The Foamy Virus Gag Proteins: What Makes Them Different?
... Several studies show that the N terminus of FV Gag is essential for the interaction of Gag with Env [18,24-26]. Thereby, the structural integrity of a predicted coiled-coil motif (CC1) at aa 4–19 seems to be important for the interaction [18]. Other retroviral Gag proteins, like HIV-1 Gag, contain s ...
... Several studies show that the N terminus of FV Gag is essential for the interaction of Gag with Env [18,24-26]. Thereby, the structural integrity of a predicted coiled-coil motif (CC1) at aa 4–19 seems to be important for the interaction [18]. Other retroviral Gag proteins, like HIV-1 Gag, contain s ...
Full Article - PDF - Journal of Biotech Research
... space (Figures 1C-3C). The proteins consist of two domains that are clearly connected by a long central loop. These domains have also been observed by Jiang et al. [30] and others [31, 32, 33, 34]. The inward and outward opening of the pore through the membrane is a major property of MFS transporter ...
... space (Figures 1C-3C). The proteins consist of two domains that are clearly connected by a long central loop. These domains have also been observed by Jiang et al. [30] and others [31, 32, 33, 34]. The inward and outward opening of the pore through the membrane is a major property of MFS transporter ...
Characterization of the Cytosolic Proteins Involved in the Amoeboid
... actin, these cells power their movement through modulation of the major sperm protein (MSP) cytoskeleton. MSP forms dense filament meshworks that pack the sperm lamellipod. Protrusion is associated with the assembly of MSP filaments at the leading edge of the lamellipod, and retraction is connected ...
... actin, these cells power their movement through modulation of the major sperm protein (MSP) cytoskeleton. MSP forms dense filament meshworks that pack the sperm lamellipod. Protrusion is associated with the assembly of MSP filaments at the leading edge of the lamellipod, and retraction is connected ...
The role of c-di-GMP signaling in an Aeromonas veronii biovar
... screening system (PhP-AE), which is based on the kinetics of fermentation of 11 reagents especially selected to discriminate between individual Aeromonas strains (Möllby et al., 1993; Kuhn et al., 1997). The isolates were distributed over a large number of common (192) and single PhP types. Eightee ...
... screening system (PhP-AE), which is based on the kinetics of fermentation of 11 reagents especially selected to discriminate between individual Aeromonas strains (Möllby et al., 1993; Kuhn et al., 1997). The isolates were distributed over a large number of common (192) and single PhP types. Eightee ...
Ageing and the aggregating proteoglycans of
... appears to be at the N-terminus of the protein, and the smallest of the link proteins appears to be derived from either of the larger by proteolytic cleavage within this region [42]. Irrespective of the heterogeneity, all the link proteins are able to stabilize the proteoglycan aggregate towards dis ...
... appears to be at the N-terminus of the protein, and the smallest of the link proteins appears to be derived from either of the larger by proteolytic cleavage within this region [42]. Irrespective of the heterogeneity, all the link proteins are able to stabilize the proteoglycan aggregate towards dis ...
Identification of Saccharomyces cerevisiae proteins that bind to
... Figure 1.4: Proposed models for chromatin secondary 6 structure. (A) The proposed “one-start” helix or solenoid model is defined by interactions between neighbouring nucleosomes. The sequential histones thus follow each other, bending the DNA to form a helical structure (Robinson & Rhodes 2006). (B) ...
... Figure 1.4: Proposed models for chromatin secondary 6 structure. (A) The proposed “one-start” helix or solenoid model is defined by interactions between neighbouring nucleosomes. The sequential histones thus follow each other, bending the DNA to form a helical structure (Robinson & Rhodes 2006). (B) ...
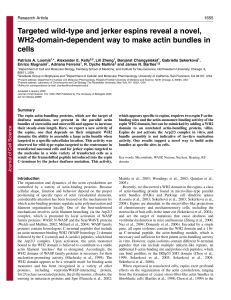
Targeted wild-type and jerker espins reveal a novel, WH2
... recovery of photobleached GFP--actin observed throughout the length of the long microvilli of espin-expressing epithelial cells, suggesting that the WH2 domain of PAB-associated espins can also bind actin monomer in vivo (Loomis et al., 2003). Beyond its amino acid sequence and ability to bind acti ...
