Slides for Earth and the Solar System Unit #1
... Think about what you know about the effect of gravity. Why do you think the smaller terrestrial planets are closer to the sun than the gas giants? For a hint, look at the size of the planets in the picture below. ...
... Think about what you know about the effect of gravity. Why do you think the smaller terrestrial planets are closer to the sun than the gas giants? For a hint, look at the size of the planets in the picture below. ...
P2_5 The Apparent Magnitude of α Orionis Supernova
... The star α Orionis (Betelgeuse) is to become a type II supernova at the end of its life. Some have postulated that this supernova will be bright enough that it will be visible during the day. Betelgeuse will have an apparent magnitude of around -8.7, brighter than Venus, which can be seen when the s ...
... The star α Orionis (Betelgeuse) is to become a type II supernova at the end of its life. Some have postulated that this supernova will be bright enough that it will be visible during the day. Betelgeuse will have an apparent magnitude of around -8.7, brighter than Venus, which can be seen when the s ...
The Moon, Planets and Polaris
... We can study these topics together because they are all variations on a theme. You should find few problems with them if you have managed to work with sun sights and they fall reasonably logically into a group of minor RYA exercises. There’s not much to add. The sights are all straightforward and th ...
... We can study these topics together because they are all variations on a theme. You should find few problems with them if you have managed to work with sun sights and they fall reasonably logically into a group of minor RYA exercises. There’s not much to add. The sights are all straightforward and th ...
Jupiter and Saturn: Lords of the Planets Chapter Fourteen
... 2. Why are there important differences between the atmospheres of Jupiter and Saturn? 3. What is going on in Jupiter’s Great Red Spot? 4. What is the nature of the multicolored clouds of Jupiter and Saturn? 5. What does the chemical composition of Jupiter’s atmosphere imply about the planet’s origin ...
... 2. Why are there important differences between the atmospheres of Jupiter and Saturn? 3. What is going on in Jupiter’s Great Red Spot? 4. What is the nature of the multicolored clouds of Jupiter and Saturn? 5. What does the chemical composition of Jupiter’s atmosphere imply about the planet’s origin ...
Powerpoint Presentation (large file)
... 2. Why are there important differences between the atmospheres of Jupiter and Saturn? 3. What is going on in Jupiter’s Great Red Spot? 4. What is the nature of the multicolored clouds of Jupiter and Saturn? 5. What does the chemical composition of Jupiter’s atmosphere imply about the planet’s origin ...
... 2. Why are there important differences between the atmospheres of Jupiter and Saturn? 3. What is going on in Jupiter’s Great Red Spot? 4. What is the nature of the multicolored clouds of Jupiter and Saturn? 5. What does the chemical composition of Jupiter’s atmosphere imply about the planet’s origin ...
Is there life in space? Activity 2: Moving Stars and Their Planets
... Q. Most of the planets that have been discovered orbit their stars at a tilt closer to 0 degrees than to 90 degrees. Why? A. The signal is more evident when the tilt is lower. The telescopes are not perfect, so they can only detect star motions that are very large. The largest motions occur when the ...
... Q. Most of the planets that have been discovered orbit their stars at a tilt closer to 0 degrees than to 90 degrees. Why? A. The signal is more evident when the tilt is lower. The telescopes are not perfect, so they can only detect star motions that are very large. The largest motions occur when the ...
Neptune Nachman
... outside the planet. Neptune also has many storms and powerful wind speeds (most powerful winds of all planets in solar system). A cool feature about Neptune is it’s “Great Dark Spot”. The “Great Dark Spot” is a depression in it’s atmosphere. There are also 3 faint rings. ...
... outside the planet. Neptune also has many storms and powerful wind speeds (most powerful winds of all planets in solar system). A cool feature about Neptune is it’s “Great Dark Spot”. The “Great Dark Spot” is a depression in it’s atmosphere. There are also 3 faint rings. ...
Starspots (AIP – Klaus G
... Doppler imaging is an inversion technique to recover a 2-D image of a rapidly rotating star from a series of high-resolution spectral line profiles. The inverse problem for stars with cool spots amounts to solving the integral equation relating the surface temperature distribution to the observed li ...
... Doppler imaging is an inversion technique to recover a 2-D image of a rapidly rotating star from a series of high-resolution spectral line profiles. The inverse problem for stars with cool spots amounts to solving the integral equation relating the surface temperature distribution to the observed li ...
Editorial Introduction: Planetary geosciences, the Dutch contribution
... Planetary geoscience was effectively born when Christiaan Huygens took his first look at planet Mars on Friday 28 November 1659. As one of the leading scientists of his time, Huygens was known for constructing his own telescopes to observe stars, planets and nebulae whenever the clear and spacious s ...
