The Digestive System
... • These mechanisms inhibit gastric secretion and duodenal filling • Carbohydrate-rich chyme quickly moves through the duodenum • Fat-laden chyme is digested more slowly causing food to remain in the stomach longer ...
... • These mechanisms inhibit gastric secretion and duodenal filling • Carbohydrate-rich chyme quickly moves through the duodenum • Fat-laden chyme is digested more slowly causing food to remain in the stomach longer ...
Burns GI Physiology 2017
... • GI motility must also be coordinated with secretion from pancreas and gall bladder • Receptors outside and inside the GI tract receive visual, mechanical and chemical stimuli • Receptor activation induces responses through changes in autonomic and enteric nervous systems and through the effect of ...
... • GI motility must also be coordinated with secretion from pancreas and gall bladder • Receptors outside and inside the GI tract receive visual, mechanical and chemical stimuli • Receptor activation induces responses through changes in autonomic and enteric nervous systems and through the effect of ...
AnS SI 214 Practice Exam 4 GI, Lactation, Ruminants, Appetite
... 22. If an older person is having diarrhea and gas when they try to drink much milk, what enzyme are they not producing on their brush border? A) maltase B) lactase C) carboxypeptidase D) gastric lipase E) rennin 23. The kidney engages in all of the following activities except: A) secreting a hormone ...
... 22. If an older person is having diarrhea and gas when they try to drink much milk, what enzyme are they not producing on their brush border? A) maltase B) lactase C) carboxypeptidase D) gastric lipase E) rennin 23. The kidney engages in all of the following activities except: A) secreting a hormone ...
The Digestive System
... bolus against the hard palate and the movement into the pharynx. Under conscious control. Pharyngeal phase begins when bolus comes in contact with sensory receptors around the pharynx and posterior pharyngeal wall and initiates involuntary swallowing reflex. Followed by the closure of the glottis by ...
... bolus against the hard palate and the movement into the pharynx. Under conscious control. Pharyngeal phase begins when bolus comes in contact with sensory receptors around the pharynx and posterior pharyngeal wall and initiates involuntary swallowing reflex. Followed by the closure of the glottis by ...
Practice test for Exam 4
... 22. If an older person is having diarrhea and gas when they try to drink much milk, what enzyme are they not producing on their brush border? A) maltase B) lactase C) carboxypeptidase D) gastric lipase E) rennin 23. The kidney engages in all of the following activities except: A) secreting a hormone ...
... 22. If an older person is having diarrhea and gas when they try to drink much milk, what enzyme are they not producing on their brush border? A) maltase B) lactase C) carboxypeptidase D) gastric lipase E) rennin 23. The kidney engages in all of the following activities except: A) secreting a hormone ...
Digestive System Powerpoint
... • Gastric juice is the secretion of the stomach • Gastric juice is very acidic and can damage tissues other than the stomach lining – Repeated vomiting can cause gastric juice to erode the enamel of the teeth – If gastric juice is produced in excess it can overflow into the esophagus, causing “heart ...
... • Gastric juice is the secretion of the stomach • Gastric juice is very acidic and can damage tissues other than the stomach lining – Repeated vomiting can cause gastric juice to erode the enamel of the teeth – If gastric juice is produced in excess it can overflow into the esophagus, causing “heart ...
Physiology of Digestion
... • Peristaltic waves move toward the pylorus at the rate of 3 per minute • This basic electrical rhythm (BER) is initiated by pacemaker cells (cells of Cajal) • Most vigorous peristalsis and mixing occurs near the pylorus • Chyme is either: – Delivered in small amounts to the duodenum or – Forced bac ...
... • Peristaltic waves move toward the pylorus at the rate of 3 per minute • This basic electrical rhythm (BER) is initiated by pacemaker cells (cells of Cajal) • Most vigorous peristalsis and mixing occurs near the pylorus • Chyme is either: – Delivered in small amounts to the duodenum or – Forced bac ...
No Slide Title
... Fat content in the stomach slows the passage of alcohol to the intestine where absorption is more rapid • Gastric mucosal cells contain alcohol dehydrogenase that converts some alcohol to acetaldehyde – more of this enzyme found in males than females ...
... Fat content in the stomach slows the passage of alcohol to the intestine where absorption is more rapid • Gastric mucosal cells contain alcohol dehydrogenase that converts some alcohol to acetaldehyde – more of this enzyme found in males than females ...
