chapter 19 the organization and control of eukaryotic genomes
... This methylation patterns accounts for genomic imprinting in which methylation turns off either the maternal or paternal alleles of certain genes at the start of development. ...
... This methylation patterns accounts for genomic imprinting in which methylation turns off either the maternal or paternal alleles of certain genes at the start of development. ...
Analytical and Chromatography - Sigma
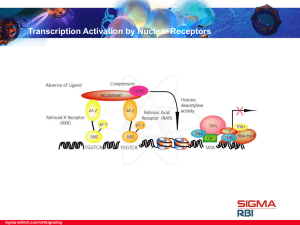
... • Retinoid X receptor (RXR) and Retinoic Acid receptor (RAR) are nuclear receptors that bind either all trans-retinoic (tRA) or 9-cis-retinoic acid (9cis-RA). In the absence of ligand, corepressors, such as Nuclear Receptor Corepressor (NCoR), Silencing Mediator of Retinoid and Thyroid Hormone Recep ...
... • Retinoid X receptor (RXR) and Retinoic Acid receptor (RAR) are nuclear receptors that bind either all trans-retinoic (tRA) or 9-cis-retinoic acid (9cis-RA). In the absence of ligand, corepressors, such as Nuclear Receptor Corepressor (NCoR), Silencing Mediator of Retinoid and Thyroid Hormone Recep ...
1 - Videolectures
... The TCF7L2 variant is associated with a sibling relative risk for type 2 diabetes of only about 1.02, whereas the overall risk of disease among siblings of affected persons is three times that in the general population. If the human genome carried scores of variants with such effects, they would col ...
... The TCF7L2 variant is associated with a sibling relative risk for type 2 diabetes of only about 1.02, whereas the overall risk of disease among siblings of affected persons is three times that in the general population. If the human genome carried scores of variants with such effects, they would col ...
Principles of Genetics
... • Human sex cells (sperm or egg) contain 23 chromosomes each. • When the egg is fertilized, the embryo will have 46 chromosomes in each of its cells, which is the correct number of chromosomes for a human. ...
... • Human sex cells (sperm or egg) contain 23 chromosomes each. • When the egg is fertilized, the embryo will have 46 chromosomes in each of its cells, which is the correct number of chromosomes for a human. ...
Chapter 14- Human Genome
... numbers of chromosomes may find their way into gametes, and a disorder of chromosome numbers may result. ...
... numbers of chromosomes may find their way into gametes, and a disorder of chromosome numbers may result. ...
Chapter 14 - River Ridge #210
... numbers of chromosomes may find their way into gametes, and a disorder of chromosome numbers may result. ...
... numbers of chromosomes may find their way into gametes, and a disorder of chromosome numbers may result. ...
Unit2Day5
... • Can arise by unequal crossing over (gene duplication) • Can arise by genome duplication (failure of meiosis to produce haploid gamete) ...
... • Can arise by unequal crossing over (gene duplication) • Can arise by genome duplication (failure of meiosis to produce haploid gamete) ...
Human Heredity
... numbers of chromosomes may find their way into gametes, and a disorder of chromosome numbers may result. ...
... numbers of chromosomes may find their way into gametes, and a disorder of chromosome numbers may result. ...
Genetics - David Bogler Home
... What did Mendel conclude? • Inheritance is determined by pair of “factors” passed on from one generation to another. • Mendel knew nothing about chromosomes, genes, or DNA. Why? These terms hadn’t yet been defined. ...
... What did Mendel conclude? • Inheritance is determined by pair of “factors” passed on from one generation to another. • Mendel knew nothing about chromosomes, genes, or DNA. Why? These terms hadn’t yet been defined. ...
What Darwin Never Knew Hout
... 21.) How many genes are in the human genome? 22.) Research on the fruit fly showed there are “switches” in DNA. What are switches? 23.) How did the lake stickleback fish lose its spikes? 24.) Finch beaks are all made by the same gene, so why are there different shaped beaks? 25.) Define transitional ...
... 21.) How many genes are in the human genome? 22.) Research on the fruit fly showed there are “switches” in DNA. What are switches? 23.) How did the lake stickleback fish lose its spikes? 24.) Finch beaks are all made by the same gene, so why are there different shaped beaks? 25.) Define transitional ...
3/1/2013 - Biloxi Public Schools
... hearing is due to its dominant allele (D). What percentage of the offspring of a normal heterozygous (Dd) dog and a deaf dog (dd) would be expected to have normal hearing? A 0% B 25% C 50% D 100% Justification---______________________________________________________________________________ ...
... hearing is due to its dominant allele (D). What percentage of the offspring of a normal heterozygous (Dd) dog and a deaf dog (dd) would be expected to have normal hearing? A 0% B 25% C 50% D 100% Justification---______________________________________________________________________________ ...
Sex, Gender and What`s the Difference, Anyway?
... “Thousands of genes show sexual dimorphism in liver, adipose, muscle and the brain: they exhibit highly tissue-specific patterns of expression.. “* “We saw striking and measurable differences in more than half of the genes’ expression pattern between males and females. We didn’t expect that. no one ...
