June, 2001 AAS poster - David P. Bennett
... The gravitational microlensing signals of terrestrial planets are visible only in the light curves of main sequence stars. These stars are very crowded in the dense central Galactic bulge fields that are the prime target fields because of the enhanced microlensing rate and the line of sight through ...
... The gravitational microlensing signals of terrestrial planets are visible only in the light curves of main sequence stars. These stars are very crowded in the dense central Galactic bulge fields that are the prime target fields because of the enhanced microlensing rate and the line of sight through ...
6th Grade Science
... and nighttime. Earth completes one rotation every 24 hours. Another major movement of planets and moons is revolution-the circling of an object in space around another object in space. It takes a year for Earth, or 365.25 days, to revolve around the sun. The Moon takes about 29 days to revolve aroun ...
... and nighttime. Earth completes one rotation every 24 hours. Another major movement of planets and moons is revolution-the circling of an object in space around another object in space. It takes a year for Earth, or 365.25 days, to revolve around the sun. The Moon takes about 29 days to revolve aroun ...
Video Lesson Information Astronomy: Observations & Theories Astronomy 1
... This video lesson explains the motion of Earth around the sun and its yearly cycle. Astronomers explain the unique orbital and size relations between the rotation of Earth, the sun, and the moon and how this makes a total solar eclipse possible at predictable intervals, known as the Saros cycle. The ...
... This video lesson explains the motion of Earth around the sun and its yearly cycle. Astronomers explain the unique orbital and size relations between the rotation of Earth, the sun, and the moon and how this makes a total solar eclipse possible at predictable intervals, known as the Saros cycle. The ...
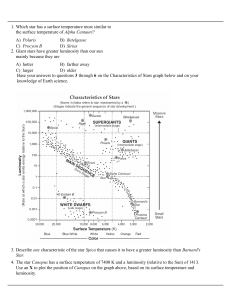
2-star-life-cycle-and-star-classification
... 59. The star Algol is estimated to have approximately the same luminosity as the star Aldebaran approximately the same temperature as the Rigel. Algol is best classified as a A) main sequence star B) red giant star C) white dwarf star D) red dwarf star 60. Two stars of the same color are plotted on ...
... 59. The star Algol is estimated to have approximately the same luminosity as the star Aldebaran approximately the same temperature as the Rigel. Algol is best classified as a A) main sequence star B) red giant star C) white dwarf star D) red dwarf star 60. Two stars of the same color are plotted on ...
Neptune The Stormy Planet Our Solar System
... neptune’s moons and rings. ... winds ever discovered in the solar system. neptune ... in 2006 when pluto lost its status as our solar system’s ninth planet. GRIFFITH OBSERVATORY - THE PLANET NEPTUNE Thu, 20 Apr 2017 05:28:00 GMT ... planets > neptune. ... our earth: mars: jupiter: saturn: uranus: ne ...
... neptune’s moons and rings. ... winds ever discovered in the solar system. neptune ... in 2006 when pluto lost its status as our solar system’s ninth planet. GRIFFITH OBSERVATORY - THE PLANET NEPTUNE Thu, 20 Apr 2017 05:28:00 GMT ... planets > neptune. ... our earth: mars: jupiter: saturn: uranus: ne ...
stellarium for beginners
... Within this use case you learn about Stellarium's main features, each presented with examples taken from its most common use. If used in the classroom this is a very simple exploration of the software tool that can be left to pupils provided with printed copies of the use case ...
... Within this use case you learn about Stellarium's main features, each presented with examples taken from its most common use. If used in the classroom this is a very simple exploration of the software tool that can be left to pupils provided with printed copies of the use case ...
1 A Re-appraisal of the Habitability of Planets Around M Dwarf Stars
... suggest a framework for research to be conducted in the next two years that should better delimit the constraints on the spectral type and ages of M dwarf stars that would be appropriate targets for missions searching for life beyond Earth, including technological civilizations. A second workshop in ...
... suggest a framework for research to be conducted in the next two years that should better delimit the constraints on the spectral type and ages of M dwarf stars that would be appropriate targets for missions searching for life beyond Earth, including technological civilizations. A second workshop in ...
Unit 7 Beyond Our Planet
... The only planet that is known to support life is Earth. Earth is warm enough to keep water from freezing and cool enough to keep it from boiling. Liquid water is a vital resource for life ...
... The only planet that is known to support life is Earth. Earth is warm enough to keep water from freezing and cool enough to keep it from boiling. Liquid water is a vital resource for life ...
October, 2006 - The Astronomical Society of Las Cruces
... billion miles beyond Neptune, and this is the closest that the two objects can approach. Here I explain this process. The last time Neptune passed between Pluto and the Sun occurred when Pluto was at aphelion. Because Pluto makes two revolutions around the Sun in the same time as Neptune makes three ...
... billion miles beyond Neptune, and this is the closest that the two objects can approach. Here I explain this process. The last time Neptune passed between Pluto and the Sun occurred when Pluto was at aphelion. Because Pluto makes two revolutions around the Sun in the same time as Neptune makes three ...
prime meridian
... back at the prime meridian at Greenwich, England (or at any other place with a known longitude). When the sun reached its highest point above your ship, you knew it was 12 p.m. your time. Each hour of difference between your time (12 p.m.) and the time back at Greenwich was equal to 15⁰ of longitude ...
... back at the prime meridian at Greenwich, England (or at any other place with a known longitude). When the sun reached its highest point above your ship, you knew it was 12 p.m. your time. Each hour of difference between your time (12 p.m.) and the time back at Greenwich was equal to 15⁰ of longitude ...
A coupling of the origin of asteroid belt, planetary ring
... compositive motion for the comet. In other words, it is rather difficult to determine the comet’s proper motion. In addition to this, the solar system itself is flat, it appears to be no reason for people to believe there will have a spherical cloud of comets at the outer reaches of the solar system ...