... recovery of photobleached GFP--actin observed throughout the length of the long microvilli of espin-expressing epithelial cells, suggesting that the WH2 domain of PAB-associated espins can also bind actin monomer in vivo (Loomis et al., 2003). Beyond its amino acid sequence and ability to bind acti ...
OUR PRODUCTS
... the "mother grain" and revered it as sacred. Each year at planting time it was traditional for the Inca leader to plant the first quinoa seed using a solid gold shovel! Quinoa was used to sustain Incan armies, which frequently marched for many days eating a mixture of quinoa and fat, known as "war b ...
... the "mother grain" and revered it as sacred. Each year at planting time it was traditional for the Inca leader to plant the first quinoa seed using a solid gold shovel! Quinoa was used to sustain Incan armies, which frequently marched for many days eating a mixture of quinoa and fat, known as "war b ...
Identification and Structural Characterization of the ATP/ADP
... amino-terminal domain identified by limited proteolysis have been determined for yeast (Prodromou et al., 1997) and human (Stebbins et al., 1997) proteins. Consistent with the high homology among all Hsp90 sequences (69% identity, yeast to human) the tertiary structure of these two domains is extrem ...
... amino-terminal domain identified by limited proteolysis have been determined for yeast (Prodromou et al., 1997) and human (Stebbins et al., 1997) proteins. Consistent with the high homology among all Hsp90 sequences (69% identity, yeast to human) the tertiary structure of these two domains is extrem ...
EVOLUTIONARILY RELATED INSERTION PATHWAYS OF
... For example, the organelles contain genomes that encode some of their proteins, using their own protein synthesizing machinery. However, the protein conducting capacity of mitochondria and chloroplasts is strongly reduced because the genes originally encoded within these organelles were transferred ...
... For example, the organelles contain genomes that encode some of their proteins, using their own protein synthesizing machinery. However, the protein conducting capacity of mitochondria and chloroplasts is strongly reduced because the genes originally encoded within these organelles were transferred ...
Comparison of the activities of protein disulphide
... the assay was then converted into the quantity of RNAase in the PDI incubation by a factor F, which depended on the volumes used. When the assay sample (A ,ll) was withdrawn from the PDI incubation (original volume V,ul) and assayed in the cuvette (C ,tl), F = CV/A. Thus I ,umol of RNAase generated ...
... the assay was then converted into the quantity of RNAase in the PDI incubation by a factor F, which depended on the volumes used. When the assay sample (A ,ll) was withdrawn from the PDI incubation (original volume V,ul) and assayed in the cuvette (C ,tl), F = CV/A. Thus I ,umol of RNAase generated ...
Protein stabilization: a common consequence of mutations
... Myc is overexpressed in many cancers as a result of gene rearrangement or ampli®cation, but coding sequence changes which cluster in the N-terminal transactivation domain also appear to play a role in tumour progression. The prototypic v-Myc gene of MC29 virus diers from avian c-Myc by a series of ...
... Myc is overexpressed in many cancers as a result of gene rearrangement or ampli®cation, but coding sequence changes which cluster in the N-terminal transactivation domain also appear to play a role in tumour progression. The prototypic v-Myc gene of MC29 virus diers from avian c-Myc by a series of ...
PDF
... histological sections, we never observed Lgl2 localisation at the basal cortex of the basal epidermal cells, where hemidesmosomes form (Fig. 1H). Instead, Lgl2 was predominantly localised to the lateral domain in the basal epidermal cells (Fig. 1H). The apparent apical staining in the basal epiderma ...
... histological sections, we never observed Lgl2 localisation at the basal cortex of the basal epidermal cells, where hemidesmosomes form (Fig. 1H). Instead, Lgl2 was predominantly localised to the lateral domain in the basal epidermal cells (Fig. 1H). The apparent apical staining in the basal epiderma ...
Jelly Facts - Institute of Food Research
... Collagen in animal skin and bones is broken down by heat and treatment with acids and alkalis. Bonds between collagen molecules (intermolecular bonds), bonds in the molecules (intramolecular bonds) and hydrogen bonds are broken down, making gelatin. When protein loses its shape it denatures. When t ...