... Planetary geoscience was effectively born when Christiaan Huygens took his first look at planet Mars on Friday 28 November 1659. As one of the leading scientists of his time, Huygens was known for constructing his own telescopes to observe stars, planets and nebulae whenever the clear and spacious s ...
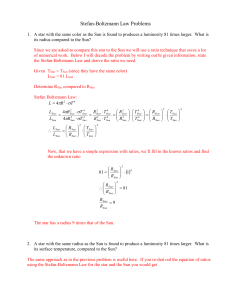
Stefan-Boltzmann Law Problems
... information in the question to find the answer directly. The Stefan-Boltzmann Law is a relationship between luminosity, temperature and radius. In this problem we are asked to determine the radii ratio of the stars given that the two stars have roughly the same temperature, but we are not given lumi ...
... information in the question to find the answer directly. The Stefan-Boltzmann Law is a relationship between luminosity, temperature and radius. In this problem we are asked to determine the radii ratio of the stars given that the two stars have roughly the same temperature, but we are not given lumi ...
Individual Lesson Plan
... 36. Ask: “Why is this sunset?” [Because the Sun is disappearing in the west.] Remind students that they can turn their head to look down their arm and see the Sun low in their western sky. 37. Ask: “Why does the Sun seem to disappear in the west?” [Because I turn away from it.] 38. Ask: “Does the Su ...
... 36. Ask: “Why is this sunset?” [Because the Sun is disappearing in the west.] Remind students that they can turn their head to look down their arm and see the Sun low in their western sky. 37. Ask: “Why does the Sun seem to disappear in the west?” [Because I turn away from it.] 38. Ask: “Does the Su ...
2016 Annual Report - International Dark
... markers is what made them most useful. Some days are marked on the day itself, but if you are going to prepare for ceremony, agriculture, etc, you must be able to predict the times. ...
... markers is what made them most useful. Some days are marked on the day itself, but if you are going to prepare for ceremony, agriculture, etc, you must be able to predict the times. ...
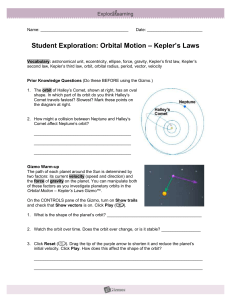
Keplers Laws
... 1. Sketch: The distance unit used her is the astronomical unit (AU), equal to the average Earth-Sun distance. Place the planet on the i axis at r = –3.00i AU. Move the velocity vector so that v = -8.0j km/s (|v| = 8.00 km/s). The resulting vectors should look like the vectors in the image at right. ...
... 1. Sketch: The distance unit used her is the astronomical unit (AU), equal to the average Earth-Sun distance. Place the planet on the i axis at r = –3.00i AU. Move the velocity vector so that v = -8.0j km/s (|v| = 8.00 km/s). The resulting vectors should look like the vectors in the image at right. ...
What causes the moon to change in appearance
... Doesn’t it seem as if the moon’s shape changes night after night? As the moon orbits –the curved path of a celestial object or spacecraft around a star or planet—Earth, it appears as though the moon is changing its shape in the sky. This is because as the moon changes its position, the amount of sun ...
... Doesn’t it seem as if the moon’s shape changes night after night? As the moon orbits –the curved path of a celestial object or spacecraft around a star or planet—Earth, it appears as though the moon is changing its shape in the sky. This is because as the moon changes its position, the amount of sun ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... 1. Sketch: The distance unit used her is the astronomical unit (AU), equal to the average Earth-Sun distance. Place the planet on the i axis at r = –3.00i AU. Move the velocity vector so that v = -8.0j km/s (|v| = 8.00 km/s). The resulting vectors should look like the vectors in the image at right. ...
... 1. Sketch: The distance unit used her is the astronomical unit (AU), equal to the average Earth-Sun distance. Place the planet on the i axis at r = –3.00i AU. Move the velocity vector so that v = -8.0j km/s (|v| = 8.00 km/s). The resulting vectors should look like the vectors in the image at right. ...
Earth-Mars Interplanetary Transport System Brian Dodson The issue
... practical approach may lie in transferring large ships between Solar System Lagrange points. The ships would not be in a perpetual orbit, but would rest between launches at a Lagrange point of the appropriate planet. Their mass never requires large application of delta-V, with the result that moveme ...
... practical approach may lie in transferring large ships between Solar System Lagrange points. The ships would not be in a perpetual orbit, but would rest between launches at a Lagrange point of the appropriate planet. Their mass never requires large application of delta-V, with the result that moveme ...
What makes a planet habitable?
