A mixed group ll/group III twintron in the Euglena
... evolution: 'introns early' versus 'introns late'. In the introns early model, genes are viewed as being assembled from exons that code for structural or functional domains. Introns represent primitive elements for mediating recombination events that assemble domains of proteins. This process is term ...
... evolution: 'introns early' versus 'introns late'. In the introns early model, genes are viewed as being assembled from exons that code for structural or functional domains. Introns represent primitive elements for mediating recombination events that assemble domains of proteins. This process is term ...
Genomic dissection of plant development and its
... We applied Model B on trait BLUEs as outlined in detail by Liu et al. (2011). This model was found to be most suited for carrying out genome-wide association study (GWAS) with multiple families (Würschum et al., 2012) and has already been shown to work properly in HEB-25 (Maurer et al., 2015). It is ...
... We applied Model B on trait BLUEs as outlined in detail by Liu et al. (2011). This model was found to be most suited for carrying out genome-wide association study (GWAS) with multiple families (Würschum et al., 2012) and has already been shown to work properly in HEB-25 (Maurer et al., 2015). It is ...
Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor
... droplets in response to peroxisome proliferators. These ultrastructural observations indicate that intracellular processing of lipids, at least in response to exogenous triggers of lipid metabolism, is aberrant in the knockout mice. Constitutive expression of lipid-metabolizing genes is significantl ...
... droplets in response to peroxisome proliferators. These ultrastructural observations indicate that intracellular processing of lipids, at least in response to exogenous triggers of lipid metabolism, is aberrant in the knockout mice. Constitutive expression of lipid-metabolizing genes is significantl ...
Inherited Motor Neurone Disease Part one: Introduction to inherited
... Inherited MND is passed down from one generation to the next when somebody inherits a certain faulty, or mutated, gene from one of their parents. Inherited MND nearly always follows what is known as a dominant inheritance pattern. This means that it only takes one faulty copy of the gene to cause th ...
... Inherited MND is passed down from one generation to the next when somebody inherits a certain faulty, or mutated, gene from one of their parents. Inherited MND nearly always follows what is known as a dominant inheritance pattern. This means that it only takes one faulty copy of the gene to cause th ...
Integration of QTL Information with Traditional Animal Breeding
... Although a marker and a linked QTL may be in linkage equilibrium across the population, LD will always exist within a family, even between loosely linked loci. Consider a double heterozygous sire with haplotypes MQ/mq. The genotype of this sire is identical to that of an F 1 cross between inbred lin ...
... Although a marker and a linked QTL may be in linkage equilibrium across the population, LD will always exist within a family, even between loosely linked loci. Consider a double heterozygous sire with haplotypes MQ/mq. The genotype of this sire is identical to that of an F 1 cross between inbred lin ...
Divergent selection and heterogeneous genomic
... exhibit stronger differentiation than neutral regions with weak or no linkage to such loci. Divergent selection can also increase genome-wide neutral differentiation by reducing gene flow (e.g. by causing ecological speciation), thus promoting divergence via the stochastic effects of genetic drift. ...
... exhibit stronger differentiation than neutral regions with weak or no linkage to such loci. Divergent selection can also increase genome-wide neutral differentiation by reducing gene flow (e.g. by causing ecological speciation), thus promoting divergence via the stochastic effects of genetic drift. ...
Detection and identification of bacteria in clinical samples by 16S
... Failure of the PCR methods to detect the 16S rRNA gene in culture-positive samples may be due to the number of bacteria present in a sample being lower than the detection limit of the method (Harris & Hartley, 2003; Schuurman et al., 2004). Schuurman et al. (2004) also reported PCRnegative and cultu ...
... Failure of the PCR methods to detect the 16S rRNA gene in culture-positive samples may be due to the number of bacteria present in a sample being lower than the detection limit of the method (Harris & Hartley, 2003; Schuurman et al., 2004). Schuurman et al. (2004) also reported PCRnegative and cultu ...
The Deletion Stocks of Common Wheat
... of aberrations in the other chromosomes, for the difference in contraction of chro- tion stocks, we selected 156, 12, and 4 plants with one or more deletions and no that is, translocations and aneuploidy. mosomes between cells. The arm ratios of When two or more deletions occurred in the normal whea ...
... of aberrations in the other chromosomes, for the difference in contraction of chro- tion stocks, we selected 156, 12, and 4 plants with one or more deletions and no that is, translocations and aneuploidy. mosomes between cells. The arm ratios of When two or more deletions occurred in the normal whea ...
