Testing - Department of Physics & Astronomy
... – They developed models of nature and emphasized that the predictions of models should agree with observations. • How did the Greeks explain planetary motion? – The Ptolemaic model had each planet move on a small circle whose center moves around Earth on a larger circle. ...
... – They developed models of nature and emphasized that the predictions of models should agree with observations. • How did the Greeks explain planetary motion? – The Ptolemaic model had each planet move on a small circle whose center moves around Earth on a larger circle. ...
Simon Dawes Jantar Mantar
... Using the instrument it is possible to calculate the dates of solar and lunar eclipses, Sun rise & set, moon rise and set etc. ...
... Using the instrument it is possible to calculate the dates of solar and lunar eclipses, Sun rise & set, moon rise and set etc. ...
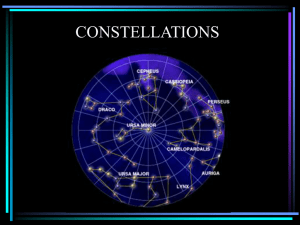
Constellations Overview
... The most famous of all the constellations are the 12 that make up the Zodiac. All planets can be observed only in these 12 constellations as they pass across the sky during the course of their year. This is because the orbits of all the planets lie within ± 8º of the ecliptic. The Sun also moves t ...
... The most famous of all the constellations are the 12 that make up the Zodiac. All planets can be observed only in these 12 constellations as they pass across the sky during the course of their year. This is because the orbits of all the planets lie within ± 8º of the ecliptic. The Sun also moves t ...
======= SPIRIT 2
... to smallest. Jovian bodies are gas giants. Terrestrial bodies are rocky worlds larger than 1000 km in diameter. Planetodal bodies are rocky with a size between 250 and 1000 km in diameter. Asteroidal bodies are rocky and are smaller than 250 km in diameter. Physical The physical characteristics of c ...
... to smallest. Jovian bodies are gas giants. Terrestrial bodies are rocky worlds larger than 1000 km in diameter. Planetodal bodies are rocky with a size between 250 and 1000 km in diameter. Asteroidal bodies are rocky and are smaller than 250 km in diameter. Physical The physical characteristics of c ...
topics and terms - Rice Space Institute
... 42. From this and Kepler’s laws, you should be able to calculate the speed of the Moon in its orbit around earth. 43. geosynchronous orbit = the orbit at which the orbital period = 1 day This orbit is very useful for communication satellites. You should be able to calculate that distance from the ce ...
... 42. From this and Kepler’s laws, you should be able to calculate the speed of the Moon in its orbit around earth. 43. geosynchronous orbit = the orbit at which the orbital period = 1 day This orbit is very useful for communication satellites. You should be able to calculate that distance from the ce ...
Making the Terrestrial Planets: N-Body Integrations of Planetary
... Recent improvements in the performance of computer workstations, and the development of a new N-body algorithm, now make it possible to carry out N-body integrations, in three dimensions, of several tens of gravitationally interacting bodies for the p108 orbits necessary to form the cores of the inn ...
... Recent improvements in the performance of computer workstations, and the development of a new N-body algorithm, now make it possible to carry out N-body integrations, in three dimensions, of several tens of gravitationally interacting bodies for the p108 orbits necessary to form the cores of the inn ...
Review Packet 2011 final edit
... Mrs. Neumann and Mr.Thomas’s Earth Science Review packet Block 2 2011 In preparation for the Regents Exam in Earth Science that will take place in June, we are asking that the students start their reviewing now. The following pages of this packet accompany the review book that was provided for the s ...
... Mrs. Neumann and Mr.Thomas’s Earth Science Review packet Block 2 2011 In preparation for the Regents Exam in Earth Science that will take place in June, we are asking that the students start their reviewing now. The following pages of this packet accompany the review book that was provided for the s ...
Some clicker questions to review
... on Earth with its gravitational force, the Earth affects the ...
... on Earth with its gravitational force, the Earth affects the ...
CELESTIAL COORDINATES
... Another special case is that for an object on the meridian, for which the hour angle is zero by definition. Hence the equation states that Sidereal time = Right ascension crossing the meridian Your current sidereal time, coupled with a knowledge of your latitude, uniquely defines the appearance of t ...
... Another special case is that for an object on the meridian, for which the hour angle is zero by definition. Hence the equation states that Sidereal time = Right ascension crossing the meridian Your current sidereal time, coupled with a knowledge of your latitude, uniquely defines the appearance of t ...
Neptune & Uranus Notes
... own search from the Berlin Observatory, using a newly completed set of more accurate sky charts He found the new planet within one or two degrees of the predicted position—on his first attempt ...
... own search from the Berlin Observatory, using a newly completed set of more accurate sky charts He found the new planet within one or two degrees of the predicted position—on his first attempt ...
Theme 10.1 -- Leftovers: Comets
... coma and the tail. So, eventually, they're bound to be disrupted. In fact, Comet Halley has an expected lifetime of only about 30,000 years. That sounds a long time but is very small in astronomical terms. Eventually comets can be disrupted in this way and vanish. Comets can suffer a fate other than ...
... coma and the tail. So, eventually, they're bound to be disrupted. In fact, Comet Halley has an expected lifetime of only about 30,000 years. That sounds a long time but is very small in astronomical terms. Eventually comets can be disrupted in this way and vanish. Comets can suffer a fate other than ...