... “Thousands of genes show sexual dimorphism in liver, adipose, muscle and the brain: they exhibit highly tissue-specific patterns of expression.. “* “We saw striking and measurable differences in more than half of the genes’ expression pattern between males and females. We didn’t expect that. no one ...
Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... Chromosome Theory of inheritance- genes are carried from parents to their offspring on chromosomes. • _______ meiosis - the process by which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half to form sex cells Sperm and egg – ____________. – Chromosome pairs separate and are distributed to two different c ...
... Chromosome Theory of inheritance- genes are carried from parents to their offspring on chromosomes. • _______ meiosis - the process by which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half to form sex cells Sperm and egg – ____________. – Chromosome pairs separate and are distributed to two different c ...
PPT File
... known as the founder of genetics. Mendel proposed that characteristics were inherited as result of the transmission of hereditary factors (genes). ...
... known as the founder of genetics. Mendel proposed that characteristics were inherited as result of the transmission of hereditary factors (genes). ...
Chapter 24 Genetics and Genomics Genotype and
... • each son with one recessive allele will have the disease • each son has no allele on the Y chromosome to mask the recessive allele • each daughter has a 50% chance of receiving the recessive allele from the ...
... • each son with one recessive allele will have the disease • each son has no allele on the Y chromosome to mask the recessive allele • each daughter has a 50% chance of receiving the recessive allele from the ...
Nucleus - Control Center of cell
... Every Organism has specific number of chromosomes • Humans have 46 (23 pairs one from each parent) • One pair determines sex. XX or XY… why? • Flies have 4 QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
... Every Organism has specific number of chromosomes • Humans have 46 (23 pairs one from each parent) • One pair determines sex. XX or XY… why? • Flies have 4 QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
Genomics: A Mapping Analogy - University of Wisconsin
... Likewise, is it possible to know the names and locations of all the genes of an organism without knowing their function? In making a map, whether of a campus or of a genome, the mapmaker gets to consider what data to show (and what data not to show), how to show it, and how to organize it and index ...
... Likewise, is it possible to know the names and locations of all the genes of an organism without knowing their function? In making a map, whether of a campus or of a genome, the mapmaker gets to consider what data to show (and what data not to show), how to show it, and how to organize it and index ...
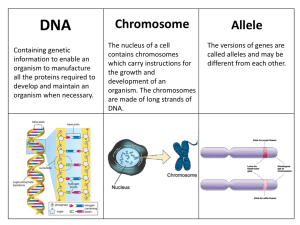
Chromosome Allele - GZ @ Science Class Online
... information to enable an organism to manufacture all the proteins required to develop and maintain an organism when necessary. ...
... information to enable an organism to manufacture all the proteins required to develop and maintain an organism when necessary. ...
Complex patterns of inheritance
... A chart that shows multiple family generations and relationships to track the inheritance of ...
... A chart that shows multiple family generations and relationships to track the inheritance of ...
Lecture 25 - life.illinois.edu
... 5. Mendel's law of segregation states that alternative forms of a particular factor (gene) remain discrete during the reproductive process; his second law, the law of independent assortment, states that different factors are inherited independently of one another. 6. Who was Thomas Hunt Morgan? Pion ...
... 5. Mendel's law of segregation states that alternative forms of a particular factor (gene) remain discrete during the reproductive process; his second law, the law of independent assortment, states that different factors are inherited independently of one another. 6. Who was Thomas Hunt Morgan? Pion ...
CH12Sec3and4
... Many Genes, Many Alleles • Multiple Alleles – 3 or more possible alleles, only to alleles for a gene can be present – Complex dominance – Blood types and Labrador coat color ...
... Many Genes, Many Alleles • Multiple Alleles – 3 or more possible alleles, only to alleles for a gene can be present – Complex dominance – Blood types and Labrador coat color ...
1 - Genetic Alliance
... the human genome; the remainder consists of non-coding regions, whose functions may include providing chromosomal structural integrity and regulating where, when, and in what quantity proteins are made. The human genome is estimated to contain 20,000-25,000 genes. Although each cell contains a full ...
... the human genome; the remainder consists of non-coding regions, whose functions may include providing chromosomal structural integrity and regulating where, when, and in what quantity proteins are made. The human genome is estimated to contain 20,000-25,000 genes. Although each cell contains a full ...
SNPs - Bilkent University
... 2.94 near D20S906 and a second MLS of 2.94 at D20S482. • 218 nuclear families, the asthma plus BHR phenotype increased the evidence for linkage (MLS of 3.93 at D20S482, 35% excess allele sharing) and refined the candidate region to the second peak • The region spanned 4.28 centimorgans (cM) (from 9. ...
... 2.94 near D20S906 and a second MLS of 2.94 at D20S482. • 218 nuclear families, the asthma plus BHR phenotype increased the evidence for linkage (MLS of 3.93 at D20S482, 35% excess allele sharing) and refined the candidate region to the second peak • The region spanned 4.28 centimorgans (cM) (from 9. ...