Journal of Bacteriology
... Phase variation is a process of reversible, high-frequency phenotypic switching that is mediated by mutation, reorganization, or modification of DNA. This process is used by several bacterial species to generate population diversity that increases bacterial fitness and is important in niche adaptati ...
... Phase variation is a process of reversible, high-frequency phenotypic switching that is mediated by mutation, reorganization, or modification of DNA. This process is used by several bacterial species to generate population diversity that increases bacterial fitness and is important in niche adaptati ...
Aalborg Universitet The reason why profitable firms do not necessarily grow
... Economic selection – the increasing predominance of superior routines through the propensity of business units with superior performance to increase in relative size – is generally studied empirically or formally modelled in a simplified manner where it is assumed to be directional and depending on ...
... Economic selection – the increasing predominance of superior routines through the propensity of business units with superior performance to increase in relative size – is generally studied empirically or formally modelled in a simplified manner where it is assumed to be directional and depending on ...
Exome sequencing as a tool for Mendelian disease gene discovery
... individuals are affected with a common trait, one approach is to sequence the most distally related individuals: the more distantly related the individuals, the fewer genetic variants they share. However, even distantly related individuals share many variants that require further stratification (for ...
... individuals are affected with a common trait, one approach is to sequence the most distally related individuals: the more distantly related the individuals, the fewer genetic variants they share. However, even distantly related individuals share many variants that require further stratification (for ...
Effect of the Polymorphisms of Keratin Associated Protein 8.2 Gene
... cashmere weight and hair length (Table 3). The goats with genotypes AA had over 3.1% thinner fibre diameter (<15 µm) than those of other genotypes. The animals with genotype BB had the thicker fibre diameter in the population, higher by 0.54 µm than genotype AA. However, this difference did not reac ...
... cashmere weight and hair length (Table 3). The goats with genotypes AA had over 3.1% thinner fibre diameter (<15 µm) than those of other genotypes. The animals with genotype BB had the thicker fibre diameter in the population, higher by 0.54 µm than genotype AA. However, this difference did not reac ...
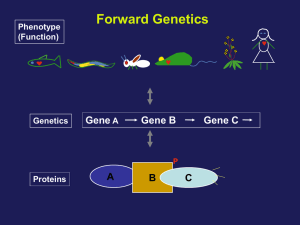
Forward Genetics
... The frequency of rare recombinants that segregate Dpy animals is correlated with the genetic distance between the two genes. ...
... The frequency of rare recombinants that segregate Dpy animals is correlated with the genetic distance between the two genes. ...
Finding New Clock Components: Past and Future
... mutations that alter period length by more than 15% (3-4 h) or lead to a complete loss of circadian rhythms. When multiple alleles are available, period-shortening and -lengthening mutations are observed, as well as loss-of-rhythm mutants. Ironically, per met all of these criteria from the beginning ...
... mutations that alter period length by more than 15% (3-4 h) or lead to a complete loss of circadian rhythms. When multiple alleles are available, period-shortening and -lengthening mutations are observed, as well as loss-of-rhythm mutants. Ironically, per met all of these criteria from the beginning ...
Genetic balancers
... chromosomal rearrangements adapted for use as balancers. There are two types of balancing rearrangements: (1) those that reduce or eliminate recombination between a lethal-bearing chromosome and a homologue carrying a wild-type allele of the locus, and (2) those that provide an extrachromosomal or i ...
... chromosomal rearrangements adapted for use as balancers. There are two types of balancing rearrangements: (1) those that reduce or eliminate recombination between a lethal-bearing chromosome and a homologue carrying a wild-type allele of the locus, and (2) those that provide an extrachromosomal or i ...
Identification of the mRNA targets of tRNA
... stability and translational decoding properties, may be central to regulating particular genes, or groups of genes. Mutations in the yeast TRM9 tRNA modification gene drive altered expression of genes enriched in codons targeted by Trm9-modified tRNAs (39). Similarly, mutations in the eukaryotic Elo ...
... stability and translational decoding properties, may be central to regulating particular genes, or groups of genes. Mutations in the yeast TRM9 tRNA modification gene drive altered expression of genes enriched in codons targeted by Trm9-modified tRNAs (39). Similarly, mutations in the eukaryotic Elo ...
PPT
... Represent localization of each protein by the state vector P(loc) and each feature by the feature vector P(feature|loc). Use Bayes rule to update. ...
... Represent localization of each protein by the state vector P(loc) and each feature by the feature vector P(feature|loc). Use Bayes rule to update. ...