... Where are they? Star-types and expected preferred habitats Class I Earth-like habitable planets may preferably be found in ...
... Where are they? Star-types and expected preferred habitats Class I Earth-like habitable planets may preferably be found in ...
The Stability of Exomoons in the Habitable Zone
... conditions must then be upheld for quite some time to allow potential life to arise, meaning the orbit of the body must be fairly stable. In this investigation, all the objects at exoplanets.org (as of 2014-04-29) were evaluated to see which of these that could possibly have habitable moons, taking ...
... conditions must then be upheld for quite some time to allow potential life to arise, meaning the orbit of the body must be fairly stable. In this investigation, all the objects at exoplanets.org (as of 2014-04-29) were evaluated to see which of these that could possibly have habitable moons, taking ...
On the correlation between stellar chromospheric flux and the
... show signatures of condensations absorbing in Hα, that are located a few stellar radii above the surface (Collier Cameron & Robinson 1989a,b). Prominence-like structures were also observed in CoRoT-2 (Czesla et al. 2012). In late-type stars that are accompanied by close-in planets, different magneti ...
... show signatures of condensations absorbing in Hα, that are located a few stellar radii above the surface (Collier Cameron & Robinson 1989a,b). Prominence-like structures were also observed in CoRoT-2 (Czesla et al. 2012). In late-type stars that are accompanied by close-in planets, different magneti ...
by Kendrick Frazier Pluto turns out not to be responsible for
... next several nights and observed definite motion. He thought his discovery was a comet, but within two months other astronomers had decided correctly that it was indeed a new planet. A Finnish astronomer, A n d e r s Lexell, determined that its distance from the sun was 18.9 astronomical units (the ...
... next several nights and observed definite motion. He thought his discovery was a comet, but within two months other astronomers had decided correctly that it was indeed a new planet. A Finnish astronomer, A n d e r s Lexell, determined that its distance from the sun was 18.9 astronomical units (the ...
Astrobiological Stoichiometry
... abundances for the same element in the same star. Figure 2, from the work of Hinkel (2012), illustrates how different research groups measured the elements Na, Si, O, Sc, Al, and Fe in five different stars (the data sets are discussed and the research groups identified by Hinkel, 2012). The maximum ...
... abundances for the same element in the same star. Figure 2, from the work of Hinkel (2012), illustrates how different research groups measured the elements Na, Si, O, Sc, Al, and Fe in five different stars (the data sets are discussed and the research groups identified by Hinkel, 2012). The maximum ...
Peer-reviewed Article PDF - e
... silicon than carbon in the Earth. Silicon is a very important element for the development of life on the Earth, because it forms silicates which make up much of the land areas that are not as heavy as basalt. Therefore the silicon rich continents float upon the basalt beneath. All of this makes the ...
... silicon than carbon in the Earth. Silicon is a very important element for the development of life on the Earth, because it forms silicates which make up much of the land areas that are not as heavy as basalt. Therefore the silicon rich continents float upon the basalt beneath. All of this makes the ...
Embedding Comets in the Asteroid Belt - SwRI Boulder
... Our simulations were performed in the context of the so-called Nice model [10, 11, 5] because it is the most successful model to date at explaining the characteristics of the outer Solar System. In the Nice model, the giant planets are assumed to have formed in a compact configuration (all were loca ...
... Our simulations were performed in the context of the so-called Nice model [10, 11, 5] because it is the most successful model to date at explaining the characteristics of the outer Solar System. In the Nice model, the giant planets are assumed to have formed in a compact configuration (all were loca ...
Planetary system formation in thermally evolving viscous
... Planetary orbital eccentricity can strongly influence Lindblad migration torques [25] and eccentricity/inclination damping rates of embedded planets [26]. In a recent study, Bitsch & Kley [18] showed that corotation torques decrease significantly with modest growth of eccentricity. We present here a b ...
... Planetary orbital eccentricity can strongly influence Lindblad migration torques [25] and eccentricity/inclination damping rates of embedded planets [26]. In a recent study, Bitsch & Kley [18] showed that corotation torques decrease significantly with modest growth of eccentricity. We present here a b ...
Orrery

An orrery is a mechanical model of the solar system that illustrates or predicts the relative positions and motions of the planets and moons, usually according to the heliocentric model. It may also represent the relative sizes of these bodies; but since accurate scaling is often not practical due to the actual large ratio differences, a subdued approximation may be used instead. Though the Greeks had working planetaria, the first orrery that was a planetarium of the modern era was produced in 1704, and one was presented to Charles Boyle, 4th Earl of Orrery — whence came the name. They are typically driven by a clockwork mechanism with a globe representing the Sun at the centre, and with a planet at the end of each of the arms.