Chapter 6 The Outer Solar System © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
... How did they get there? • Kuiper belt comets formed in the Kuiper belt: flat plane, aligned with the plane of planetary orbits, orbiting in the same direction as the planets • Oort cloud comets were once closer to the Sun, but they were kicked out there by gravitational interactions with jovian pla ...
... How did they get there? • Kuiper belt comets formed in the Kuiper belt: flat plane, aligned with the plane of planetary orbits, orbiting in the same direction as the planets • Oort cloud comets were once closer to the Sun, but they were kicked out there by gravitational interactions with jovian pla ...
Comets
... • Comets are thought to be the left over debris from during the time of formation of the solar system. • The elliptical orbits of comets suggest that they underwent gravitational pull from the giant planets. • This all lead us to infer two possible locations where comets could start their journey to ...
... • Comets are thought to be the left over debris from during the time of formation of the solar system. • The elliptical orbits of comets suggest that they underwent gravitational pull from the giant planets. • This all lead us to infer two possible locations where comets could start their journey to ...
The Voyager pictures show four additional faint rings. Saturn`s rings
... orbit: 1,429,400,000 km (9.54 AU) from Sun diameter: 120,536 km (equatorial) mass: 5.68e26 kg In Roman mythology, Saturn is the god of agriculture. The associated Greek god, Cronus, was the son of Uranus and Gaia and the father of Zeus (Jupiter). Saturn is the root of the English word "Saturday" (se ...
... orbit: 1,429,400,000 km (9.54 AU) from Sun diameter: 120,536 km (equatorial) mass: 5.68e26 kg In Roman mythology, Saturn is the god of agriculture. The associated Greek god, Cronus, was the son of Uranus and Gaia and the father of Zeus (Jupiter). Saturn is the root of the English word "Saturday" (se ...
How High can you jump on another planet
... planets in orbit around the sun. The force of gravity is defined by Newton’s law the F=mg. Although this equation is not directly used in the lesson, students will focus on gravity as it relates to mass. Gravity anomalies are important in the study of both Earth and Mars. Scientists look for small d ...
... planets in orbit around the sun. The force of gravity is defined by Newton’s law the F=mg. Although this equation is not directly used in the lesson, students will focus on gravity as it relates to mass. Gravity anomalies are important in the study of both Earth and Mars. Scientists look for small d ...
S STR RO ONO OM MY - Supercharged Science
... Clean up Messes: Your lab area should be neat, organized, and spotless before you start, during your experiment, and when you leave. Scientists waste more time hunting for lost papers, pieces of an experiment, and trying to reposition sensitive equipment … all of which could have easily been avoid ...
... Clean up Messes: Your lab area should be neat, organized, and spotless before you start, during your experiment, and when you leave. Scientists waste more time hunting for lost papers, pieces of an experiment, and trying to reposition sensitive equipment … all of which could have easily been avoid ...
Basic principles of celestial navigation
... through" the observer’s meridian from east to west at intervals of 23 hour, 56 minute, 4 second of mean solar time, also called the sidereal rotational period of the Earth or the sidereal day. The observer’s zenith is defined by the outward extension of the line from the center of the Earth through ...
... through" the observer’s meridian from east to west at intervals of 23 hour, 56 minute, 4 second of mean solar time, also called the sidereal rotational period of the Earth or the sidereal day. The observer’s zenith is defined by the outward extension of the line from the center of the Earth through ...
looking up! - Discover the universe
... half gets no sun (where it is night on the Moon). • The Moon orbits the Earth with an orbital period (time to complete a full revolution) is about a month. • During this month, the illuminated fraction that is visible from Earth varies. Sometimes the half we see is the fully illuminated half: this ...
... half gets no sun (where it is night on the Moon). • The Moon orbits the Earth with an orbital period (time to complete a full revolution) is about a month. • During this month, the illuminated fraction that is visible from Earth varies. Sometimes the half we see is the fully illuminated half: this ...
Photometry`s bright future: Detecting Solar System analogues with
... Our sun’s noise varies by a factor of ∼2 during the 11year solar cycle, from 7.8ppm (2007.77, quiet period) in 6.5hrs bins to 14.7ppm (2002.39, active period) (Gilliland et al. 2011; Fröhlich et al. 1997). This is at the quiet side of G-type stars, of which the most quiet 1% have 6ppm, with a total ...
... Our sun’s noise varies by a factor of ∼2 during the 11year solar cycle, from 7.8ppm (2007.77, quiet period) in 6.5hrs bins to 14.7ppm (2002.39, active period) (Gilliland et al. 2011; Fröhlich et al. 1997). This is at the quiet side of G-type stars, of which the most quiet 1% have 6ppm, with a total ...
Orrery

An orrery is a mechanical model of the solar system that illustrates or predicts the relative positions and motions of the planets and moons, usually according to the heliocentric model. It may also represent the relative sizes of these bodies; but since accurate scaling is often not practical due to the actual large ratio differences, a subdued approximation may be used instead. Though the Greeks had working planetaria, the first orrery that was a planetarium of the modern era was produced in 1704, and one was presented to Charles Boyle, 4th Earl of Orrery — whence came the name. They are typically driven by a clockwork mechanism with a globe representing the Sun at the centre, and with a planet at the end of each of the arms.