Digestive System
... Man and pig have a simple stomach with an extensive intestinal system Ruminants have a complex stomach with a simpler intestinal system Horses and rabbits have a simple stomach with an extensive intestinal system and an enlarged ...
... Man and pig have a simple stomach with an extensive intestinal system Ruminants have a complex stomach with a simpler intestinal system Horses and rabbits have a simple stomach with an extensive intestinal system and an enlarged ...
Digestive System
... • The largest serous membrane of the body lining all organs of the abdominal cavity and the cavity wall – Parietal peritoneum: lines walls – Visceral peritoneum: lines organs – Peritoneal cavity: potential space between membranes; produces serous fluid ...
... • The largest serous membrane of the body lining all organs of the abdominal cavity and the cavity wall – Parietal peritoneum: lines walls – Visceral peritoneum: lines organs – Peritoneal cavity: potential space between membranes; produces serous fluid ...
164 study guide digestion
... Focus on how the structure of the layers of a particular portion of the digestive tract is related to its specific function. E.g. The stomach has three (3), not two (2), layers of smooth muscle in its muscularis externa → a major function of the stomach is mechanical digestion. E.g. Brunner’s glands ...
... Focus on how the structure of the layers of a particular portion of the digestive tract is related to its specific function. E.g. The stomach has three (3), not two (2), layers of smooth muscle in its muscularis externa → a major function of the stomach is mechanical digestion. E.g. Brunner’s glands ...
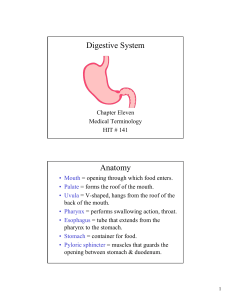
Digestive System Anatomy
... • Adhesion = growing together of two surfaces, after surgery. • Anorexia nervosa = psychoneurotic disorder, prolonged refusal to eat. • Bulimia = gorging with food then vomiting. • Cirrhosis = chronic disease of the liver, caused by alcoholism. • Crohn’s disease = chronic inflammation, of the ileum ...
... • Adhesion = growing together of two surfaces, after surgery. • Anorexia nervosa = psychoneurotic disorder, prolonged refusal to eat. • Bulimia = gorging with food then vomiting. • Cirrhosis = chronic disease of the liver, caused by alcoholism. • Crohn’s disease = chronic inflammation, of the ileum ...
Name: Period: Date: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Study Guide Chapter 14
... 7) What is the function of the mucus secreted by glands in the stomach and small intestine? *418 To prevent friction so food can move down the digestive tract And *protects organs against acidic gastric juices 8) What are the three portions of the stomach? In what portion does the most digestive act ...
... 7) What is the function of the mucus secreted by glands in the stomach and small intestine? *418 To prevent friction so food can move down the digestive tract And *protects organs against acidic gastric juices 8) What are the three portions of the stomach? In what portion does the most digestive act ...
Human Digestive System
... The esophagus is a tube connecting the mouth to the stomach running through the Thoracic cavity. Your teeth and tongue move food around in the mouth turning the food into a mushy bolus. The tongue moves the bolus to the back of the throat for swallowing. The bolus enters the esophagus. The esophagus ...
... The esophagus is a tube connecting the mouth to the stomach running through the Thoracic cavity. Your teeth and tongue move food around in the mouth turning the food into a mushy bolus. The tongue moves the bolus to the back of the throat for swallowing. The bolus enters the esophagus. The esophagus ...
Biology 11 - Human Anatomy Lecture
... 3) Somatostatin – inhibits gastric secretion and motility 6. Gastric motility – stomach movements have two phases a. Receptive-relaxation response – arriving food stretches the stomach, causing it to relax b. Peristaltic contractions of the smooth muscle churns the bolus and mixes it with gastric ju ...
... 3) Somatostatin – inhibits gastric secretion and motility 6. Gastric motility – stomach movements have two phases a. Receptive-relaxation response – arriving food stretches the stomach, causing it to relax b. Peristaltic contractions of the smooth muscle churns the bolus and mixes it with gastric ju ...
The Digestive System
... Small intestine- long small diameter tube made up of the duodenum, jejunum and ileum. Large intestine (colon)- locate the large diameter tube usually a dark green color. The associated organs: Liver- the large brownish gland (the largest internal organ composed of 3 lobes) Gall bladder- small green ...
... Small intestine- long small diameter tube made up of the duodenum, jejunum and ileum. Large intestine (colon)- locate the large diameter tube usually a dark green color. The associated organs: Liver- the large brownish gland (the largest internal organ composed of 3 lobes) Gall bladder- small green ...
