • The nine planets of the Solar System are named for Greek and Roman Gods and ...
... What’s in Our Solar System? • Our Solar System consists of a central star (the Sun), the nine planets orbiting the sun, moons, asteroids, comets, meteors, interplanetary gas, dust, and all the “space” in between them. • The nine planets of the Solar System are named for Greek and Roman Gods and ...
Ch. 23: “Touring Our Solar System”
... Ch. 23: “Touring Our Solar System” 23.3: “The Outer Planets” ...
... Ch. 23: “Touring Our Solar System” 23.3: “The Outer Planets” ...
The Sun
... The asteroid belt is the region of the Solar System located roughly between the orbits of the planets Mars and Jupiter. ...
... The asteroid belt is the region of the Solar System located roughly between the orbits of the planets Mars and Jupiter. ...
History of Planets
... so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape (c) has not cleared the neighborhood around its orbit (d) is not a satellite. ...
... so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape (c) has not cleared the neighborhood around its orbit (d) is not a satellite. ...
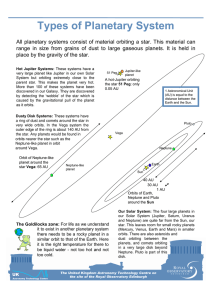
Types of Planetary System
... All planetary systems consist of material orbiting a star. This material can range in size from grains of dust to large gaseous planets. It is held in place by the gravity of the star. Hot Jupiter Systems: These systems have a very large planet like Jupiter in our own Solar System but orbiting extre ...
... All planetary systems consist of material orbiting a star. This material can range in size from grains of dust to large gaseous planets. It is held in place by the gravity of the star. Hot Jupiter Systems: These systems have a very large planet like Jupiter in our own Solar System but orbiting extre ...
Our Solar System - superscientists5456
... • Period of Revolution: time it takes an object to revolve around the sun once. (1 year) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=97Ob0x ...
... • Period of Revolution: time it takes an object to revolve around the sun once. (1 year) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=97Ob0x ...
Late Heavy Bombardment

The Late Heavy Bombardment (abbreviated LHB and also known as the lunar cataclysm) is a hypothetical event thought to have occurred approximately 4.1 to 3.8 billion years (Ga) ago, corresponding to the Neohadean and Eoarchean eras on Earth. During this interval, a disproportionately large number of asteroids apparently collided with the early terrestrial planets in the inner Solar System, including Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. The LHB happened after the Earth and other rocky planets had formed and accreted most of their mass, but still quite early in Earth's history.Evidence for the LHB derives from lunar samples brought back by the Apollo astronauts. Isotopic dating of Moon rocks implies that most impact melts occurred in a rather narrow interval of time. Several hypotheses are now offered to explain the apparent spike in the flux of impactors (i.e. asteroids and comets) in the inner Solar System, but no consensus yet exists. The Nice model is popular among planetary scientists; it postulates that the gas giant planets underwent orbital migration and scattered objects in the asteroid and/or Kuiper belts into eccentric orbits, and thereby into the path of the terrestrial planets. Other researchers argue that the lunar sample data do not require a cataclysmic cratering event near 3.9 Ga, and that the apparent clustering of impact melt ages near this time is an artifact of sampling materials retrieved from a single large impact basin. They also note that the rate of impact cratering could be significantly different between the outer and inner zones of the Solar System.