... compositive motion for the comet. In other words, it is rather difficult to determine the comet’s proper motion. In addition to this, the solar system itself is flat, it appears to be no reason for people to believe there will have a spherical cloud of comets at the outer reaches of the solar system ...
Lecture14
... • The Trojan asteroids are located far beyond the main belt at about the same distance as Jupiter • The Trojan asteroids are dark and sizable • There is one group ahead and one group behind ...
... • The Trojan asteroids are located far beyond the main belt at about the same distance as Jupiter • The Trojan asteroids are dark and sizable • There is one group ahead and one group behind ...
ori pro 02 semifin [sfn] - SwRI Boulder
... for the formation of Uranus and Neptune that includes an explanation of the LHB on the Moon and terrestrial planets. The simplest form of this model includes the following steps: (1) Four icy giant-planet cores of 1015 M grow in the Jupiter-Saturn zone due to oligarchic growth (Ida and Makino 1993; ...
... for the formation of Uranus and Neptune that includes an explanation of the LHB on the Moon and terrestrial planets. The simplest form of this model includes the following steps: (1) Four icy giant-planet cores of 1015 M grow in the Jupiter-Saturn zone due to oligarchic growth (Ida and Makino 1993; ...
Whence Comets?
... There is no doubt that comets did not form in to the Sun and at higher temperatures. Forming this mixing of near-Sun condensates with orbits even remotely similar to the ones in which in among the giant planets, these comets were preserved circumstellar grains has been sugwe now observe them (Fig. 1 ...
... There is no doubt that comets did not form in to the Sun and at higher temperatures. Forming this mixing of near-Sun condensates with orbits even remotely similar to the ones in which in among the giant planets, these comets were preserved circumstellar grains has been sugwe now observe them (Fig. 1 ...
The Formation of Systems with Tightly
... understanding of planet formation (Borucki et al. 2011; Batalha et al. 2013). Among the quicklygrowing data is a subclass of multi-planet configurations referred to as Systems with Tightlypacked Inner Planets (STIPs). Their large abundance (> 10% of stars) suggests that they are one of the principal ...
... understanding of planet formation (Borucki et al. 2011; Batalha et al. 2013). Among the quicklygrowing data is a subclass of multi-planet configurations referred to as Systems with Tightlypacked Inner Planets (STIPs). Their large abundance (> 10% of stars) suggests that they are one of the principal ...
Astronomy 10 Measuring Stars
... The sun has a temperature of about 6000K. Given the data you have calculated so far, what is the ratio of the radius of Sirius A to that of the sun? ...
... The sun has a temperature of about 6000K. Given the data you have calculated so far, what is the ratio of the radius of Sirius A to that of the sun? ...
ADDENDUM TO PRODUCT MANUAL
... will help the telescope better predict the available bright stars and planets that are above the horizon. Remember to select alignment stars that are as far apart in the sky as possible. For best results make sure that the third alignment star does not lie in a straight line between the first two st ...
... will help the telescope better predict the available bright stars and planets that are above the horizon. Remember to select alignment stars that are as far apart in the sky as possible. For best results make sure that the third alignment star does not lie in a straight line between the first two st ...
Lecture 6: Planet migration
... The impulse approximation yields approximately the right answer in this case, but it is clear that this analysis has skated over the more subtle details of the problem. A full analysis instead considers the evolution of linear perturbations in a fluid disc, and was first applied to planet-disc inter ...
... The impulse approximation yields approximately the right answer in this case, but it is clear that this analysis has skated over the more subtle details of the problem. A full analysis instead considers the evolution of linear perturbations in a fluid disc, and was first applied to planet-disc inter ...
Chapter 10
... 4. Describe the interior of Jupiter and draw a labeled sketch of a cross section through Jupiter. 5. Be able to identify by sight, and to describe the Galilean satellites of Jupiter, including the origin and properties of their surface features. How can these moons be warm even though they are so sm ...
... 4. Describe the interior of Jupiter and draw a labeled sketch of a cross section through Jupiter. 5. Be able to identify by sight, and to describe the Galilean satellites of Jupiter, including the origin and properties of their surface features. How can these moons be warm even though they are so sm ...
CUMULATIVE C
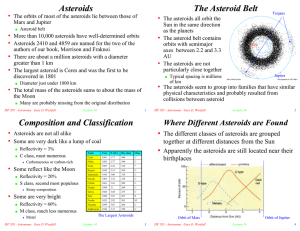
... An asteroid is an irregularly shaped celestial object made up of rock or metal. They are smaller than planets and have irregular shapes rather than spherical shapes. A comet is a celestial object made up of ice, rock, and dust that has a very long orbit around the sun. As they move closer to the sun ...
... An asteroid is an irregularly shaped celestial object made up of rock or metal. They are smaller than planets and have irregular shapes rather than spherical shapes. A comet is a celestial object made up of ice, rock, and dust that has a very long orbit around the sun. As they move closer to the sun ...
Orrery

An orrery is a mechanical model of the solar system that illustrates or predicts the relative positions and motions of the planets and moons, usually according to the heliocentric model. It may also represent the relative sizes of these bodies; but since accurate scaling is often not practical due to the actual large ratio differences, a subdued approximation may be used instead. Though the Greeks had working planetaria, the first orrery that was a planetarium of the modern era was produced in 1704, and one was presented to Charles Boyle, 4th Earl of Orrery — whence came the name. They are typically driven by a clockwork mechanism with a globe representing the Sun at the centre, and with a planet at the end of each of the arms.













![ori pro 02 semifin [sfn] - SwRI Boulder](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003452881_1-e283be02461ddda633f82ba57bf90f9d-300x300.png)