Mink Digestive System Dissection
... 2. Observe the yellowish, fat-filled “apron” that covers the abdominopelvic region. You can actually pick it up like it is an apron. This is the greater omentum, a double layered serous membrane. Photograph the greater omentum looking like an apron. Remove the greater omentum by removing it from whe ...
... 2. Observe the yellowish, fat-filled “apron” that covers the abdominopelvic region. You can actually pick it up like it is an apron. This is the greater omentum, a double layered serous membrane. Photograph the greater omentum looking like an apron. Remove the greater omentum by removing it from whe ...
Function
... pumping action called pyloric pump. In the pylorus the thickness of the circular muscle becomes grater than in earlier portions of the antrum and remains tonically contracted. This site is called pyloric sphincter. It prevents passage of food particles until they are completely mixed in the chyme to ...
... pumping action called pyloric pump. In the pylorus the thickness of the circular muscle becomes grater than in earlier portions of the antrum and remains tonically contracted. This site is called pyloric sphincter. It prevents passage of food particles until they are completely mixed in the chyme to ...
Notes on Digestion
... haustral contractions - slow acting segmental motion; moves chyme from one segment to next mass movements - peristaltic waves that move food to the rectum during/after eating a. diverticula - herniation of the mucosa through the wall of the colon (sigmoid colon) ...
... haustral contractions - slow acting segmental motion; moves chyme from one segment to next mass movements - peristaltic waves that move food to the rectum during/after eating a. diverticula - herniation of the mucosa through the wall of the colon (sigmoid colon) ...
Lecture: Physiology of Digestion
... haustral contractions - slow acting segmental motion; moves chyme from one segment to next mass movements - peristaltic waves that move food to the rectum during/after eating a. diverticula - herniation of the mucosa through the wall of the colon (sigmoid colon) ...
... haustral contractions - slow acting segmental motion; moves chyme from one segment to next mass movements - peristaltic waves that move food to the rectum during/after eating a. diverticula - herniation of the mucosa through the wall of the colon (sigmoid colon) ...
Chapter 24
... 2. mass movements - peristaltic waves that move food to the rectum during/after eating a. diverticula - herniation of the mucosa through the wall of the colon sigmoidd colon) D. Defecation 1. defecation reflex - when feces (stool) enters rectum, spinal cord reflex is triggered a. internal sphincter ...
... 2. mass movements - peristaltic waves that move food to the rectum during/after eating a. diverticula - herniation of the mucosa through the wall of the colon sigmoidd colon) D. Defecation 1. defecation reflex - when feces (stool) enters rectum, spinal cord reflex is triggered a. internal sphincter ...
powerpoint jeopardy
... • Organs are made up of four different tissues. • The mucosa is epithelium or covering. • The submucosa is connective tissue with blood vessels and nerves • The fourth tissue would be muscle found in the three muscle layers ...
... • Organs are made up of four different tissues. • The mucosa is epithelium or covering. • The submucosa is connective tissue with blood vessels and nerves • The fourth tissue would be muscle found in the three muscle layers ...
Implications of Low Stomach Acid: An Update
... role in digestion and the regulation of pH in the stomach is critical for maintaining our health in a number of ways. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) secretion assists protein digestion by activating pepsinogen to pepsin, renders the stomach sterile against orally-ingested pathogens,prevents bacterial or fu ...
... role in digestion and the regulation of pH in the stomach is critical for maintaining our health in a number of ways. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) secretion assists protein digestion by activating pepsinogen to pepsin, renders the stomach sterile against orally-ingested pathogens,prevents bacterial or fu ...
Adjustable gastric band

A laparoscopic adjustable gastric band, commonly called a lap-band, A band, or LAGB, is an inflatable silicone device placed around the top portion of the stomach to treat obesity, intended to slow consumption of food and thus reduce the amount of food consumed.Adjustable gastric band surgery is an example of bariatric surgery designed for obese patients with a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or greater — or between 35 and 40 in cases of patients with certain comorbidities that are known to improve with weight loss, such as sleep apnea, diabetes, osteoarthritis, GERD, Hypertension (high blood pressure), or metabolic syndrome, among others.In February 2011, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) expanded approval of adjustable gastric bands to patients with a BMI between 30 to 40 and one weight-related medical condition, such as diabetes or high blood pressure. However, an adjustable gastric band may be used only after other methods such as diet and exercise have been tried.