... Collagen in animal skin and bones is broken down by heat and treatment with acids and alkalis. Bonds between collagen molecules (intermolecular bonds), bonds in the molecules (intramolecular bonds) and hydrogen bonds are broken down, making gelatin. When protein loses its shape it denatures. When t ...
Chicken Acidic Leucine-rich EGF-like Domain Containing Brain
... mass differs from that of the carbohydrate-depleted polypeptide (110 kD) as analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Such differences between predicted and observed sizes have also been reported for other proteins (Rauch et al., 1992 and references therein) and might be due to low binding of SDS by the highly negative ...
... mass differs from that of the carbohydrate-depleted polypeptide (110 kD) as analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Such differences between predicted and observed sizes have also been reported for other proteins (Rauch et al., 1992 and references therein) and might be due to low binding of SDS by the highly negative ...
Effects of macromolecular crowding on protein folding and
... chains of similar molecular weight (dextran 70), this observation suggests that additional factors besides size exclusion effects play a role in determining protein refolding yields. The exact nature of any interactions of lysozyme with BSA and ovalbumin is unknown, but the fact that hen lysozyme is ...
... chains of similar molecular weight (dextran 70), this observation suggests that additional factors besides size exclusion effects play a role in determining protein refolding yields. The exact nature of any interactions of lysozyme with BSA and ovalbumin is unknown, but the fact that hen lysozyme is ...
DLocalMotif: a discriminative approach for discovering local motifs in
... Motivation: Local motifs are patterns of DNA or protein sequences that occur within a sequence interval relative to a biologically defined anchor or landmark. Current protein motif discovery methods do not adequately consider such constraints to identify biologically significant motifs that are only ...
... Motivation: Local motifs are patterns of DNA or protein sequences that occur within a sequence interval relative to a biologically defined anchor or landmark. Current protein motif discovery methods do not adequately consider such constraints to identify biologically significant motifs that are only ...
Turnover of protein phosphorylation evolving under
... Most proteins are regulated by posttranslational modifications and changes in these modifications contribute to evolutionary changes as well as to human diseases. Phosphorylation of serines, threonines, and tyrosines are the most common modifications identified to date in eukaryotic proteomes. While the ...
... Most proteins are regulated by posttranslational modifications and changes in these modifications contribute to evolutionary changes as well as to human diseases. Phosphorylation of serines, threonines, and tyrosines are the most common modifications identified to date in eukaryotic proteomes. While the ...
Supplementary Table 1
... Up-regulated and down-regulated genes after the addition of 100 mM L-serine by microarray analysis Genes of strain BWG1-7A significantly up- or down-regulated during the four hours time-course of growth in the presence of 100 mM L-serine are listed in table IA and table IB respectively. Genes listed ...
... Up-regulated and down-regulated genes after the addition of 100 mM L-serine by microarray analysis Genes of strain BWG1-7A significantly up- or down-regulated during the four hours time-course of growth in the presence of 100 mM L-serine are listed in table IA and table IB respectively. Genes listed ...
Rubisco Synthesis, Assembly, Mechanism, and Regulation
... organization of domains that constitute the L-subunit and confirmed that the active site of the enzyme is shared between elements of both subunits of the dimer (for review, see Hartman and Harpel, 1993). Therefore, although there are two active sites per dimer, amino acids essential for the function ...
... organization of domains that constitute the L-subunit and confirmed that the active site of the enzyme is shared between elements of both subunits of the dimer (for review, see Hartman and Harpel, 1993). Therefore, although there are two active sites per dimer, amino acids essential for the function ...
Protein domain

A protein domain is a conserved part of a given protein sequence and (tertiary) structure that can evolve, function, and exist independently of the rest of the protein chain. Each domain forms a compact three-dimensional structure and often can be independently stable and folded. Many proteins consist of several structural domains. One domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. Domains vary in length from between about 25 amino acids up to 500 amino acids in length. The shortest domains such as zinc fingers are stabilized by metal ions or disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be ""swapped"" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimeric proteins.